Введение
В настоящее время проблема хронической болезни почек (ХБП), ее влияния на кардиальную и церебральную сосудистые системы приобретает все бóльшую актуальность. Диагностические критерии ХБП: альбуминурия, гематурия (признаки почечного повреждения) и/или снижение скорости клубочковой фильтрации (СКФ) менее 60 мл/мин/1,73 м2, которые прослеживаются в течение 3 и более месяцев независимо от их характера и этиологии [1]. В настоящее время в мире от различных заболеваний почек страдают около 850 млн человек [2]. По данным исследователей, в официальной статистике ХБП как причина смертности недооценивается [3]. По сведениям Всемирной организации здравоохранения, ежегодная смертность от заболеваний мочеполового тракта составляет 830 на 100 тыс. человек [3]. В результате увеличения заболеваемости сахарным диабетом (СД) 2 типа, артериальной гипертензией (АГ), ишемической болезнью сердца (ИБС), хронической обструктивной болезнью легких (ХОБЛ), коморбидной патологией (КП), а также продолжительности жизни населения в ближайшее время распространенность ХБП будет расти. Результаты многочисленных исследований показали, что сердечно-сосудистая заболеваемость (ССЗ) и смертность среди пациентов с ХБП намного выше по сравнению с лицами без данной патологии [1]. В связи с этим все более актуальным становится вопрос ранней диагностики сердечно-сосудистых и церебральных расстройств при ХБП. В последнее время у исследователей и клиницистов особый интерес приобретает исследование ростовых факторов, маркеров воспаления и жесткости артерий, отражающих важные патофизиологические процессы в сосудистой стенке при ХБП. Эндотелиальный фактор роста сосудов (VEGF – Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor) представляет собой семейство сходных по структуре и функциям ростовых факторов, участвующих в стимуляции роста новых кровеносных сосудов [4]. VEGF относится к группе эндотелий-специфических полипептидов, ускоряющих рост сосудов, их пролиферацию и проницаемость [4]. Показано, что VEGF принимает участие в развитии эндотелиальной дисфункции, атеросклероза и ССЗ [5]. Концентрация VEGF тесно связана с воспалением и увеличением риска прогрессирования сердечно-сосудистых и церебральных осложнений [6]. Кроме того, высокие уровни VEGF сигнализируют о нарушении репаративных процессов в органах и тканях. Роль про- и противовоспалительных цитокинов, механизмов самозащиты ткани почки, противостоящих процессам иммунного воспаления и фиброза при ХБП, детально обсуждалась в ранее проведенных исследованиях [7, 8]. В то же время роль VEGF, маркеров воспаления и их связь с параметрами жесткости сосудов на разных стадиях ХБП изучена недостаточно.
Исходя из этого, целью нашего исследования стала оценка уровня VEGF, маркеров воспаления и их взаимосвязи с индексами жесткости сосудов при ХБП.
Материал и методы
Обследован 261 пациент с ХБП 1–5-й стадий, средний возраст составил 51,3±15,8 года. Критерием включения в исследование служили лица с ХБП 1–5-й стадий. Из исследования исключались больные, находящиеся на почечной заместительной терапии, с лихорадкой, заболеваниями крови и печени. ХБП диагностировали на основании критериев, предложенных международными рекомендациями [1]. В обследованной выборке больных причиной развития ХБП стали: АГ – 59 (22,6%), СД – 46 (17,6%), ИБС – 48 (18,4%), ХОБЛ – 23 (8,8%), хронический гломерулонефрит (ХГН) – 38 (14,6%) и хронический тубулоинтерстициальный нефрит (ХТИН) – 47 (18,0%). Согласно клиническим рекомендациям, за коморбидную патологию (КП) принимали сочетание у одного больного двух или более хронических заболеваний, этиопатогенетически взаимосвязанных или совпадающих по времени появления вне зависимости от активности каждого из них [9]. Среди всех обследованных (n=261, 100%) КП как причина развития ХБП встретилась у 97 (37,1%) пациентов. В соответствии с целями нашего исследования все обследованные пациенты были распределены на группы, согласно причинам развития у них ХБП (табл. 1–5). Клиническая часть исследования включала определение роста (см), массы тела (кг) с расчетом индекса массы тела (ИМТ, кг/м2), уровней систолического (САД) и диастолического (ДАД) артериального давления (мм рт.ст.). В инструментальной части работы изучали частоту сердечных сокращений (ЧСС, уд/мин), величину центрального АД (ЦАД, мм рт.ст.) и показатели жесткости сосудов на приборе «АнгиоСкан-01» (ООО «АнгиоСкан-Электроникс», Россия) в соответствии с требованиями по подготовке испытуемого и процедуре проведения тестов [10]. Анализ жесткости сосудов включал оценку величин индекса жесткости (SI, м/с), индекса аугментации (AIP, %), альтернативного индекса жесткости (aSI, м/с), индекса отражения (RI, %) и индекса увеличения при частоте пульса 75 в минуту (AIP75, %). Биохимическое исследование включило определение содержания уровней кальция, фосфора, магния (ммоль/л), креатинина (мкмоль/л), С-реактивного белка – СРБ (МЕ/л), фибриногена (г/л) крови. Уровни СРБ, превышающие 5 МЕ/л, рассматривались как повышенные. Для оценки состояния липидного обмена измеряли уровни общего холестерина (ХС, ммоль/л), холестерина липопротеидов низкой плотности (ЛПНП, ммоль/л), холестерина липопротеидов высокой плотности (ЛПВП, ммоль/л) и триглицеридов (ТГ, ммоль/л). Концентрацию VEGF (пг/мл) оценивали количественным методом твердофазного иммуноферментного анализа. За верхнюю границу нормы VEGF принята концентрация, равная 700 пг/мл. Для расчета скорости клубочковой фильтрации (рСКФ) использовалась формула CKD-EPI (Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration) [11].
Статистическую обработку результатов проводили с использованием пакета прикладных программ Statistica 10,0. Значимость различий между группами оценивалась с помощью t-ритерия Стьюдента (для переменных с нормальным распределением) и теста Манна–Уитни (для переменных с непараметрическим распределением). Данные представлены как среднее±стандартное отклонение для переменных с нормальным распределением, медианы и квартильного отклонения (Ме±Q) для переменных с непараметрическим распределением. Для оценки корреляционной взаимосвязи применяли способ Пирсона в случаях с нормальным и Спирмена – при непараметрическом распределении переменных. Уровнем статистической достоверности считалось значение p<0,05.
 Результаты исследования
Результаты исследования
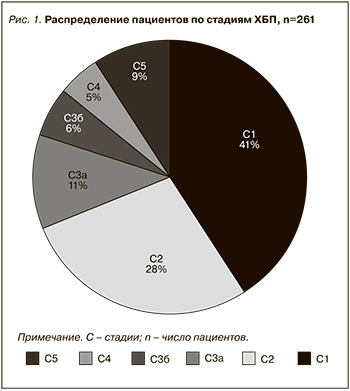
Среди обследованных пациенты с 1-й и 2-й стадиями ХБП были наиболее многочисленными (рис. 1), а доля лиц с преддиализной стадией ХБП оказалась, напротив, малочисленной.
Средний возраст больных ХГН и ХТИН был ниже, ХОБЛ и КП – существенно выше по сравнению с остальными подгруппами (табл. 1). Показатели ИМТ в анализируемых группах существенно различались и были наиболее высокими у больных ХТИН (p<0,05). Варьировались также величины систолического и диастолического АД. Так, показатели систолического АД у больных с АГ, СД2 и КП были достоверно выше по сравнению с лицами ИБС, ХОБЛ, ХГН и ХТИН (табл. 1). Как и следовало ожидать, значения диастолического и центрального АД оказались наивысшими у лиц с АГ (табл. 1, 2). В исследуемых группах статистически значимых различий в показателях ЧСС получено не было.
При рассмотрении результатов исследования АнгиоСкан (за исключением больных АГ) средние показатели ЦАД оказались существенно выше у лиц с КП (табл. 2). Наивысшие показатели индекса жесткости и альтернативного индекса жесткости были выявлены у лиц с ХГН и ХОБЛ, тогда как существенное увеличение индекса аугментации и индекса увеличения при частоте пульса 75 в минуту регистрировалось в группах АГ, СД 2 типа и КП (табл. 2). Более высокие уровни индекса отражения сосудистой стенки отмечены у больных АГ и КП.
Исследование состояния липидного обмена показало, что медиана уровней ХС, ТГ и ХС ЛПНП плазмы крови была достоверно выше у лиц с АГ (табл. 3). Уровень ХС ЛПВП оказался наиболее низким среди больных с ХГН. Стоить отметить, что за исключением лиц с АГ и СД2показатели общего ХС и ХС ЛПНП были существенно выше в группе больных ХГН (табл. 3).
Оценка уровней маркеров воспаления в обследованных нами выборках показала, что больные с повышенным содержанием СРБ плазмы крови достоверно превалируют в группах АГ и ИБС (табл. 4). Медиана уровней фибриногена во всех анализируемых группах достоверно не различалась за исключением группы КП, где ее содержание было существенно выше. Более высокое содержание фосфора отмечено среди больных СД2 и ХГН, кальция – в группе лиц с АГ. Следует отметить, что по сравнению с другими группами содержание магния оказалось существенно ниже у лиц СД2 (табл. 4).
Концентрация VEGF плазмы крови и степень гиперкреатининемии были достоверно выше в группах ХГН, ХТИН и КП (табл. 5). Однако снижение почечной функции были более выраженными среди больных СД 2 типа и КП. Диапазон экскреции белка с мочой (утренняя), достигающий степени протеинурии, как и следовало ожидать, наблюдался у лиц с ХГН. В 35,0 и 45,6% случаев протеинурия выявлялась у больных КП и СД2 соответственно (табл. 5).
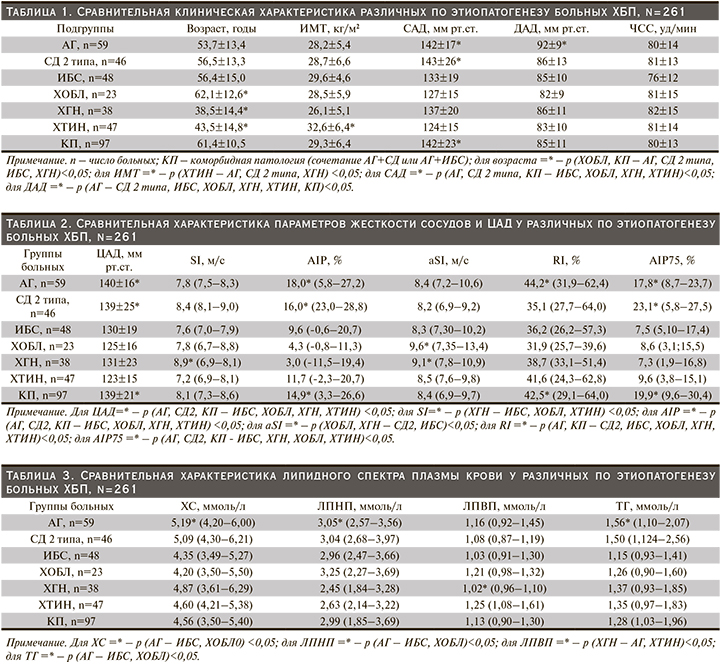
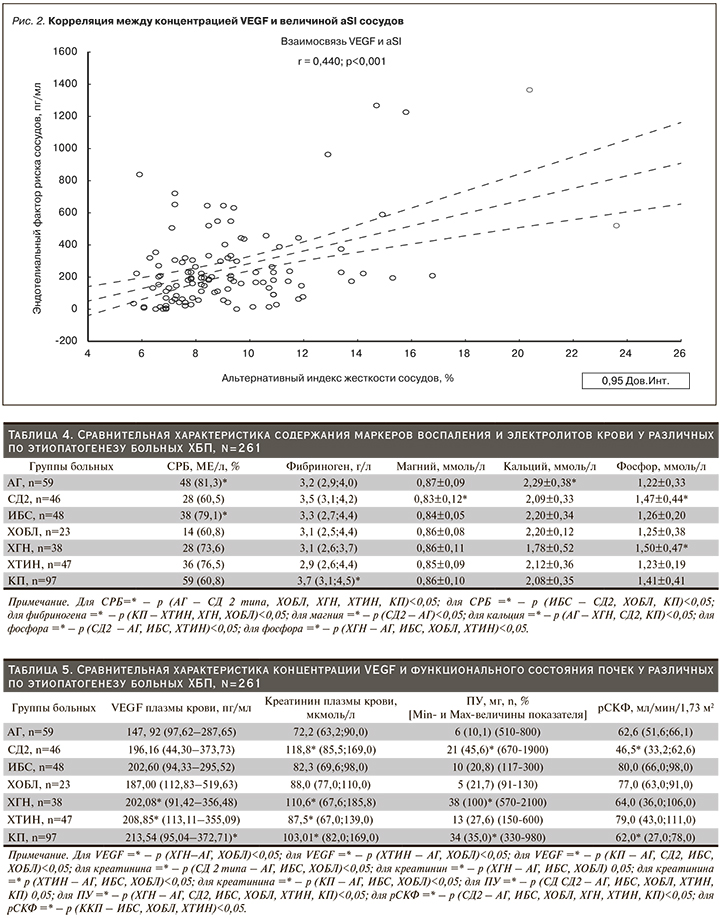
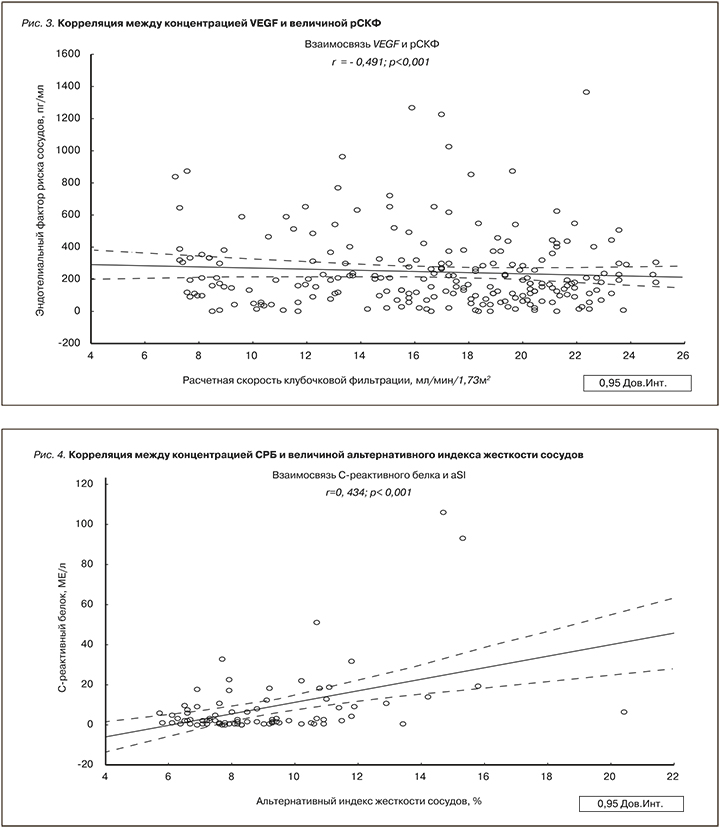
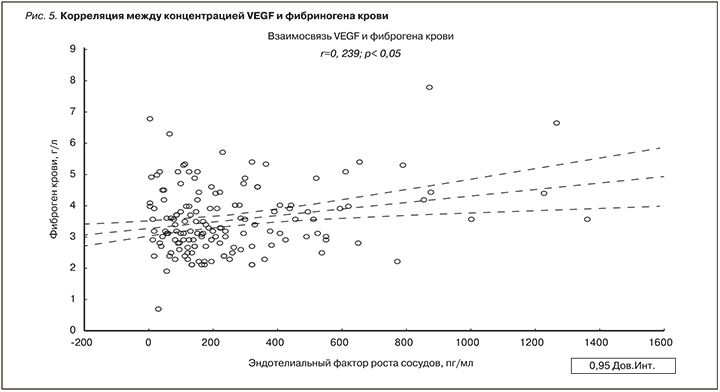
Корреляционный анализ между клинико-лабораторными данными и параметрами АнгиоСкана показал значимую прямую связь концентрации VEGF с величиной альтернативного индекса жесткости сосудов (рис. 2), обратную – с величиной рСКФ (рис. 3). Наличие положительной связи отмечено между содержанием СРБ плазмы крови и альтернативным индексом жесткости сосудов в общей выборке (рис. 4). Статистически значимые корреляционные связи между концентрацией фибриногена крови и индексами жесткости сосудов отмечены не были. Между тем, как показано на рис. 4, нам удалось продемонстрировать тесную прямую взаимосвязь концентрации VEGF с уровнем фибриногена.
Обсуждение
Как показывают результаты многочисленных исследований, ведущим патогенетическим звеном, объединяющим развитие таких нозологических единиц, как атеросклероз, АГ, СД2, ИБС, ХОБЛ и ХБП, служит эндотелиальная дисфункция [12]. В свою очередь дисфункция эндотелия является следствием хронических провоспалительных и протромботических процессов [13]. Недавние исследования показали, что VEGF – один из ранних маркеров поражения почек при ССЗ [14]. Высокие уровни VEGF подтверждают наличие активации механизмов фиброгенеза клубочкового аппарата почки и связанного с ней снижения почечной функции [15]. В нашем исследовании содержание VEGF было достоверно выше у лиц с ХГН, ХТИН и КП, при этом сочетаясь с гиперкреатининемией (табл. 5). В ранее опубликованных работах отмечалось, что VEGF является важнейшим фактором регуляции функций гломерулярного барьера в норме и при патологии, а его продукция способствует развитию склеротического процесса и прогрессирования ХБП [16, 17]. В нашей работе продемонстрирована связь между увеличением концентрации VEGF плазмы крови и снижением рСКФ (рис. 3). Имеются сообщения, что при поражении почек усиливается синтез VEGF подоцитами [18] и эпителиальными клетками канальцев [19]. Внутрипочечная гиперпродукция VEGF запускает воспалительные изменения в паренхиме почки, способствуя привлечению в нее мононуклеаров, макрофагов и моноцитов [20, 21]. Кроме того, негативное влияние высокого уровня VEGF плазмы крови на почки заключается в том, что при этом повышается синтез коллагена IV типа в клубочках и стимулируется пролиферация мезангиальных клеток [15, 20]. Следует отметить, что коллаген IV типа является одним из основных компонентов базальной мембраны клубочка и поэтому при прогрессировании ХБП наблюдается повышение его экскреции с мочой [22]. Указанные патофизиологические эффекты долговременной продукции VEGF сопровождаются альбуминурией, развитием тубулоинтерстициального фиброза и ухудшением азотовыделительной функции почек [1, 15]. Снижение СКФ рассматривается не только как признак повреждения почек, но и как самостоятельный фактор риска неблагоприятных сердечно-сосудистых и церебральных заболеваний [1]. При ХБП замедление СКФ провоцирует эндотелиальную дисфункцию и гиперпродукцию маркеров воспаления, в результате чего повышается жесткость сосудов [23]. Снижение СКФ – также один из индукторов синтеза СРБ и фибриногена крови [24]. Следует подчеркнуть, что СРБ оказывает прямое стимулирующее влияние на процессы инициации атеросклеротического повреждения сосудов – активацию макрофагов, выработку сосудистым эндотелием молекул клеточной адгезии и VEGF [25]. В проведенном нами исследовании (табл. 4), практически во всех группах у большей части больных отмечалось повышенное содержание СРБ, в группах с АГ и ИБС доля лиц с повышенным содержанием СРБ составила 81,3 и 79,1% соответственно (табл. 4). Прогностическая ценность повышенного уровня СРБ и гиперфибриногенемии у людей с сердечно-сосудистыми и церебральными заболеваниями общеизвестна. В условиях повышенной продукции СРБ в печени VEGF стимулирует процессы проницаемости, воспаления, ангиогенеза и роста сопротивления сосудов [24, 25]. В результате этого жесткость сосудов становится выше и ускоряется атеросклероз. Как показано на рис. 2, нам удалось установить значимую положительную связь между повышением концентрации VEGF плазмы крови и ростом альтернативного индекса жесткости сосудов. Возраст и снижение СКФ – наиболее изученные детерминанты жесткости сосудов, что также справедливо для СРБ и VEGF [24, 25]. В ряде исследований отмечено, что пациенты с преобладанием процессов ремоделирования сосудов эластического типа имели достоверно бóльшие значения маркера системного воспаления – СРБ [26]. Взаимосвязи СРБ и жесткости сосудов хорошо изучены в серии зарубежных исследований [27]. В недавно опубликованной работе выявлена не зависимая от других факторов риска ассоциация фибриногена с показателями жесткости сосудов [28]. Наше исследование показало, что медиана фибриногена крови была достоверно выше у лиц с КП (табл. 4). К тому же в указанной группе отмечались и высокие значения параметров жесткости сосудов (табл. 2), а также ухудшение азотовыделительной функции почек (табл. 5). Хотя в нашей работе тесная связь фибриногена с индексами жесткости сосудов не получена, тем не менее прямая связь концентрации VEGF с содержанием фибриногена крови все-таки обнаружена (рис. 5). Можно полагать, что повышенный уровень VEGF имеет значение в возникновении протромботических состояний, т.к. повышение уровня VEGF способствует гиперфибриногенемии. В свою очередь гиперфибриногенемия, являясь важным маркером воспаления, тесно связана с сердечно-сосудистыми и церебральными заболеваниями [29]. В частности, повышенный уровень фибриногена значительно ассоциирован с утолщением интимы сосудов и субклиническими проявлениями их атеросклеротического поражения, а также независимо прогнозирует будущий риск развития церебрального инсульта и АГ [29].
Накопленные результаты исследований свидетельствуют о том, что ХБП – это независимый фактор, ассоциированный с повышенной жесткостью сосудов [30]. Особенностью формирования жесткости сосудов у больных ХБП является его тесная связь с тяжестью заболевания, системным воспалением и нарушениями электролитного бмена. Отдельно отметим, что в нашей работе в группах больных СД 2 типа и ХГН отмечались достоверно высокие уровни фосфора плазмы крови (табл. 4), что связано со снижением СКФ у этих больных (табл. 5). В то же время, несмотря на сниженную функцию почек у лиц с СД2 (табл. 4), содержание магния плазмы крови было сравнительно низким, что требует дальнейшего изучения. Повышение содержания кальция плазмы крови среди лиц с АГ является общепризнанным фактом. Что касается данных литературы о взаимосвязи элементного состава плазмы крови с VEGF у больных ХБП, они оказались крайне ограниченными.
Заключение
У больных ХБП повышенный уровень VEGF плазмы крови служит маркером снижения функции почек и фактором сердечно-сосудистого и церебрального прогноза. При ХБП наиболее высокие уровни VEGF наблюдаются у лиц с хроническим тубулоинтерстициальным нефритом и гломерулонефритом, а также с коморбидными патологиями. При ХБП уровень VEGF в крови коррелирует со степенью снижения функции почек и степенью повышения жесткости артерий, что является неблагоприятным прогнозом в отношении развития кардиоренальных и церебральных осложнений.



