Введение
Хроническая болезнь почек (ХБП) относится к группе хронической неинфекционной патологии и считается серьезной медикосоциальной проблемой, значение которой в практическом здравоохранении недооценено ввиду отсутствия яркой клинической картины, патогномоничных признаков и поздней манифестации. Вместе с тем ее вклад в развитие и прогрессирование сердечно-сосудистой патологии представляется существенным [1]. Распространенность ХБП в популяции достигает 13,4% и имеет отчетливую тенденцию к росту [2], составляя значительное бремя для системы здравоохранения [3]. Число пациентов, достигших терминальной почечной недостаточности (ТПН) и нуждающихся в проведении заместительной почечной терапии (ЗПТ) соответственно, повторяет обозначенный тренд [4, 5].
Пациенты с ХБП чаще страдают сердечно-сосудистыми заболеваниями (ССЗ), которые более чем в половине случаев служат причиной их смерти, особенно на поздних стадиях заболевания почек [6]. В связи с этим ХБП фактически является независимым фактором риска ССЗ [7]. Стоит отметить, что патогенетические механизмы, характерные для ХБП, способствуют повышению сердечно-сосудистого риска в группе пациентов с ТПН, получающих лечение гемодиализом (ГД), и тем самым реализуют кардиоренальные взаимоотношения [8, 9]. Вместе с тем патофизиология развития ССЗ, вызванных ХБП, до конца не изучена, что требует дальнейшего исследования и представляет научный интерес [10].
Возраст, пол, высокое артериальное давление, сахарный диабет, курение, ожирение и дислипидемия представляют собой факторы риска ССЗ и могут объяснить высокий уровень смертности больных ХБП [11]. Кроме того, при ХБП известны нетрадиционные факторы риска ССЗ: минерально-костные нарушения, оксидативный стресс, белково-энергетическая недостаточность, саркопения, уремическая интоксикация, системное воспаление, анемия и др. [12, 13]. Обсуждаемые факторы риска у пациентов с ХБП индуцируют сосудистое ремоделирование и приводят к развитию эндотелиальной дисфункции, которая считается неблагоприятным предиктором сердечно-сосудистых событий [14].
Одним из известных маркеров изменения сосудистой стенки в обсуждаемой группе пациентов является толщина комплекса интима-медиа (КИМ). Причем определение этого показателя в общей сонной артерии (ОСА) может выступать в качестве суррогатной конечной точки [15]. Было установлено, что в группе пациентов с ХБП на этот показатель оказывали свое влияние перечисленные выше факторы, такие как атеросклероз, оксидативный стресс и воспалительный процесс, опосредованный действием, в частности интерлейкина 6 (ИЛ-6) [16].
В связи с чем комплексная оценка факторов, оказывающих влияние у пациентов с ХБП-5Д на толщину КИМ ОСА как ключевого маркера сосудистого ремоделирования, отражающего выраженность эндотелиальной дисфункции, и стала целью настоящей работы.
Материал и методы
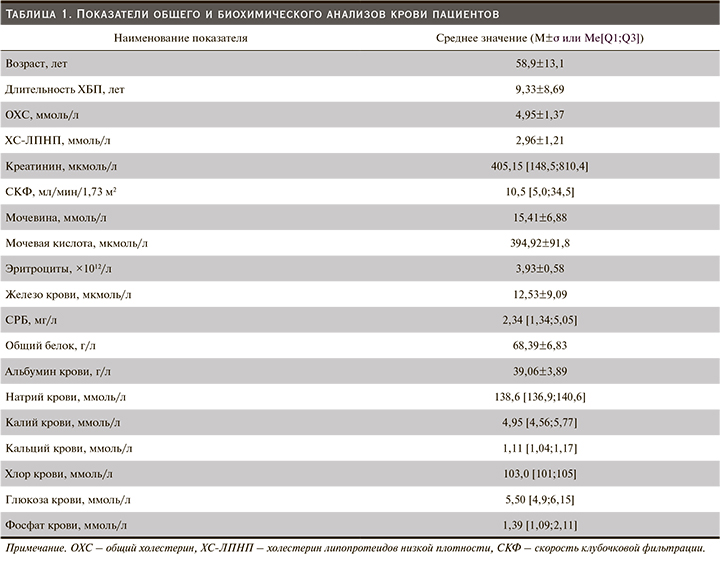
В исследование были включены 40 больных (22 мужчины и 18 женщин) с ХБП, получавших лечение ГД. Средний возраст пациентов в выборке составил 58,9±13,1 года, средняя продолжительность заболевания, приведшего к ТПН, – 10,9±1,5 года, средняя продолжительность ЗПТ – 53,6±7,5 месяцев.
У всех пациентов были взяты образцы крови для оценки качественного и количественного состава крови (на анализаторе Sysmex XT 2000i, Япония), электролитного состава, биохимического анализа крови (на анализаторе ARCHITECT CI8200, CША). Был произведен количественный иммуноферментный анализ крови для определения сывороточной концентрации интерлейкина-6 (ИЛ-6) на аппарате Luminex MAGPIX (США). Использовался лабораторный набор «Интерлейкин-6» (ИЛ-6) (ELISa Cloud-Clone Corp, США); диапазон измерения – 7,8–500 пг/мл, чувствительность метода – 0,1 нг/мл.
Биоимпедансометрия проводилась с помощью портативного анализатора компонентного состава «Диамант АИСТ-мини», (ООО «Диамант», Санкт-Петербург, 2014). Оценивали следующие параметры: жировую массу (ЖМ), безжировую массу (БЖМ), общую воду (ОВ), общий объем жидкости (ООЖ), объем внутриклеточной жидкости (О.внутр.ж.), объем внеклеточной жидкости (О.внекл.ж.).
Всем больным на аппарате TOSHIBA Aplio 300 TUS-A300 было проведено ультразвуковое исследование (УЗИ) почечных, сонных артерий и определена толщина КИМ ОСА по задней стенке на 1,5 см ниже бифуркации. При измерении КИМ учитывались границы артериальной стенки, а толщина >0,9 мм считалась отклонением от нормы.
Статистический анализ проведен с использованием программы Statistica, 10.0. Распределение признаков анализировали с применением анализа Колмогорова–Соколова, при р>0,05 распределение считали отличным от нормального. Средние значения признака с нормальным распределением определяли с помощью средней арифметической с учетом стандартного отклонения; признака с распределением, отличающимся от нормального – медианы и интерквартильного размаха. При нормальном распределении признаков оценивали корреляционную связь Пирсона, при ненормальном – ранговые корреляции Спирмена. Использовали методы линейного множественного регрессионного анализа в отношении количественных признаков и логит-регрессионного анализа в отношении количественных и качественных признаков.
Результаты
Клиническая характеристика пациентов, включенных в исследование, представлена в табл. 1.
В ходе исследования оценивалась толщина КИМ ОСА и взаимосвязь с клиническими показателями. Так, с возрастом у больных ХБП наблюдался прирост толщины КИМ ОСА с обеих сторон (r=0,55; p<0,05, табл. 2).

Кроме того, продолжительность анамнеза основного заболевания имела прямую корреляционную связь с толщиной КИМ, что отражало проявление сосудистого ремоделирования ОСА (r=0,19; p<0,05). При этом корреляционный анализ не продемонстрировал связи стажа ЗПТ и толщины КИМ ОСА, однако логит-регрессионный анализ показал влияние длительности ГД на обсуждаемый показатель (χ2 – 3,79; p<0,05, табл. 3).
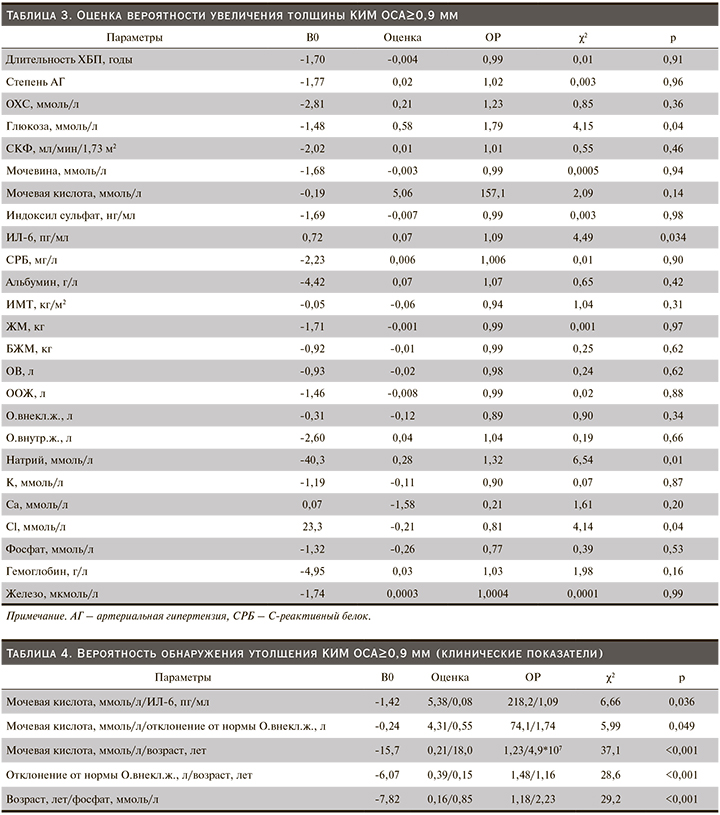
Следует отметить, что значимость традиционных факторов риска, таких как АГ, дислипидемия и СКФ, в отношении толщины КИМ у пациентов с ХБП-5Д, по полученным данным, была снижена. Вместе с тем на толщину КИМ ОСА влиял уровень глюкозы крови. Было показано, что при гипергликемии вероятность обнаружения увеличенной толщины КИМ ОСА≥0,9 мм повышалась (χ2=4,15, р=0,04).
Вместе с тем была обнаружена отрицательная корреляционная связь средней силы между низкой концентрацией альбумина и величиной толщины КИМ ОСА (r=-0,32; p<0,05). Так, чем ниже был уровень этого альбумина, тем выше обсуждаемый параметр. Вероятно, это связано с интегративной ролью альбумина и его участием в различных процессах в организме, в т.ч. в обмене липидов, системном воспалении и др. В то же время гипоальбуминемия ассоциирована с белково-энергетической недостаточностью и саркопенией у больных ХБП и считается фактором риска сердечно-сосудистой смерти в этой группе.
Дизэлектролитемия при ХБП – еще один фактор, связанный с сосудистым ремоделированием. Было обнаружено, что по мере нарастания уровня натрия (χ2=6,54; р=0,01) и снижения уровня хлора сыворотки крови (χ2=2,09; р=0,14) вероятность увеличения толщины КИМ ОСА повышается (рис. 1, 2).
Системное воспаление также оказывало негативное влияние на эндотелиальную функцию. Так, прирост ИЛ-6 в сыворотке крови как ключевого цитокина воспаления у пациентов с ХБП-5Д ассоциирован с повышением вероятности обнаружения утолщенного КИМ ОСА (χ2=4,49; р=0,034).
Несмотря на то что уровень мочевой кислоты в крови самостоятельно не влиял на КИМ ОСА, а зависимость носила лишь характер тенденции (χ2=2,09; р=0,14), была оценена вероятность утолщения КИМ ОСА при совместном нарастании уровня мочевой кислоты с изменением других клинических параметров. В том случае, когда наблюдалось повышение уровня мочевой кислоты с увеличением возраста пациентов (χ2=37,1; р=0,001) и нарастанием уровня ИЛ-6 (χ2=6,65; р=0,036), гиперурикемия влияла на вероятность утолщения КИМ ОСА (табл. 4).
Кроме этого гиперурикемия при внеклеточной гипергидратации негативно влияла на риск выявления утолщения КИМ ОСА (χ2=5,99; р=0,049). При анализе других показателей биоимпедансометрии взаимосвязи массы тела, ИМТ, ЖМ и КИМ ОСА выявлено не было. Однако установлено, что выявленные отклонения от ООЖ, сопровождавшиеся увеличением КИМ ОСА, происходили преимущественно за счет О.внекл.ж. (гиперволемия, отеки) (r=0,29; p<0,05). Так, при отклонении от должного О.внекл.ж. более чем на 2 литра с возрастом увеличивался риск утолщения КИМ ОСА, особенно у пациентов старше 60 лет (χ2=28,6; р<0,001).
Исследование других лабораторных показателей позволило установить, что гиперфосфатемия изолированно не оказывала действия на риск утолщения КИМ ОСА, однако при увеличении возраста больных нарастание уровня фосфора в крови способствовало увеличению вероятности утолщения КИМ ОСА (χ2=29,2; р<0,001).
При анализе влияния гемодинамических показателей, по данным УЗИ, показано, что увеличение сосудистого сопротивления в устье почечной артерии (χ2=3,79; р<0,05) и рено-аортального индекса (χ2=1,67; р=0,01) ассоциированы с увеличением риска утолщения КИМ ОСА.
Через 2 года после начала наблюдения мы проанализировали выживаемость пациентов, составившую 80%. При оценке толщины КИМ ОСА установлено, что в группе умерших этот показатель был достоверно выше, чем в группе выживших, и составил 1,02±0,11 против 0,8±0,4 мм соответственно (p<0,05).
Обсуждение
Увеличение толщины КИМ ОСА, очевидно, служит свидетельством сосудистого ремоделирования у пациентов с ХБП-5Д. Безусловно, возраст– важный фактор риска этого процесса и развития ССЗ, и в проведенном исследовании он продемонстрировал сильную корреляцию с толщиной КИМ ОСА. Это влияние было наибольшим в сочетании с таким фактором, как гиперфосфатемия. Известно, что в группе пациентов с ХБП, получающих лечение ГД, наблюдаются системные нарушения минерального и костного метаболизма. Развитие сосудистого ремоделирования и эндотелиальной дисфункции происходит за счет процессов внеоссальной кальцификации, прогрессирования атеросклероза, как следствие – приводит к сердечно-сосудистой смертности. Патогенетический механизм влияния гиперфосфатемии на сосудистую стенку обусловлен в т.ч. действием фактора роста фибробластов-23 [17, 18]. Высокое содержание фосфатов крови индуцирует дифференцировку гладкомышечных клеток сосудов в остеобластоподобные/хондроцитарные клетки [19]. Так, у пациентов с ТПН, получающих ЗПТ ГД, толщина КИМ ОСА положительно коррелирует с сывороточным уровнем фосфатов (r=0,6; p<0,01) и отрицательно с показателями альбумина сыворотки (r=-0,095; p<0,01). Вместе с тем низкий уровень сывороточного альбумина также связан с низким нутритивным статусом пациентов с ТПН и отрицательно коррелирует с толщиной КИМ ОСА (r=-0,291; p=0,016) [20].
Системное воспаление играет важную роль в механизме развития сосудистого ремоделирования: такой провоспалительный цитокин, как ИЛ-6, является фактором риска эндотелиальной дисфункции развития атеросклеротических ССЗ [21]. В то же время ИЛ-6 индуцирует в почках экспрессию активных форм кислорода, активных липидов и молекул адгезии, что повышает обозначенные риски пациентов и способствует прогрессированию сосудистого ремоделирования [16]. В связи с этим полученные данные указывают на значимый вклад ИЛ-6 в риск увеличения толщины КИМ ОСА, что ассоциировано с неблагоприятным прогнозом.
Помимо этого на толщину КИМ ОСА оказывали влияние уровни электролитов крови и дизэлектролитемия. Так, по мере увеличения уровня натрия и снижения уровня хлора сыворотки крови происходило увеличение обсуждаемого показателя. По всей видимости, гипернатриемия способствовала повреждению эндотелиального гликокаликса, ответственного за регуляцию сосудистой проницаемости, активацию коагуляции и фибринолиза, защиту эндотелия от клеточной адгезии [22]. Патогенетические механизмы влияния хлора на сосудистое ремоделирование до конца не изучены. Вместе с тем по результатам исследования K. Kubota et al. (2020) установлено, что более низкие уровни хлора в сыворотке крови были неблагоприятным предиктором сердечно-сосудистых событий [23].
В работе A. Bulut et al. (2019) установлено, что в условиях гипергликемии возрастала вероятность утолщения КИМ, а у пациентов с сахарным диабетом 2 типа толщина КИМ ОСА была больше по сравнению c таковой у пациентов с нарушенной толерантностью к глюкозе [24].
Заключение
Толщина КИМ – интегративный показатель, на который оказывает влияние множество факторов. Было установлено, что в группе пациентов с ТПН к ним можно отнести длительность анамнеза ХБП, продолжительность ЗПТ, уремическую интоксикацию, системное воспаление, дизэлектролитемию, гипергликемию, гипоальбуминемию, а также повышенное сосудистое сопротивление в устье почечной артерии и высокий рено-аортальный индекс. Стоит отметить, что это не полный перечень факторов и их дальнейшее изучение представляет научный интерес. В то же время нами установлена предиктивная роль толщины КИМ ОСА, которая может быть использована в клинической практике в качестве доступного дополнительного метода оценки прогноза заболевания и риска развития сердечно-сосудистых событий у пациентов с ХБП, получающих ГД.



