Введение
Микро-РНК – это некодирующие РНК длиной около 22 нуклеотидов, являющиеся мощным регулятором экспрессии генов на посттранскрипционном уровне [1].
Высказываются предположения, согласно которым более 60% транскриптомы человека могут контролироваться с помощью микро-РНК, тем самым делая этот путь посттранскриптационной регуляции одним из важнейших для общего функционирования клетки. При этом микро-РНК играют ключевую роль в регулировании разнообразных функций как здоровых, так и поврежденных клеток. Отмечены изменения их профилей при многих патологических процессах [2]. Исследования показали, что помимо регуляции процессов внутри клетки микро-РНК секретируются и могут быть обнаружены в биологических жидкостях организма, таких как кровь и моча. С точки зрения возможности клинического использования важно, что циркулирующие микро-РНК очень стабильны и устойчивы к различным повреждающим факторам, что делает их перспективными биомаркерами [3].
В нефрологии активно изучается возможное влияние микро-РНК в механизмах повреждения почечной ткани при различных нефропатиях [4]. Профили эскпрессии микро-РНК исследуются также в популяции диализных пациентов [5], у пациентов с реакциями острого и хронического отторжения трансплантата почки [6].
Тем не менее роль микро-РНК в развитии сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний и минерально-костных нарушений в популяции именно диализных пациентов остается малоизученной темой. В настоящее время не исследовали сравнение профиля микро-РНК у пациентов на гемо- и перитонеальном диализах.
Изучение параметров экспрессии микро-РНК позволит определить их потенциальную роль как биомаркеров сердечно-сосудистого риска, минерально-костных нарушений и, возможно, способствовать поиску дальнейшего направления терапевтических воздействий.
Цель исследования: оценить ассоциации между уровнями микро-РНК-21, микро-РНК-126 и микро-РНК-210 в сыворотке крови с данными Kt/v, липидного обмена, эхокардиографии у пациентов на заместительной почечной терапии (ЗПТ) гемо- и перитонеальным диализами.
Методы исследования. Нами были обследованы 40 пациентов, из которых 18 получали терапию программным гемодиализом (ПГ), 28 – перитонеальным диализом (ПД). Группу контроля составили 28 здоровых добровольцев. Всем пациентам определяли уровень экспрессии микро-РНК-21, микро-РНК-126 и микр-оРНК-210 методом полимеразной цепной реакции в реальном времени. Критерии невключения в исследование: возраст младше 18 или старше 70 лет, сосудистый доступ для гемодиализа посредством перманентного катетера, сосудистого протеза, а также пациенты с тяжелыми сопутствующими заболеваниями (злокачественные новообразования, болезни системы крови), предшествующая трансплантация почки, наличие активного инфекционного процесса, низкая комплаентность пациента.
Были изучены клинико-анамнестические сведения о всех пациентах: возраст, стаж на диализе, систолическое и диастолическое давление, рост, вес до процедуры диализа.
Забор крови был осуществлен перед началом процедуры диализа, до подключения к диализному контуру.
Все биохимические параметры определяли на автоматическом биохимическом анализаторе.
Адекватность диализа Kt/V рассчитывали по формуле Даугирдаса [Kt/V=-ln (R–0,008×t)+(4–3,5×R)×UF/W, где R – отношение уровней мочевины до после и диализа, t – время сеанса в часах, UF – объем ультрафильтрации в литрах, W – масса тела в кг].
Всем больным выполнена Эхо-КГ. Исследование проводилось на аппарате Siemens Acusonx х300 в В- и М-режимах импульсным датчиком 3,5 МГц в положении больного на левом боку. Фракцию выброса определяли по методу Simpson и считали низкой при ФВ <40%. Все Эхо-КГ-исследования проведены одним специалистом. Измерения проводили согласно рекомендациям Американского эхокардиографического общества.
Молекулярно-генетические исследования проводили в клинической лаборатории на базе кафедры клинической лабораторной диагностики с курсом молекулярной медицины ФГБОУ ВО ПСПбГМУ им. акад. И.П. Павлова. Для выделения микро-РНК использовали сыворотку крови. Микро-РНК выделяли с использованием набора miRNeasy Mini Kit (QIAGEN, США). Концентрацию водного раствора микро-РНК определяли на спектрофотометре Nanodrop 1000 (Thermo Scientific, США). Обратная транскрипция проводилась с использованием набора реагентов для обратной транскрипции микро-РНК TaqMan. Полимеразную цепную реакцию в реальном времени проводили с использованием набора для определения экспрессии микро-РНК-21, -126 и -210 производства Applied Biosystems (США) TaqMan® GeneExpressionAssays.
Статистический анализ результатов выполняли с использованием пакета прикладных статистических программ Statistica, 12.0 («StatSoftInc», США). Результаты представлены как медиана [нижний–верхний квартиль]. Для попарного сравнения использовали критерий Манна–Уитни для связанных групп, для оценки силы связи между изучаемыми переменными – коэффициент ранговой корреляции Спирмена. Нулевую статистическую гипотезу об отсутствии различий и связей отвергали при p<0,05.
Результаты
В табл. 1 представлена общая характеристика обследованных пациентов.
Уровень экспрессии микро-РНК-21 и микро-РНК-210 достоверно различался в группе пациентов на ПГ и группе контроля. Также было выявлено достоверное различие микро-РНК-210 по сравнению с пациентами на ПД и в группе контроля (табл. 2). Каких-либо межгрупповых различий между ПГ и ПД по уровням экспрессии всех изученных микро-РНК установлено не было (табл. 2). В связи с этим для дальнейшей статистической обработки использовали объединенную группу, включившую пациентов как на ПГ, так и на ПД.
 Между уровнем экспрессии микро-РНК-126 и показателем адекватности диализа по Кt/V определена высокодостоверная отрицательная корреляционная связь (rs=-0,687; p=0,002).
Между уровнем экспрессии микро-РНК-126 и показателем адекватности диализа по Кt/V определена высокодостоверная отрицательная корреляционная связь (rs=-0,687; p=0,002).
Уровень микро-РНК-21 и микро-РНК-126 был повышен у пациентов с наличием сахарного диабета (p=0,003 и p=0,01 соответственно).
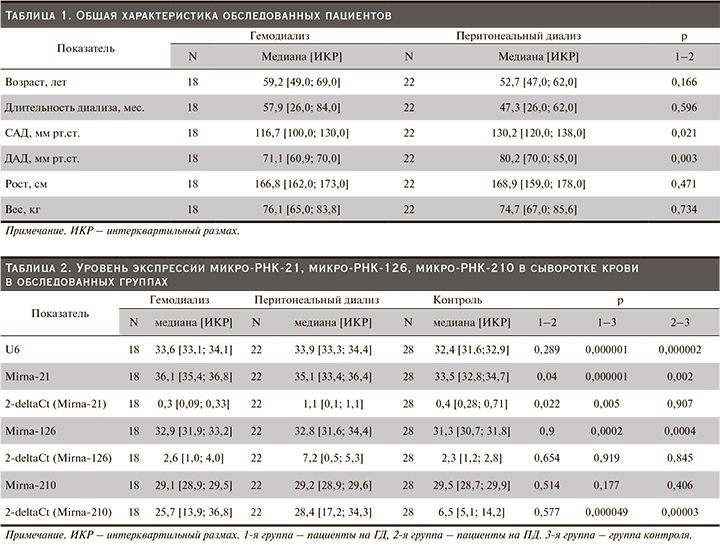
Экспрессия микро-РНК-210 была выше у пациентов с нарушениями липидного спектра. Уровень экспрессии микро-РНК-210 отрицательно коррелировал с величиной фракции выброса, измеренной по Симпсону по данным Эхо-КГ -rs= -0,5; p=0,01 (рис. 1).
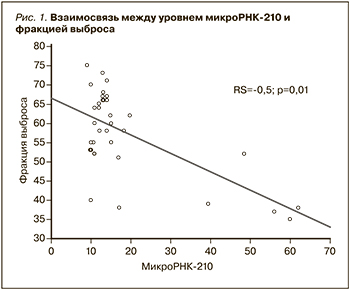
Уровень микро-РНК-21 отрицательно коррелировал с величиной общего холестерина – rs= -0,409; p=0,009 (рис. 2) и уровнем липопротеидов низкой плотности – rs = -0,4; p=0,01.
Как микро-РНК-21, так и микро-РНК-126 обратно коррелировали с уровнем общего холестерина сыворотки. Однако низкие значения микро-РНК-21 ассоциировались с более высокими уровнями липопротеидов низкой плотности (rs =-0,4; p=0,01), тогда как микро-РНК-126 отрицательно коррелировала с уровнем липопротеидов высокой плотности (rs=-0,36; p=0,024). Каких-либо ассоциаций между уровнем экспрессии микро-РНК-210 с показателями липидограммы не было установлено.
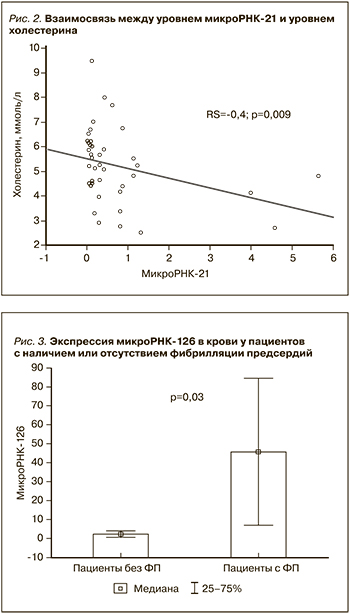 Уровень экспрессии микро-РНК-21 и -126 был выше у пациентов с фибрилляцией предсердий (p=0,003) (рис. 3).
Уровень экспрессии микро-РНК-21 и -126 был выше у пациентов с фибрилляцией предсердий (p=0,003) (рис. 3).
Обсуждение
Кардиоваскулярные заболевания служат основной причиной смертности пациентов на диализе. Недавние исследования показали дисрегуляцию ряда микро-РНК у пациентов с патологией сердечно-сосудистой системы [17].
На сегодняшний день ряд микро-РНК стали рассматриваться как новые диагностические и прогностические маркеры у больных с различными патологиями [7]. Их использование может стать актуальным и целесообразным в рутинной клинической практике с учетом относительной простоты и доступности определения их уровня экспрессии, в частности, в сыворотке крови.
Несмотря на достаточноую массу работ, изучавших роль микро-РНК, существуют единичные исследования, в которых оценивался уровень микро-РНК именно в популяции диализных пациентов [8–16].
Наше исследование позволяет рассматривать ряд микро-РНК, такие как микро-РНК-21, -126, -210, возможными ранними биомаркерами кардиоваскуляного риска. Они также играют роль в кальцификации сосудов, развитии атеросклероза, являются предикторами развития сердечной недостаточности и легочной гипертензии [18], что нашло отражение и в нашей работе, показав достоверное повышение уровня экспресии микро-РНК-210 у пациентов со сниженной фракцией выброса.
В исследовании, проведенном A. Zampetaki [19], уровень микро-РНК-126 был снижен при сахарном диабете 2 типа. Исследуя популяцию пациентов на диализе, в нашем исследовании показано, что микро-РНК-126 и микро-РНК-21 были повышены в когорте диализных пациентов с сахарным диабетом.
Ранее не исследовалась ассоциация уровней микро-РНК с показателями адекватности диализа.
В клинических исследованиях и экспериментальных моделях на животных показано увеличение уровня микро-РНК в предсердиях, что было сопряжено с ремоделированием миокарда предсердий [20]. Микро-РНК-21 воздействует на активность пути внеклеточного сигнала/митоген-активируемой протеинкиназы, которые воздействуют на структуры сердца [21].
В нашем исследовании получены данные, показывающие повышение уровня экспрессии микро-РНК-21 и микро-РНК-126 у пациентов с фибрилляцией предсердий.
В представленном нами исследовании показатели экспрессии микро-РНК отражают состояние липидного обмена у пациентов, находившихся на ЗПТ. Это согласуется с данными B. Aryal et al. [22].
Заключение
Таким образом, на основании полученных данных можно констатировать, что более высокий уровень экспрессии микро-РНК-126 ассоциируется с низкими показателями адекватности гемодиализа.
Уровень микро-РНК-21 и микро-РНК-126 повышен у пациентов с наличием как сахарного диабета, и так аритмии.
Экспрессия микро-РНК-210 выше у пациентов с дислипидемией, а также низкой фракцией выброса сердца. Показатели экспрессии микро-РНК также отражают состояние липидного обмена у диализных пациентов. В частности, низкие уровни микро-РНК-21 ассоциируются с повышенными показателями проатерогенных липопротеидов низкой плотности, а высокие уровни микро-РНК-126 – с низкими показателями липопротеидов высокой плотности.

