Введение
Хроническая болезнь почек (ХБП) представляет собой персистирующее в течение 3 месяцев или более поражение органа вследствие действия различных этиологических факторов, анатомической основой которого служит процесс замещения нормальных анатомических структур фиброзом, приводящий к его дисфункции [1]. За последние три десятилетия ХБП стремительно поднялась в рейтинге причин смерти населения по всему миру. Если в 2016 г. она занимала 13-е место в этом списке, то, по прогнозу Института измерения показателей и оценки состояния здоровья, в 2040 г. ХБП уже войдет в пятерку основных причин смерти [2]. Поскольку около 850 млн человек сегодня страдают заболеваниями почек, ХБП в настоящее время по праву рассматривается в качестве одной из глобальных проблем общественного здравоохранения [3].
Сердечно-сосудистые заболевания служат частым и неблагоприятным преморбидным фоном для этих пациентов, запускают кардиоренальный континуум, приводят к прогрессированию ХБП [4, 5]. В то же время нарушение функции почек становится неблагоприятным предиктором сердечно-сосудистых событий, замыкая порочный круг [6, 7].
Общим патоморфологическим субстратом при этом выступает дисфункция эндотелия, с которой начинается развитие и прогрессирование как патологии почек, так и сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний [7, 8]. В исследованиях последних десятилетий отмечается зависимость выраженности эндотелиальной дисфункции (ЭД) от степени снижения скорости клубочковой фильтрации (СКФ) [9, 10]. Важно отметить, что сосудистый эндотелий наделен множеством функций, среди которых регуляция гемодинамики, поддержание сосудистого тонуса, обеспечение проницаемости сосудистой стенки, обмен веществ, движение лейкоцитов, про- и антикоагулянтные свойства и др. Следовательно, дисфункция этого типа клеток имеет множество последствий [11].
При ХБП повреждение эндотелия сосудов происходит на ранних стадиях, развивается вместе с прогрессированием основного заболевания и в значительной степени способствует развитию сердечно-сосудистых осложнений у этих пациентов [12]. Дисфункция эндотелия при патологии почек – это многофакторный процесс, вклад в который вносят развивающиеся осложнения основного заболевания: атеросклероз, уремическая интоксикация, системный воспалительный процесс, оксидативный стресс, метаболический ацидоз, гиперфосфатемия, саркопения и др. [13, 14]. В связи с этим поиск молекулярных основ патогенеза нарушения функциональной способности эндотелия представляет исследовательский интерес.
Одним из известных биологических маркеров, регулирующих сосудистый тонус, водный баланс и артериальное давление, является эндотелин-1 [15]. Он представляет собой белок, синтезируемый в эндотелии, который обладает в первую очередь вазоконстрикторными свойствами. Фундаментальные научные исследования, в т.ч. на животных, демонстрируют, что эндотелин-1 напрямую влияет на вазомоторную функцию, ингибирует реабсорбцию воды и натрия в канальцах нефрона, следовательно, влияет на почечный кровоток, что приводит к нарушению функции почек. Он также способствует пролиферации мезангиальных клеток и гломерулосклерозу [16]. Однако имеющиеся сведения о гендерных особенностях синтеза эндотелина-1, о его связи с ЭД и функцией почек носят противоречивый характер и их все еще недостаточно, что создает основу для дальнейшего изучения этой научной проблемы [17, 18].
В связи с этим цель настоящего исследования состояла в том, чтобы выявить связь между уровнем эндотелина-1 в сыворотке крови, функцией почек и наличием ЭД. Полученные результаты помогут расширить знания в области патогенеза этого клинического состояния.
Материал и методы
Для проведения исследования выбраны 80 пациентов с ХБП в возрасте от 26 до 79 (58,9±1,4) лет: 43 женщины (средний возраст – 60,1±1,9 года) и 37 мужчин (средний возраст – 57,4±2,3 года). Когорта пациентов была распределена в две группы: первую составили 40 пациентов (28 женщин и 12 мужчин) с ХБП-3А–5 (средний возраст – 59,9±2,1 года), вторую – 40 пациентов (18 женщин и 22 мужчины) с ХБП-5Д (средний возраст – 58,1±2,1 года).
Всем пациентам проведены общий осмотр, сбор жалоб и анамнеза, физикальное обследование. СКФ оценивали по формуле CKD-EPI (мл/мин/1,73 м2). Лабораторное обследование включило общий анализ крови, общий анализ мочи, биохимический анализ крови, липидограмму, электролиты крови (калий, натрий, хлор). С помощью биоимпедансометрического анализа (аппарат «Диамант АИСТ-мини», Россия) проводилась оценка компонентного состава тела с определением жировой массы (ЖМ), безжировой массы (БЖМ), объема воды (ОВ), общего объема жидкости (ООЖ), объема внутриклеточной жидкости (Овнутрикл. Ж), объема внеклеточной жидкости (Овнекл. Ж) и общего обмена. Для каждого показателя определяли процентное отклонение от нормальных значений.
С использованием открытого иммуноферментного анализа (аппарат «Luminex MAGPIX», США) в сыворотке крови всех пациентов определили уровень эндотелина-1 (лабораторный набор «ELISA Kit», США).
Для выявления ЭД и оценки степени ее выраженности проводили пробу с эндотелийзависимой вазодилатацией плечевой артерии на фоне реактивной гиперемии (метод разработан Е.М. Шиловым, Н.Л. Козловской, С.Ю. Сериковой в 2008 г.): измеряли диаметр плечевой артерии в покое, затем производили компрессию плечевой артерии в течение 5 минут с помощью манжеты сфигмоманометра, в которой создавали давление, превысившее систолическое артериальное давление пациента не менее чем на 50 мм рт.ст. Сразу после снятия манжеты, а затем через 30 и 60 секунд измеряли диаметр плечевой артерии и линейную скорость кровотока в ней с применением ультразвукового аппарата («Toshiba Aplio 300», Япония). В соответствии с этой методикой после проведения пробы просвет плечевой артерии в систолу должен увеличиваться не менее чем на 10%. Меньшая степень дилатации плечевой артерии свидетельствовала о наличии ЭД.
Статистическая обработка материала проводилась с применением программ Microsoft и «STATISTICA 10.0» (StatSoft Inc.). С целью оценки характера распределения количественных показателей в группах нами использован анализ нормальности распределения Колмогорова–Смирнова, при значениях p≥0,05 распределение значений показателя считалось не отличающимся от нормального, при р<0,05 – отличающимся от нормального. Для ранговых признаков при анализе связей между признаками использовали критерий Фишера с расчетом χ2. Корреляционный анализ осуществлялся с помощью коэффициента Спирмена.
Результаты
При сравнительном межгрупповом анализе лабораторных показателей, имевших значение в прогрессировании ХБП и ЭД, были получены статистически значимые различия в уровнях эндотелина-1: его уровень был выше в группе пациентов, получавших лечение гемодиализом.
Среди других маркеров, уровни которых также оказались значимо выше во 2-й группе, были калий, кальций, фосфор, креатинин, мочевина и мочевая кислота. Вместе с тем уровни хлора, общего белка, альбумина, общего холестерина, триацилглицеридов и индекс атерогенности оказались выше в 1-й группе (табл. 1).
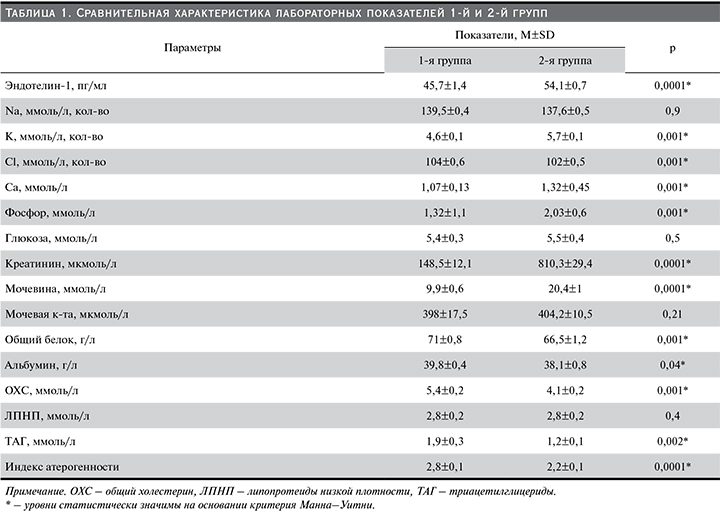
Проведение биоимпедансометрии позволило определить компонентный состав тела, а также оценить выраженность отклонения от нормы основных показателей. Было установлено, что у пациентов 1-й группы объем ЖМ был значительно выше, чем во 2-й группе, а процент отклонения этого параметра от нормы составил 32,5 против 3,6% соответственно. Объем и распределение жидкости в организме практически не имели статистически значимых различий между группами. Вместе с тем такой параметр, как Овнекл. Ж, продемонстрировал небольшую разницу и был выше во 2-й группе (табл. 2).
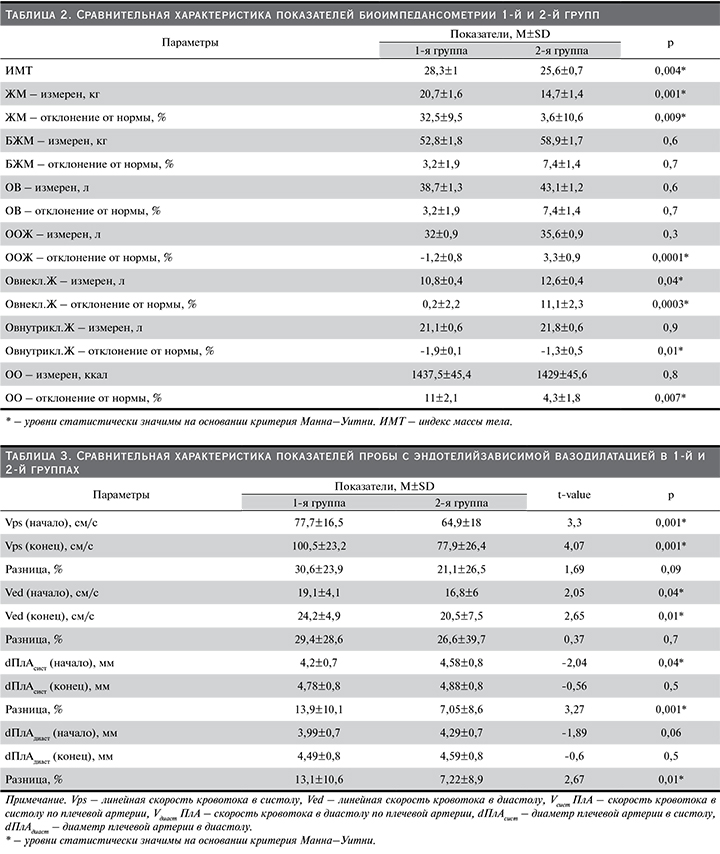
Анализ полученных данных после проведения пробы с эндотелийзависимой вазодилатацией продемонстрировал значимые различия в группах. Применение критерия Вилкоксона позволило обнаружить изменения как диаметра плечевой артерии, так и линейной скорости кровотока в ответ на механическую стимуляцию эндотелия. После пробы мы наблюдали разной степени прирост линейной скорости кровотока и увеличение просвета плечевой артерии в систолу по сравнению с показателями, полученными перед ее проведением (табл. 3).
Среднее повышение линейной скорости кровотока в систолу по плечевой артерии в общей когорте больных составило 25,9±2,9% (в 1-й группе 30,6±3,8%, во 2-й – 21,1±4,2%; p=0,09). Стоит отметить, что среднее увеличение диаметра плечевой артерии, использованное в качестве критерия для выявления ЭД, составило 10,2±1,1% (в 1-й группе 13,9±1,6%, а во 2-й – 7,1±1,4%; p=0,002). Таким образом, 10%-ный порог отсечения (соответственно методике) не преодолели 48,8% пациентов (в 1-й группе 27,5%, а во 2-й – 70%; p=0,001), что соответствует распространенности ЭД в этих группах. В табл. 4 представлен сравнительный анализ некоторых клинико-лабораторных показателей в подгруппах пациентов с положительными и отрицательными результатами пробы с эндотелийзависимой вазодилатацией.
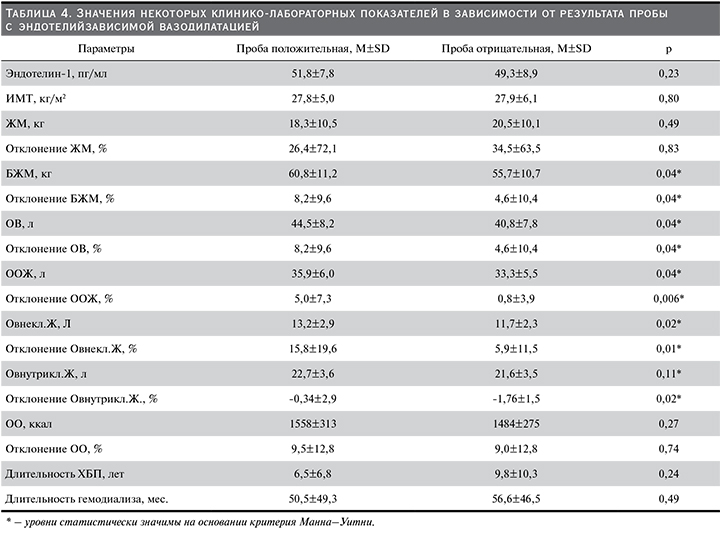
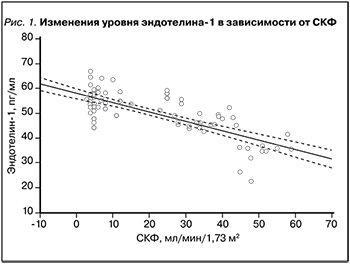
Проведение корреляционного анализа позволило выявить взаимосвязи уровня эндотелина-1 и некоторых клинико-лабораторных показателей. Так, сильная отрицательная корреляционная связь обсуждаемого маркера была установлена с СКФ (рис. 1) и, соответственно, сильная положительная связь – с уровнем креатинина. Умеренная по силе связь у эндотелина-1 установлена с мочевиной, отклонениями ООЖ и Овнекл. Ж длительностью ХБП, уровнями натрия и общего белка сыворотки крови (табл. 5).
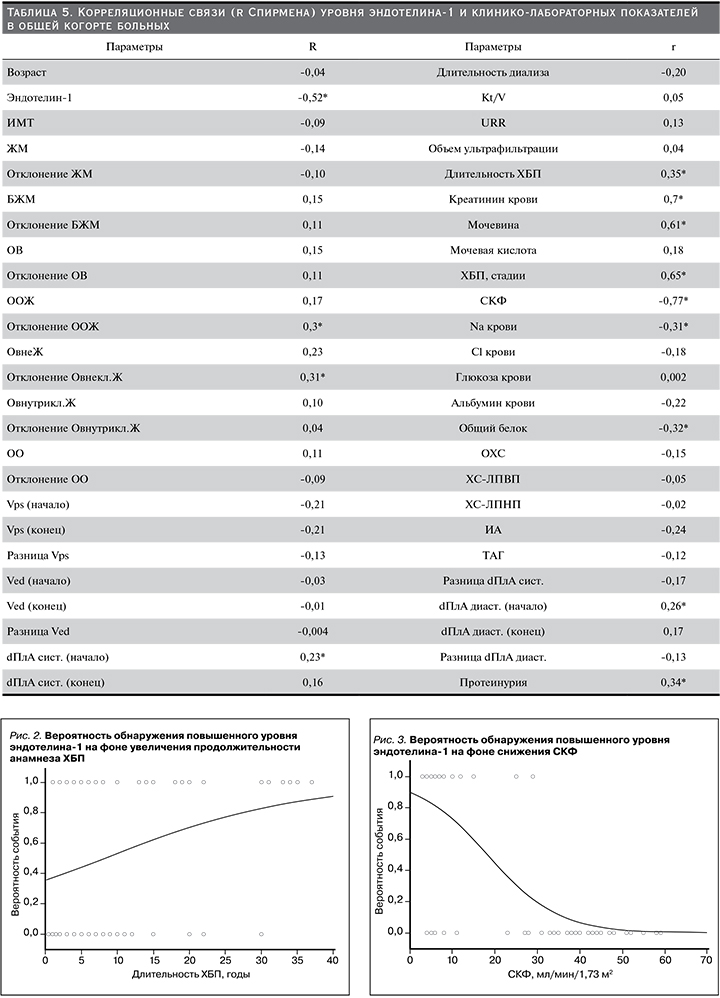
В связи с тем что референсных значений уровня эндотелина-1 для здоровых лиц и пациентов с ХБП не разработано, мы рассчитали медиану этого показателя (52,3±1 пг/мл) и применили этот порог отсечения для оценки распространенности и выраженности ЭД.
В общей когорте пациентов у 36,3% уровень эндотелина-1 был выше медианного значения (в 1-й группе 17,5%, во 2-й – 55%). В подгруппе пациентов 1-й группы, имевших ЭД по результатам пробы, повышенные уровни эндотелина-1 встречались в 14,3% случаев, в то время как аналогичный показатель во 2-й группе составил 60%. Во 2-й группе чаще, чем в 1-й группе, наблюдалось содружественное повышение уровня эндотелина-1 и положительная проба с эндотелиальной вазодилатацией: 30 против 2,5%.
По мере увеличения продолжительности анамнеза ХБП, а также на фоне снижения СКФ нарастала вероятность обнаружения повышенного значения эндотелина-1 в крови (рис. 2 и 3).
Обсуждение
Функция эндотелия зависит от широкого спектра факторов, которые условно можно разделить на две группы: вызывающие вазоконстрикцию или вазодилатацию. Действие таких факторов у относительно здорового человека уравновешенно, что поддерживает нормальный сосудистый тонус, общее периферическое сосудистое сопротивление и артериальное давление. У пациента с ХБП уремическая интоксикация, оксидативный стресс, метаболический ацидоз, гиперпаратиреоз, гиперхолестеринемия и другие факторы приводят к повышению сосудистого тонуса, превалированию вазоконстрикторных влияний и прогрессированию ЭД. В проведенном исследовании предпринята попытка оценки вклада эндотелина-1 в развитие и прогрессирование ЭД у пациентов с ХБП 3А–5Д-стадий. Известно, что этот биологический маркер представляет собой пептид, обладающий сосудосуживающими свойствами. Нами установлено, что уровень эндотелина-1 прямо коррелировал с длительностью анамнеза ХБП, имел обратную зависимость от СКФ и был статистически значимо выше в группе пациентов, получавших лечение гемодиализом. Это косвенно демонстрирует вклад обсуждаемого белка в развитие ЭД.
В подтверждение этой гипотезы мы провели пробу с эндотелийзависимой вазодилатацией, в результате которой установлено, что распространенность ЭД была выше во 2-й группе. При проведении субанализа подгрупп с верифицированной ЭД в каждой группе оказалось, что повышенный уровень эндотелина-1 (выше медианных значений) значительно чаще встречался в диализной группе и этот показатель составил 60 против 14,3% в 1-й группе. Полученные данные свидетельствуют: по мере прогрессирования ХБП уровень эндотелина-1 нарастает, что, вероятно, вносит вклад в развитие сердечно-сосудистого ремоделирования и имеет большое прогностическое значение.
Заключение
Проведенное исследование позволило оценить распространенность и выраженность ЭД у пациентов с ХБП на разных стадиях. В этом аспекте проба с эндотелийзависимой вазодилатацией может применяться в качестве доступного метода ее косвенной оценки в рамках рутинного ультразвукового обследования пациента с ХБП. Своевременное обнаружение ЭД позволит на ранних стадиях стратифицировать пациента в определенную группу риска и индивидуализировать подходы к выбору профилактической стратегии и лечебной тактики. Эндотелин-1 продемонстрировал высокий прогностический потенциал в отношении ЭД и может не только претендовать на роль маркера этого клинического состояния, но и применяться для прогнозирования темпов потери функции почек.



