Введение
Чрезвычайно высокий риск смертности пациентов, находящихся на гемодиализе (ГД), стал стимулом для широкого спектра терапевтических вмешательств помимо самого диализа. Изменения образа жизни и рациона питания, лечение анемии, изменение режима и продолжительности диализа, а также оптимизация традиционных факторов риска, включая артериальную гипертензию и дислипидемию, не смогли существенно улучшить исход, за исключением трансплантации почки и, возможно, гемодиафильтрации большого объема у отдельных пациентов.
Минерально-костные нарушения при хронической болезни почек (МКН-ХБП) – широко распространенное осложнение ХБП, которое возникает на ранних стадиях заболевания и прогрессирует по мере уменьшения функционирующих нефронов. Вторичный гиперпаратиреоз (ВГПТ) при ХБП считается частью системного клинического синдрома МКН, традиционно определяемого аномальными сывороточными концентрациями фосфатов (Р), фактора роста фибробластов-23 (ФРФ-23), кальция (Са), паратиреоидного гормона (ПТГ), щелочной фосфатазы (общей и костного изофермента), витамина D; эктопической (внескелетной) кальцификацией артерий, клапанов сердца, мягких тканей, уремической кальцинирующей артериолопатией и костной патологией с нарушением обновления, минерализации, объема, линейного роста и/или прочности костной ткани [1–3].
В отсутствие своевременного контроля ВГПТ часто становится невосприимчивым к терапии, что может способствовать увеличению скорости костного метаболизма, деминерализации кости, боли в костях, суставах и мышцах, переломам, когнитивным нарушениям, сосудистой и висцеральной кальцификации, кожному зуду, артериальной гипертензии, снижению качества жизни, повышению риска сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний и смерти [3–6].
Патогенез, развитие и клинические особенности МКН-ХБП зависят от множества факторов. Они включают тип нефропатии, скорость прогрессирования ХБП, возраст, пол, этническую принадлежность, географический регион, дефицит витамина D, привычки питания, лекарства и сопутствующие патологические состояния, такие как сахарный диабет. Ведение пациентов с МКН представляет огромную клиническую проблему, потому что эффективность существующих терапевтических режимов профилактики и лечения ограниченны. Чрезвычайно высокий риск смертности пациентов, находящихся на ГД, стал стимулом для широкого спектра терапевтических вмешательств, направленных на оптимизацию контроля MКН, в частности ВГПТ [7].
Несмотря на достаточное количество публикаций высококачественных исследований в течение последних лет, все еще существуют значительные пробелы в базе знаний об оптимизированных подходах к лечению пациентов с МКН-ХБП.
В этом обзоре мы кратко резюмируем патогенез ВГПТ при ХБП с акцентом на ключевые молекулярные регуляторы МКН, на которые нацелены кальцимиметики (КМ), рассмотрим результаты исследований, извлеченные из применения перорального КМ первого поколения цинакальцета (ЦК), сравним и сопоставим фармакологические характеристики ЦК и нового внутривенного препарата второго поколения этелкальцетида (ЭК), обсудим результаты клинических испытаний с участием этих препаратов и последствия их использования в клинической практике.
Дополнения к представлению о патогенезе вторичного гиперпаратиреоза при ХБП
Почки и паращитовидные железы (ПЩЖ) играют центральную роль в минеральном гомеостазе. В физиологических условиях небольшие колебания уровней Ca в сыворотке крови обнаруживаются рецепторами, чувствительными к Ca (CaSR), встроенными в мембраны клеток ПЩЖ и почечных канальцев. CaSR реагируют на минимальные колебания концентрации внеклеточного Са, выделяя соответствующие уровни ПТГ. Паратиреоидный гормон стимулирует резорбцию костной ткани, высвобождая ионы Ca и P во внеклеточное пространство, стимулирует синтез в почках кальцитриола (1,25(ОН)2D3), который в свою очередь способствует всасыванию Ca и P кишечником. ПТГ, стимулируя канальцевую реабсорбцию Р, снижает почечную экскрецию Са, при этом оказывая фосфатурическое действие. Все вместе эти действия в основном направлены на поддержание соответствующих концентраций Ca в сыворотке. Уровень сывороточного P регулируется преимущественно ФРФ-23, который уменьшает его реабсорбцию в канальцах. Важно отметить, что сам по себе ПТГ стимулирует секрецию ФРФ-23 напрямую и косвенно за счет усиленного синтеза 1,25(ОН)2D3, вторичного по отношению к индуцированной ПТГ стимуляции 1α-гидроксилазы канальцев. Функция ПЩЖ подавляется высокими уровнями Ca, 1,25(ОН)2D3 и ФРФ-23 [8].
Развитие МКН при ХБП происходит в ответ на уменьшение массы действующих нефронов, что сопровождается снижением способности почек к выведению Р с временным увеличением его содержания в сыворотке крови. Как адаптивный ответ на повышение Р увеличивается ФРФ-23 (гормон фосфатонин), синтезируемый остеоцитами и остеобластами, который немедленно корректирует увеличение Р в плазме постоянным ингибированием его реабсорбции в проксимальных канальцах независимо от ПТГ []. ПТГ также обладает фосфатоническими свойствами и, подобно ФРФ-23, снижает реабсорбцию Р в проксимальных канальцах [9]. Схематическое представление сложной взаимосвязи нарушений минерального и гормонального обменов в процессе прогрессирования ХБП показано на рис. 1.
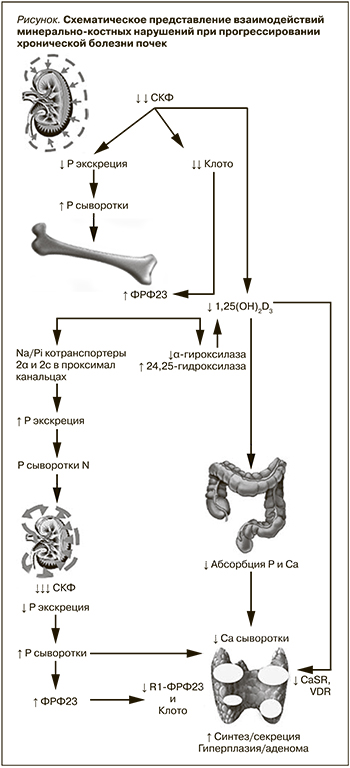
У людей без патологии почек ФРФ-23 ингибирует секрецию ПТГ, однако у пациентов с ХБП этого не происходит вследствие дефицита Клото, экспрессированного в канальцах и ПЩЖ. Для активации ФРФ-23 своих рецепторов ФРФR-1 и ФРФR-3 на эпителиальных клетках канальцев требуется наличие Клото, который в своей функции корецептора придает рецепторам специфичность к ФРФ-23. Благодаря этому компенсаторному механизму уровень Р сыворотки длительно остается в пределах нормы. Однако Клото также оказывает не зависимые от ФРФ-23 ауто- или паракринные эффекты, регулирует функцию различных ионных каналов и транспортеров, может индуцировать фосфатурию, возможно, через активацию Na-P котранспортеров в проксимальных канальцах. Существует все больше доказательств в пользу мнения, согласно которому снижение синтеза почечного Клото предшествует увеличению синтеза костными клетками ФРФ-23.
Прогрессирующее снижение СКФ сопровождается увеличением канальцевой нагрузки P и ростом уровней ФРФ-23 (хотя последний обычно не измеряется в клинических условиях) при снижении экспрессии корецептора Клото в канальцах и уровней растворимого Клото до такой степени, что увеличение ПТГ и постоянно повышенный уровень ФРФ-23, необходимый для поддержания нормального сывороточного Р, не способны увеличивать экскрецию P и развивается гиперфосфатемия. Как гиперфосфатемия, так и избыток ФРФ-23 неизбежно пролонгируют подавление синтеза 1,25(ОН)2D3 – кальцитриола (КТ), которое сопровождается уменьшением активной абсорбции Р и Са в кишечнике с развитием гипокальциемии. Ингибирование синтеза КТ не только возникает вследствие непосредственного подавления активности 1ɑ-гидроксилазы ФРФ-23 и Р, но и обусловлено прогрессирующей деструкцией проксимальных канальцев (места образования КТ), дополнительной супрессией 1ɑ-гидроксилазы ацидозом, накапливающимися при уремии соединениями (например, ксантин, мочевая кислота). Кроме того, Р стимулирует продукцию ПТГ независимо от изменений концентрации Са и 1,25(ОН)2D3 и напрямую вызывает гиперплазию клеток ПЩЖ. У пациентов, находящихся на диализе, гиперфосфатемия непосредственно стимулирует секрецию ПТГ и поддерживает постоянный стимул для гиперплазии ПЩЖ [10].
Поддержание уровня сывороточного Са в узком референтном диапазоне крайне важно для нормального функционирования всех систем организма (прежде всего сердечно-сосудистой и передачи сигнала в нейромышечных синапсах и др.). Быстрота восстановления потерь Са осуществляется за счет резорбции костной ткани (легкодоступного резервуара Са в организме) под воздействием ПТГ, стимулирующего остеокласты, во вторую очередь – за счет активации 1ɑ-гидроксилазы с повышением синтеза D-гормона и увеличения кишечной абсорбции Са и выведения избыточного Р, высвобождающегося из кости и всасывающегося в кишечнике параллельно с Са,
Гормон ПЩЖ помогает поддерживать баланс Са в организме, регулируя уровень Са в крови, высвобождение из кости, всасывание в кишечнике и выведение с мочой. Кроме того, ПТГ поддерживает активацию 25(OH)D до 1,25(OH)2D3 или КТ и корректирует Р в сыворотке постоянным ингибированием канальцевой реабсорбции фосфата. При прогрессирующей ХБП эти механизмы постепенно становятся неспособными преодолеть непрерывное поступление фосфатов из рациона питания, что приводит к положительному фосфатному балансу и гиперфосфатемии.
Другим важным эффектом P является выработка устойчивости скелета к кальциемическому эффекту ПТГ, что дополнительно способствует развитию гипокальциемии с последующим стимулом гиперплазии ПЩЖ. При нарушении функции почек синтез 1,25(ОН)2D3 очень низкий и его последствием является гипокальциемия, которая увеличивает экспрессию ядерного антигена пролиферирующих клеток. С другой стороны, несколько исследований показало, что отсутствие или снижение антипролиферативного действия 1,25(ОН)2D3, нарушение регуляции специфического паращитовидного рецептора R1 к ФРФ23 (R1ФРФ23))/Клото, предотвращает любое ингибирующее действие ФРФ-23, что также способствует развитию гиперплазии ПЩЖ [11, 12].
Ключевыми молекулярными регуляторами функции ПЩЖ и секреции ПТГ являются CaSR и ядерный рецептор витамина D (VDR). Активация VDR снижает транскрипцию ПТГ, в то время как снижение КТ стимулирует синтез ПТГ. Что касается сигнальных механизмов, участвующих в развитии гиперплазии ПЩЖ, в недавнем исследовании S. Kan et al. сообщалось, что дефицит витамина D способствует активации ядерного фактора каппа В (NFkB) как в ПЩЖ у пациентов, находящихся на ГД, так и в экспериментальных моделях уремии [13].
CaSR – это первый рецептор, где роль природного лиганда выполняет ион, а не пептидный гормон, гликопротеин или внеклеточное органическое вещество. Повышение концентрации циркулирующих ионов Са приводит к конформационным изменениям в экстрацеллюляром домене этого трансмембранного белка с дальнейшим преобразованием его в интрацеллюлярный сигнал, подавляющий секрецию ПТГ и модулирующий процессы транспорта бивалентных ионов и воды в почечных канальцах. Снижение концентрации Са++ в крови быстро стимулирует секрецию ПТГ, длительная гипокальциемия увеличивает синтез ПТГ, и это вызывает гиперплазию клеток ПЩЖ.
Хотя доказательства прямого стимулирующего влияния Р на секрецию ПТГ продемонстрированы более 20 лет назад, недавние исследования P. Centeno et al. [] показали, что CaSR может действовать как датчик Р в ПЩЖ, регистрируя изменения концентрации внеклеточного Р. Фосфат подавляет активность CaSR посредством неконкурентного антагонизма и таким образом увеличивает секрецию ПТГ. У здоровых лиц CaSR отрицательно модулирует секрецию ПТГ для контроля гомеостаза Ca. Резкое повышение P подавляет CaSR и увеличивает секрецию ПТГ, который стимулирует экскрецию Р почками, чтобы восстановить нормальный уровень P в сыворотке крови. Однако при ХБП гиперфосфатемия стабилизирует неактивную конформацию CaSR, позволяя хронически повышать секрецию ПТГ и способствуя прогрессированию ВГПТ [14].
Механизмы, лежащие в основе патофизиологии ВГПТ, в значительной степени известны, но недавние работы пролили свет на наши знания этой патологии. Так, установлено, что Клото служит корецептором для ФРФ-23, однако использование генетических подходов показало, что существует взаимодействие между Клото и CaSR, и Клото играет ключевую роль в подавлении синтеза ПТГ и пролиферации ПЩЖ [15, 16].
Существует по меньшей мере два основных различных механизма, определяющих развитие ВГПТ. Первый – это увеличение синтеза и секреции ПТГ, второй – увеличение массы ПЩЖ, в основном за счет усиленной пролиферации клеток (гиперплазия) и в меньшей степени также увеличения размера клеток (гипертрофия). По мере прогрессивной потери почечной паренхимы повышающаяся нагрузка Р, снижение синтеза КТ и гипокальциемия запускают важный компенсаторный механизм: повышают секрецию ПТГ главными клетками ПЩЖ, что приводит ко всевозрастающей ее гиперплазии. Помимо комплексного воздействия на ПЩЖ вышеперечисленных системных нарушений, снижение экспрессии рецептора VDR, CaSR и ФРФR-1 и его Клото-локального корецептора еще больше усугубляют нарушение контроля синтеза и секреции ПТГ. Рецептор витамина D и CaSR в разной степени не экспрессируются или менее функциональны при ХБП, что делает клетки ПЩЖ неспособными реагировать на Са и/или КТ, увеличивает количество активных секреторных клеток и приводит к гиперплазии ПЩЖ.
В связи с этим представляет интерес исследование транскриптомной сигнатуры, в котором были проведены сравнительные анализы аденом ПЩЖ со здоровыми тканями []. Кроме того, растет осведомленность об участии микро-РНК (мРНК) – небольших некодирующих молекул РНК, которые модулируют экспрессию РНК, в патофизиологии гиперплазии ПЩЖ [17, 18].
Увеличение пролиферации паращитовидных клеток не компенсируется сопутствующим увеличением апоптоза клеток, регулируемого рядом гормонов и факторов роста. Гиперплазия ПЩЖ первоначально имеет диффузный, поликлональный тип и сопровождается снижением экспрессии рецепторов ПЩЖ, в т.ч. ФРФR-1 и Клото. На поздних стадиях ХБП гиперплазия ПЩЖ часто прогрессирует в сторону узлового, моноклонального или мультиклонального типа роста. Прогрессирование от диффузной гиперплазии клеток ПЩЖ к узловой характеризуется прогрессирующим снижением экспрессии рецепторов CaSR, VDR и ФРФFR1 и развитием третичного гиперпаратиреоза, при котором железа не восприимчива к действию как своих естественных ингибиторов, так и к антипаратиреоидной терапии. В совокупности эти результаты могут помочь раскрыть новые механизмы, лежащие в основе развития ВГПТ, а также разработать стратегии профилактики гиперплазии ПЩЖ и управления секрецией ПТГ.
Клинические последствия вторичного гиперпаратиреоза
Нарушения минерально-костного метаболизма на ранних стадиях ХБП характеризуются бессимптомными отклонениями лабораторных показателей и усугубляются по мере прогрессирования ХБП. Клинические симптомы, как правило, возникают преимущественно у пациентов с ХБП С4–5Д при развитии ВГПТ и характеризуются когнитивными нарушениями, эндокринной патологией, эктопической (внекостной) кальцификацией сосудов, проксимальной мышечной слабостью, мышечными судорогами, обусловленными гипокальциемией.
ВГПТ может быть связан с устойчивостью к эффектам терапии эритропоэтином пациентов с анемией, ассоциированной с ХБП, которая определяется как неспособность нормализовать гемоглобин после 4–6 месяцев терапии эритропоэтином в отсутствие дефицита железа. Механизмы, с помощью которых ВГПТ может способствовать развитию анемии или снижать реакцию костного мозга на эритропоэз, четко не изучены. Высокие уровни ПТГ могут влиять на выработку эритроцитов напрямую через токсическое действие ПТГ на эритроидные предшественники костного мозга и усиление гемолиза либо косвенно, способствуя фиброзу костного мозга [19].
Костная патология проявляется развитием фиброзного остеита, адинамической болезни кости, остеомаляцией, остеопорозом или смешанными поражениями. Вследствие поражения костей пациентов беспокоят оссалгии, разрушение зубов и ломкость волос. Со временем происходит грубая деформация скелета, при котором бедренная кость приобретает форму «пастушьей палки», позвонки – «рыбьих», таз – «карточного сердца», грудная клетка становится похожей на колокол, формируется «утиная» походка. На фоне патологических изменений позвонков происходит общая деформация позвоночного столба – кифозы (искривление кзади с формированием горба), сколиозы (искривление вбок с нарушением общей симметрии тела), кифосколиозы. Вследствие выраженных костных деформаций пациенты могут потерять в росте 10–15 см и более.
Из-за тяжелых патологических повреждений костной ткани происходят переломы костей даже при незначительной нагрузке или спонтанно (патологические переломы). В отличие от обычных патологические переломы менее болезненны, что часто затрудняет своевременную диагностику и приводит к неправильному срастанию костей или к образованию ложных суставов (отломки кости не срастаются, а приобретают патологическую подвижность), что приводит к стойкой потере трудоспособности. Заживление переломов происходит медленно, и при срастании кости формируется достаточно плотная костная мозоль, так что повторных переломов в одном и том же месте не происходит. Могут развиваться спонтанные разрывы сухожилий.
Переломы кости встречаются в 2–4 раза чаще у пациентов с ВГПТ по сравнению со здоровыми людьми, соответствующими их возрасту и полу. Риск переломов костей находится в диапазоне 15,0; 20,5; 24,2; 31,2 и 46,3% на 1000 человеко-лет для стадий ХБП-1, -2, -3a, -3б и -4 соответственно [20]. Риск переломов скелета в 5 раз выше у лиц с рСКФ < 15 мл/мин/1,73м2 по сравнению с >60 мл/мин/1,73м2. Кроме того, частота переломов значительно выше у пациентов, находящихся на ГД, чем в общей популяции, что связано с увеличением нескорректированного относительного риска смерти в 3,7 раза [21]. Следует учитывать другие причины повышения хрупкости и переломов костей, такие как метаболический ацидоз, анемия, гипогонадизм, воспаление, диализный амилоидоз, дефицит витамина D, ингибирование образования кости, вторичное по отношению к ингибированию клеток остеобластов [22]. Поражение суставов связано как с деформацией скелета, так и с периартикулярными кальцинатами или отложением кристаллов мочевой кислоты в суставах (истинная подагра).
ВГПТ вносит существенный вклад в кальцификацию сосудов как медиального, так и интимального слоев, которая сопровождается ишемическими сердечно-сосудистыми событиями и сердечной недостаточностью. Кроме того, высокий уровень ПТГ увеличивает симпатическое возбуждение и эндотелиальный стресс [23].
ВГПТ приводит к неблагоприятным исходам: сердечно-сосудистой патологии, патологическим переломам, инвалидизации пациентов, ухудшению качества жизни, повышению сердечно-сосудистой и летальности от всех причин [24].
Рекомендуемые целевые значения паратиреоидного гормона при ХБП-С5Д
В отличие от предложенного в руководстве KDOQI (2003), целевого показателя ПТГ при ХБП-С5Д в диапазоне 150–300 пг/мл [25], международное Руководство по клинической практике KDIGO (2009) для диагностики, оценки, профилактики и лечения МКН-ХБП (и в обновлении 2017 г.) предлагают поддерживать уровень ПТГ в крови в интервале от 2- до 9-кратного превышения верхней границы нормы (≈130-585 пг/мл) в соответствии с используемым методом определения ПТГ, но следует отметить, что данная рекомендация основана на доказательствах низкого уровня (2С) [2, 26].
Изменения в рекомендациях KDIGO привели к внезапному и резкому изменению верхнего целевого уровня ПТГ у пациентов с ХБП-С5Д с 300 до 585 пг/мл, что, по данным DOPPS, сопровождалось повышением доли пациентов с ПТГ в сыворотке крови выше 600 пг/мл [3, 27]. Сложность ведения пациентов с МКН в сочетании с ограничениями в рекомендациях, основанными на фактических данных в этой области, способствовали тенденции к большей вариабельности уровней ПТГ и, соответственно, менее агрессивному ведению пациентов с ВГПТ [28]. Негативными последствиями данного изменения служат отсроченная стратегия контроля ВГПТ, потребность в назначении значимо более высоких доз препаратов и снижение эффективности терапии со всеми вытекающими неблагоприятными клиническими последствиями. Несколько крупных обсервационных исследований последовательно демонстрировали более высокие риски смертности для пациентов с БГ с высоким ПТГ (≥600 пг/мл) [29–31].
Чтобы выполнить ограничения в рекомендации по клинической практике KDIGO и попытаться не преодолевать предложенные диапазоны ПТГ, необходимо учитывать не только концепцию «тенденций», но и учитывать, что по данным ряда исследований выявлен возможный оптимальный уровень ПТГ – от 150 до 450 пг/мл, при котором обеспечивается самый низкий риск смертности от всех причин и сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний среди пациентов, находящихся на диализе [8, 32–35]. Исходя из изложенного, целесообразно назначать медикаментозную терапию не при превышении верхнего уровня ПТГ, а при его нарастании в интервале от 300 до 585 пг/мл по результатам двух последовательных измерений, чтобы поддерживать ПТГ в пределах диапазона (желательно без превышения 450 пг/мл).
Основные принципы контроля вторичного гиперпаратиреоза
Терапевтические решения у пациентов с МКН (определение лечебной тактики, назначение терапии, титрация дозы препаратов, оценка эффективности, побочных эффектов, появление новых МКН) следует основывать не на единичных результатах лабораторных исследований, а на серийных оценках тенденции развития заболевания с учетом всех ранее выполненных исследований. В обновленных рекомендациях KDIGO (2017) приводится следующее обоснование акцента на отказ от начала лечения при единственном повышенном значении ПТГ [2, 36].
- оптимальная сывороточная концентрация ПТГ остается неопределенной;
- умеренное повышение концентрации ПТГ является подходящей адаптивной реакцией, способствующей фосфатурии при ХБП, следовательно, может быть полезной для поддержания нормального уровня Р в сыворотке крови при снижении СКФ;
- устойчивость к влиянию ПТГ на скелет может не требовать коррекции умеренно повышенного уровня ПТГ при ХБП до референтных значений.
Основные цели лечения ВГТП:
- достижение и поддержание оптимального уровня ПТГ;
- предотвращение эктопической кальцификации, нормализация процессов ремоделирования костной ткани, снижение частоты переломов, предотвращение развития фиброза костного мозга, способствующего развитию анемии и резистентности к проводимой терапии;
- увеличение продолжительности и качества жизни пациентов.
Текущие варианты лечения ВГПТ заключаются в использовании комбинированного подхода, направленного на:
1. Отслеживание уровней ПТГ, Р и Са в сыворотке крови;
2. Лечение, снижающее уровень фосфатов: ограничение потребления Р с пищей, уточнение источника фосфатов (например, животные, растительные, пищевые добавки), предпочтение источников белка с отношением Р(мг)/белок (г) >12, ограничение приема лекарств с высоким содержанием фосфатов и применения фосфатных связующих на основе кальция;
3. Адекватные процедуры заместительной почечной терапии (ЗПТ);
4. Коррекцию ацидоза;
5. Ингибирование синтеза и секреции ПТГ назначением антипаратиреоидной терапии или паратиреоидэктомией (ПТЭ).
Для достижения при ВГПТ оптимальных значений ПТГ существуют два основных варианта антипаратиреоидной терапии, а именно активаторы рецепторов витамина D (VDRА) и кальцимиметики (модуляторы CaSR). В руководстве по клинической практике KDIGO (2017) предлагается пациентам с ВГПТ на ЗПТ диализом использовать кальцимиметики (КМ), кальцитриол (КТ), аналоги витамина D или их комбинацию. При неэффективности фармакотерапии и при развитии третичного гиперпаратиреоза (аденомы ПЩЖ) как вариант контроля следует рассмотреть хирургическое удаление ПЩЖ – ПТЭ []. При уровне доказательности 2B ни один подход не является предпочтительным по сравнению с другим [2, 36].
Лечение следует начинать с модификации показателей МКН до достижения референсных значений локальной лаборатории в любом смысле, поскольку именно от этих пределов в сторону как уменьшения, так и увеличения наблюдается наибольшая связь с высоким относительным риском смерти. Несмотря на то что клинических данных недостаточно, чтобы дать точные рекомендации по целевым значениям показателей минерально-костного обмена для поддержания оптимального здоровья костей и предотвращения сердечно-сосудистых осложнений, установлено, что только последовательный контроль основных биохимических параметров МКН у пациентов на ЗПТ диализом был связан с лучшей выживаемостью и улучшением других результатов [37–39].
Достижения в контроле вторичного гиперпаратиреоза – новые кальцимиметические агенты
Идентификация и клонирование CaSR позволили разработать новый класс препаратов – кальцимиметиков (КМ), которые индуцируют конформационное изменение рецептора, повышают чувствительность к внеклеточному ионизированному Са, что приводит к снижению синтеза и секреции ПТГ [40, 41].
В доклинических экспериментальных моделях КМ также доказали свою эффективность в предотвращении развития сосудистых кальцинатов и даже ускорении регрессирования установленных кальцинатов в доклинических экспериментальных моделях [42, 43]. В ряде исследований установлено, что КМ – эффективные и безопасные методы лечения серьезного осложнения МКН – ВГПТ, который развивается примерно у 80% пациентов, получающих поддерживающий диализ [4, 41, 44, 45].
Уроки, извлеченные из применения кальцимиметического препарата первого поколения
Цинакальцет (ЦК) – первый кальцимиметический препарат, одобренный для клинического применения в отношении диализных пациентов с ВГПТ. Его принимают внутрь 1 раз в день с рекомендуемой начальной дозой 30 мг. Для достижения целевых показателей ПТГ возможно повышение дозы до максимальной разовой дозы 180 мг [46, 47]. В отличие от неселективных VDRA, которые, как правило, повышают уровни Са, Р и ФРФ-23 в сыворотке крови при одновременном снижении ПТГ, лечение ЦК улучшает биохимические показатели при МКН по сравнению с пациентами, получавшими стандартную схему, содержавшую КТ или другой VDRA [48–50].
Рандомизированное клиническое исследование (РКИ) фазы IV ADVANCE показало тенденцию к более медленному прогрессированию кальцификации коронарной артерии и аортального клапана после 52 недель лечения ГД пациентов с ВГПТ от средней до тяжелой степени тяжести, получавших ЦК и низкие дозы активного витамина D по сравнению с субъектами, получавшими различные дозы VDRA в качестве монотерапии. Данный результат наблюдался при оценке по объемной шкале; результату при оценке по шкале Агатстона слегка недоставало статистической значимости (р=0,07). Последующие анализы показали, что пациенты, которые соблюдали режим лечения или имели кальцинаты коронарных артерий и/или сердечных клапанов, продемонстрировали значительное замедление прогрессирования кальцификации даже при оценке по шкале Агатстона. Так, снижение риска прогрессирования кальцификации аортального клапана составило 74% (ОШ=0,26; 95% ДИ: 0,10–0,64) [51–53].
В крупнейшем плацебо-контролируемом двойном слепом РКИ EVOLVE, когда-либо проводившемся у диализных пациентов с ВГПТ, в которое были включены 3883 пациента, получавших ЦК в дополнение к стандартному лечению, показали лучший контроль ПТГ и более низкий риск развития тяжелого рефрактерного ВГПТ по сравнению с группой плацебо [54]. Однако исследование не смогло доказать превосходство ЦК над плацебо в достижении более амбициозной композитной первичной конечной точки – время до смерти или первое возникновение нефатального сердечно-сосудистого события, включая инфаркт миокарда, госпитализацию по поводу нестабильной стенокардии, сердечной недостаточности и события с периферическими сосудами (ОР=0,93; 95% ДИ: 0,85–1,02; p=0,11). Статистическая неубедительная значимость исследования обусловлена снижением его статистической мощности с 90 до 54% вследствие как решения врачей, ответственных за лечение пациентов плацебо или ЦК, так и частоты отмены ЦК из-за нежелательных побочных эффектов, в основном желудочно-кишечных событий. Поэтому, с одной стороны, клинические испытания с использованием суррогатных конечных точек, таких как контроль биохимических маркеров, доказали эффективность ЦК, с другой – исследование EVOLVE не смогло доказать влияние модуляции CaSR на жесткие конечные точки.
Вторичный анализ исследования EVOLVE показал, что ЦК был более эффективным у лиц в возрасте старше 65 лет по сравнению с более молодыми, снижал риск кальцификации, кальцифилаксии [55–57], уровни ФРФ-23, в связи с чем высказано предположение, согласно которому снижение ФРФ-23 связано с более низкими показателями неатеросклеротических сердечно-сосудистых событий и сердечно-сосудистой смерти [58, 59]. Установлено увеличение минеральной плотности костной ткани (МПК) при назначении ЦК пациентам, находящимся на программном гемодиализе (ПГД) [60, 61]. Совсем недавняя работа показала, что этот эффект возникает независимо от изменений уровня ПТГ [62].
Кроме того, у пациентов группы ЦК продемонстрировано значительное снижение риска ПТЭ, переломов и увеличение минеральной плотности костной ткани [60, 61], а совсем в недавнем экспериментальном исследовании J.M. Díaz-Tocados et al. [62] установлено, что этот эффект возникает независимо от изменений уровня ПТГ. Эффективность ЦК установлена даже у пациентов с персистирующим или рецидивирующим гиперпаратиреозом после ПТЭ [63].
Этелкальцетид (ЭК) – новый КМ второго поколения, одобренный для лечения ВГПТ у пациентов, находящихся на ГД. Несмотря на одинаковую точку приложения ЦК и ЭК (CaSR), они различаются в отношении структуры, способа введения, длительности периода полувыведения и потенциала лекарственных взаимодействий с участием системы цитохрома P-450. В табл. 1 представлен краткий обзор ключевых различий между КМ первого (цинакальцет) и второго (этелкальцетид) поколений.
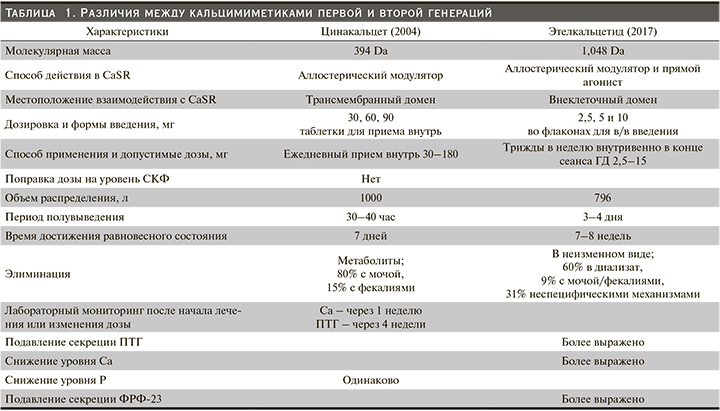
Фармакокинетический профиль ЭК у пациентов с ХБП отличается от ЦК. В то время как ЦК является аллостерическим модулятором CaSR и подобно ЦК вызывает быстрое и дозозависимое снижение концентрации ПТГ, Са, Р и ФРФ-23, но в отличие от ЦК этелкальцетид способен активировать CаSR даже в условиях, не содержащих Са, что свидетельствует о наличии у него дополнительной функции прямого агониста CаSR. Этелкальцетид практически полностью выводится почками посредством клубочковой фильтрации. Вследствие этого период полувыведения ЭК из плазмы значительно увеличивается при снижении функции почек и составляет от 3 до 5 дней. Длительность снижения уровня ПТГ при однократном внутривенном введении ЭК пациентам на программном ГД (ПГД) достигает 72 часов, что позволяет вводить его 3 раза в неделю, таким образом преодолевая проблему соблюдения ежедневного режима приема внутрь. Поскольку при ГД происходит довольно быстрая элиминация препарата, ЭК рекомендуется вводить при отключении от аппарата [64–67].
Этелкальцетид устойчив к ферментативной деградации протеазами и не является ни ингибитором, ни индуктором печеночных ферментов цитохрома Р-450 (CYP450) (в отличие от ЦК, который метаболизируется CYP3A4 и CYP1A2 и ингибирует CYP2D6), поэтому риск метаболических или фармакокинетических взаимодействий между лекарственными средствами с ЭК низок до незначительного. С другой стороны, фармакодинамические взаимодействия могут возникать с другими терапевтическими препаратами, снижающими уровень Са в сыворотке крови, соответственно, в случае необходимости следует соблюдать осторожность при их применении. Этелкальцетид и ЦК не следует назначать одновременно с учетом дополнительного риска гипокальциемии, возникающего в результате сходных механизмов действия и влияния на уровни ПТГ, Са и фосфора в сыворотке крови [68, 69].
Эффективность и безопасность ЭК при лечении ВГПТ у пациентов, находящихся на диализе, исследованы в нескольких РКИ по сравнению с плацебо или ЦК [67, 70–73]. G.A. Block et al. [71] провели два параллельных, фаза III, двойных слепых РКИ, в которые были включены 1023 пациента с ВГПТ (ПТГ >400 пг/мл), находящихся на ПГД. Этелкальцетид либо плацебо применяли после каждого сеанса ГД в течение 26 недель в дополнение к традиционной терапии ВГПТ. Первичной конечной точкой была доля пациентов, достигших снижения ПТГ >30% от исходного уровня на этапе оценки эффективности с 20-й по 27-ю неделю. Начальная доза ЭК составляла 5 мг, и лечение было скорректировано в соответствии с уровнями ПТГ и Са до максимальной дозы 15 мг.
В первом исследовании зарегистрированы 508 пациентов, из которых 254 получали ЭК (средняя доза за сеанс – 7,1 мг).
Второе исследование включило 515 пациентов, из которых 255 были рандомизированы на исследуемый препарат (средняя доза за сеанс – 5,0 мг). В обоих исследованиях у пациентов, получавших ЭК, было значительно больше шансов достичь конечной точки первичной эффективности: 74,0 против 8,3% (р<0,001) и 75,3 против 9,6% (р<0,001) соответственно. Кроме того, в группе ЭК большее количество пациентов достигли среднего уровня ПТГ ≤300 пг/мл (49,6 против 5,1% и 53,3 против 4,6%, р<0.001). Этелкальцетид продемонстрировал снижение концентрации ПТГ независимо от исходного значения, продолжительности ЗПТ диализом, а также от стратегии применения стероловых форм витамина D. Показано, что наибольшая способность к достижению целевых значений ПТГ и наименьшая потребность дозы достигались при назначении пациентам препарата при уровне ПТГ менее 600 пг/мл. По сравнению с плацебо уровень Са в сыворотке крови значительно снизился в группе ЭК, но доля пациентов, получавших добавки Са, Са-содержащие ФСП или VDRA, увеличилась. Снижение уровня сывороточного Са регистрировалось при ранних сроках применения препарата, причем самые низкие его концентрации наблюдались в течение 10–12 недель лечения. Кроме того, ЭК снижал уровни Р и ФРФ-23 в сыворотке крови.
В двойном слепом РКИ III фазы «head-to-head» G.A. Block et al. [70] оценивали у 683 ГД пациентов с ВГПТ (ПТГ ≥500 пг/мл) из диализных центров Европы и США эффективность и безо-пасность ЭК (n=340) по сравнению с ЦК (n=343). Первичной конечной точкой являлось достижение снижения ПТГ >30% от исходного уровня на этапе оценки эффективности ЭК (20–27 недель). Ключевые вторичные конечные точки включали превосходство в достижении биохимических конечных точек (>50 и >30% снижения уровня ПТГ) и частоту побочных эффектов (тошнота и рвота) в течение первых 8 недель. Средняя недельная доза ЭК составляла 15,0 мг, средняя суточная доза ЦК – 51,4 мг. Этелкальцетид не уступал ЦК в снижении уровня ПТГ и продемонстрировал превосходство в нескольких конечных точках. Так, доля пациентов, достигших снижения ПТГ >30%, составила 68,2% в группе ЭК против 57,7% в группе ЦК (р=0.004). Значительно больше пациентов в группе ЭК по сравнению с ЦК достигли снижения уровня ПТГ >50% (52,4 против 40,2%, р=0,001) и значительного снижения ФРФ-23 >30% (74,4 против 57,5%, р<0,0001). По сравнению с ЦК лечение ЭК также было связано с большим снижением уровней Са и Р в сыворотке крови. Не наблюдалось существенной разницы в самооценке тошноты и рвоты между группой, получавшей ЭК, и группой, получавшей ЦК. Таким образом, эти желудочно-кишечные побочные эффекты, по-видимому, системные, а не локальный классовый эффект КМ, возможно, опосредованный активацией CaSR в непаратиреоидных органах-мишенях.
Результаты исследования фазы III, посвященного изучению эффективности и безопасности ЭК, сообщены M. Fukagawa et al. [72]. Это многоцентровое двойное слепое плацебо-контролируемое РКИ в параллельных группах проведено на 155 японских пациентах с уровнем ПТГ ≥300 пг/мл, находящихся на ГД. Пациенты, рандомизированные на исследуемый препарат, получали ЭК трижды в неделю после каждого сеанса ГД. Начальная доза составляла 5 мг, а в соответствии с уровнями ПТГ и Са доза ЭК корректировалась до разовых значений 2,5–15,0 мг с 4-недельными интервалами в течение 12 недель. Средняя доза ЭК в конце исследования составляла 7,8 мг. Первичной конечной точкой была доля пациентов с уровнем ПТГ 60–240 пг/мл на 85-й день (целевой диапазон ПТГ, рекомендованный Японским обществом диализной терапии). По сравнению с плацебо пациенты, рандомизированные на ЭК, чаще достигали этой первичной конечной точки (59,0 против 1,3%). При применении ЭК более высокая доля пациентов достигла снижения ПТГ на ≥30% по сравнению с исходным уровнем (76,9 против 5,2%). Кроме того, лечение ЭК связано со снижением содержания Са, Р и ФРФ-23 в сыворотке крови.
В недавнем систематическом обзоре и мета-анализе 36 исследований (11 247 участников) S.C. Palmer et al. [74] провели сравнительный анализ эффективности кальцимиметических агентов, используемых в терапии ВГПТ. По сравнению с плацебо ЭК имел самые высокие шансы достижения целевого уровня ПТГ по сравнению с эвокальцетом (ОШ=4,93; 95% ДИ: 1,33–18,2) и ЦК (ОШ=2,78; 95% ДИ: 1,19–6,67). Этелкальцетид вызывал более выраженную гипокальциемию, чем ЦК и эвокальцет. Цинакальцет, в меньшей степени ЭК вызывали тошноту чаще, чем плацебо. Различия в риске смертности, сердечно-сосудистых конечных точках или переломах для КМ не могли быть обнаружены с достаточной степенью уверенности вследствие отсутствия долгосрочных данных и неоднородных определений конечной точки. В целом эффективность ЭК в снижении уровня ПТГ независимо от тяжести ГПТ была неоднократно доказана, и ряд исследований продемонстрировал аналогичные результаты [75–81].
Крупное обсервационное исследование во Франции [82] показало, что через 12 месяцев от начала терапии ЦК доля пациентов с превышением верхнего предела уровня ПТГ более чем в 9 раз, составила 41 по сравнению с 26% среди пациентов, начавших лечение ЭК. Однако вероятность достижения целевого уровня ПТГ через 12 месяцев сильно зависела от исходной тяжести ВГПТ, что свидетельствует о потенциальной пользе лечения ВГПТ на более ранних стадиях. Недавние исследования также оценили важность начала лечения при более низких уровнях ПТГ и Р для долгосрочных результатов ВГПТ, способность управлять заболеванием и последующими последствиями. В то время как в предыдущих исследованиях установлена эффективность ЭК при всех уровнях степени тяжести ВГПТ, способность достигать целевых значений была наибольшей, а потребность в дозе наименьшей, когда начальная терапия ЭК назначалась при более низких исходных уровнях ПТГ – менее 600 пг/мл [77, 82].
Исследование, проведенное в реальной клинической практике [83] с участием более 2500 пациентов, продемонстрировало эффективность после начала приема ЭК в лечении ВГПТ у ГД пациентов в достижении целевых уровней ПТГ, предложенных KDIGO. За 3 месяца до начала приема ЭК более 80% пациентов получали активный витамин D, половина пациентов принимали ЦК. Тем не менее у новых пользователей ЭК доля пациентов с исходным уровнем ПТГ ≥1000 пг/мл составила 34 в целом и 43% среди пациентов, ранее применявших ЦК. Несмотря на такие высокие уровни ПТГ в начале приема ЭК, большинство пациентов, по-видимому, были чувствительными к ЭК. Доля пациентов с целевым уровнем ПТГ (150–599 пг/мл) через год после начала лечения составила в целом 64 и 60% среди пациентов, начавших прием ЭК с ПТГ ≥600 пг/мл. Хотя пациенты, которым назначали ЦК по сравнению с пациентами, которым не назначали ЦК за 3 месяца до начала приема ЭК, имели на 200 пг/мл более высокий средний уровень ПТГ по сравнению с пациентами группы VDRA (1046 против 838 пг/мл).
Высокие уровни Са с поправкой на альбумин в сыворотке крови (≥9,5 мг/дл), ранее показанные в обсервационном исследовании как связанные с сердечно-сосудистой смертностью, присутствовали у 38% новых пользователей ЭК и снизились до 15–20% в течение последующих 12 месяцев. Доля пациентов с умеренно низким содержанием Са с поправкой на альбумин в сыворотке крови (7,5–8,3 мг/дл) увеличилась с 8 до 27% за 3 месяца после начала приема ЭК, что подтверждает необходимость контроля уровня Са в сыворотке крови после начала приема ЭК, чтобы избежать гипокальциемии. Однако распространенность симптоматической гипокальциемии с поправкой Са на сывороточный альбумин <7,5 мг/дл была очень низкой (1–2%) в первый год после начала приема ЭК. Эти результаты согласуются с недавними исследованиями безопасности, предполагающими низкую частоту симптоматической гипокальциемии при применении ЭК или вызванной гипокальциемией отмены ЭК [76, 84].
Кроме того, в аннотации применения ЭК указано, что показатели Са с поправкой на альбумин в сыворотке крови должны быть на уровне или выше нижней границы референтных значений при начале терапии [85]. Изменения уровня Р в сыворотке крови также наблюдались после начала приема ЭК, особенно у пациентов с исходным уровнем ПТГ ≥600 пг/мл.
В этой подгруппе в течение 12 месяцев после начала приема ЭК распространенность гиперфосфатемии (сывороточный фосфор >5,5 мг/дл) снизилась с 60 до 45%, щелочной фосфатазы со 131 до 107 ЕД/л. Кроме того, результаты, полученные на основе специального анализа открытого исследования показали, что 52 недели терапии ЭК были связаны с более низким уровнем циркулирующего ФРФ-23 и улучшением уровней маркеров костного обмена [86].
Вторичный анализ сравнительных исследований III фазы ЭК с плацебо и ЦК подтвердил более выраженное снижение ФРФ-23 на фоне терапии ЭК по сравнению не только с плацебо (- 56 vs +2%), но и с ЦК (-68 vs 41%). Следует отметить, что в группе ЭК дозы витамина D были выше и это могло частично нивелировать результаты в группе ЭК [67; 70; 72; 87–89].
Хроническая болезнь почек – сильный и независимый фактор риска сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний, включая сердечную недостаточность (СН), гипертрофию левого желудочка (ГЛЖ) и систолическую дисфункцию. Интерес к влиянию ЭК на сердечно-сосудистую систему высокий, и первые экспериментальные и клинические данные, полученные за последние 3 года, можно назвать многообещающими. Так, в экспериментах на крысах с уремией и ВГПТ этелкальцетид вызывал значительное снижение уровня ПТГ, а также содержание Са в аорте, предотвращая кальцификацию медиального слоя. Данные эффекты могут объясняться прямым действием ЭК на клетки эндотелия и гладких мышц кровеносных сосудов, в которых присутствует экспрессия CaSR или на ФРФ-23-чувствительный путь [90].
M. Wolf et al. [88] провели вторичный анализ 26-недельных РКИ, в которых сравнивалось влияние ЭК (n=509) на ПТГ по сравнению с плацебо (n=514) и ЭК (n=340) по сравнению с ЦК (n=343) у пациентов с ВГПТ, получающих ГД, с целью изучения потенциальных медиаторов индуцированного ЭК снижения ФРФ-23. Авторы проанализировали изменения в ФРФ-23 в связи с изменениями в ПТГ, Са, Р, маркерах обмена костной ткани, а также влияние сопутствующего лечения, направленного на смягчение гипокальциемии. Показано, что ЭК снижал ФРФ-23 от исходного уровня до конца исследования значительно больше, чем плацебо [-56% (от -85 до -7) против +2% (от -40 до +65); P<0,001] и ЦК [-68% (от -87 до -26) против -41% (от -76 до +25); р<0,001]. Снижение уровня ФРФ2-3 сильно коррелировало со снижением Са и Р, но не с ПТГ; корреляции с маркерами обмена костной ткани были непоследовательными и имели пограничное значение. Увеличение сопутствующего приема витамина D частично ослабляло эффект ЭК, снижающий уровень ФРФ-23, но увеличение концентрации Са в диализате по сравнению с отсутствием увеличения и увеличение дозы добавок Са по сравнению с отсутствием увеличения не ослабляли эффекты ЭК, снижающие уровень ФРФ-23.
К. Dörr et al. [89] в РКИ изучили влияние ЭК на прогрессирование ГЛЖ по сравнению с альфакальцидолом (АК), которую оценивали по изменению индекса массы левого желудочка (ИМЛЖ) с помощью магнитно-резонансной томографии сердца у 62 пациентов с ВГПТ, находящихся на ПГД. Уровни ФРФ-23 показали сильную положительную связь с ИМЛЖ, который снижался при приеме ЭК и увеличивался при приеме АК, несмотря на аналогичное подавление ПТГ. Авторы показали, что средняя разница в изменении ИМЛЖ от исходного уровня до 12 месяцев лечения составила -6,9 г/м2 (95% ДИ: от -12,6 до -1,2; р=0,022) в группе ЭК по сравнению с группой АК. Оценка эффекта составила -8,2 г/м2 (95% ДИ: от -14 до -2,4). Таким образом, установлено, что ЭК предотвращает прогрессирование ГЛЖ по сравнению с лечением АК и подтверждена концепция ФРФ-23 как основного прямого фактора ремоделирования сердца у пациентов с ХБП независимо от почечных эффектов избытка ФРФ-23.
Несмотря на появление ПТГ <100 пг/мл (хотя и с низкой частотой), частота переломов в группе ЭК была почти вдвое меньше, чем в группе плацебо, и при длительном воздействии ЭК не отмечено увеличения их частоты. Более того, показано, что КМ увеличивают плотность костной ткани за счет нормализации уровня ПТГ. Исследование BONAFIDE показало улучшение морфологии кости, связанное с соответствующим снижением уровня ПТГ, Са и маркеров костного обмена [91]. Аналогичные результаты наблюдались в дополнительном анализе исследования EVOLVE [92]. Биопсия кости не была процедурой, предусмотренной протоколом в клинических испытаниях; соответственно, связь между событиями перелома и возможным избыточным уровнем ПТГ с уменьшением ремоделирования кости не может быть окончательно определена. Однако отсутствие переломов у пациентов с ПТГ <100 пг/мл в сочетании со снижением маркеров костного обмена, специфичной для кости щелочной фосфатазы и С-телопептида коллагена 1 типа, в большей степени регистрировали в группе ЭК по сравнению с контрольными группами, что предполагает положительное влияние ЭК на костную массу [71, 72].
Несколько исследований посвящено проблеме перевода пациентов с терапии ЦК на ЭК в связи с недостаточной эффективностью первого. У части пациентов с тяжелым ВГПТ ЦК может оказаться неэффективным при нодулярной гиперплазии или при развитии аденомы ПЩЖ, когда в железе преобладают клетки с низкой экспрессией CaSR, не чувствительные к КМ. Например, в ретроспективном обсервационном исследовании среди 1268 пациентов, находившихся на ПГД в течение 2005–2015 гг. в 7 центрах, и получавших ЦК в среднем в течение 21±12 месяцев, 41% имели неконтролируемый ВГПТ (уровень ПТГ девятикратно больше верхней границы нормы) [93]. Перевод на терапию ЭК позволяет дифференцировать истинную резистентность к ЦК от такой псевдорезистентности [84, 94].
Данные клеточных анализов предполагают аддитивный эффект на передачу сигналов CaSR при совместном применении ЭК и ЦК. Поэтому ЭК и ЦК не следует назначать одновременно, т.к. это может приводить к повышенному риску гипокальциемии. ЦК следует отменить по крайней мере за 7 дней до начала приема ЭК, а скорректированный уровень Са в сыворотке крови должен быть на уровне или выше нижней границы нормы до начала приема ЭК [95].
Приверженность лечению
Несмотря на улучшение контроля ВГПТ с использованием ЦК в сочетании с другими вариантами лечения ВГПТ или без них, одной из сложных проблем является плохая приверженность терапии ЦК, что может ухудшать долгосрочный контроль ВГПТ. Согласно данным ВОЗ, приверженность лекарственному лечению среди пациентов с хроническими заболеваниями не превышает 50% [96]. В нескольких исследованиях отмечено отсутствие приверженности к ежедневному пероральному приему ЦК, и доля пациентов, прекративших прием ЦК внутрь в течение 12 месяцев в реальной клинической практике, варьируется от 29 до 73% [83, 97–102].
Возможным объяснением прекращения приема ЦК может быть высокая пероральная лекарственная нагрузка у пациентов, находящихся на диализе. Y.W. Chiu et al. [103] обнаружили, что среднесуточное количество таблеток составляет 19 у пациентов, находящихся на хроническом диализе, и четверти из них было назначено более 25 таблеток в день. Препараты для лечения ВГПТ составляли около половины ежедневного приема таблетированных форм препаратов. Как отмечают авторы, поскольку последствия неприверженности к лекарствам при лечении ВГПТ, как правило, не сразу замечаются пациентом, более низкая приверженность ЦК по сравнению с другими лекарственными средствами может быть еще одной причиной.
Даже в отсутствие различий в нежелательных симптомах можно ожидать, что за пределами контролируемого исследования лекарства, вводимые внутривенно в диализном отделении, будут иметь лучшую приверженность, чем пероральные препараты, предписанные для ежедневного приема в домашних условиях.
В недавно опубликованном исследовании M.D. Arenas et al. (2020) [82] приверженность терапии ЦК определяли по опроснику SMAQ, разработанному для пациентов с ВИЧ-инфекцией и опробованному с положительным результатом на пациентах на ГД [104]. Для участия в исследовании отобраны 25 пациентов (10 приверженных и 15 неприверженных) с неудовлетворительным контролем ВГПТ. Пациенты переведены на терапию ЭК через неделю (отмывочный период) по окончании приема ЦК. Дополнительным подтверждением неприверженности 15 пациентов было отсутствие повышения ПТГ через неделю после отмены ЦК. У тех, кто был оценен как приверженный терапии, уровень ПТГ несколько повысился к началу терапии ЭК. Начальная доза ЭК составила 2,5 мг/диализ в комбинации с парикальцитолом (ПК) 1–2 мкг/диализ (в зависимости от уровня Са). Дозы ЭК и ПК титровались ежемесячно в соответствии с уровнями ПТГ и Са. Лечение продолжалось 8 месяцев. У неприверженных пациентов ПТГ снизился с 818 до 367, у приверженных – с 496 до 228 пг/мл. Количество пациентов, достигших рекомендуемого интервала, увеличилось с 28 до 58%. Частота гипокальциемии <2,1 ммоль/л увеличилась с 8 до 40%, хотя и оставалась бессимптомной. Достижение целевого интервала уровня P увеличилось с 40 до 65%. Таким образом, результаты исследований подтверждают, что увеличение кальцимиметической приверженности при применении ЭК может улучшить лечение ВГПТ и снизить количество госпитализаций [105, 106].
Нельзя дать однозначного ответа на вопрос: влияет ли ЦК на качество жизни пациентов, оцениваемую по показателям шкалы HRQoL? В результате комбинированного анализа данных трех аналогично разработанных РКИ III фазы, в которых приняли участие в общей сложности 1136 пациентов (665 принимали ЦК, 471 – не только контрольная группа), HRQoL улучшился незначительно [107]. Систематический обзор влияния ЦК на качество жизни пациентов с терминальной стадией ХБП и ВГПТ, включивший два наблюдательных исследования и одно РКИ на основе EVOLVE, не выявили существенных изменений по сравнению с исходным уровнем в HRQoL при лечении ЦК [108].
Показатели качества жизни зависят от многих факторов, и по-прежнему трудно оценить истинную пользу одного-единственного вмешательства. Более того, большинство РКИ, исследующих HRQoL, о котором сообщают пациенты, в качестве вторичной конечной точки, не имеют достаточных возможностей для выявления небольших или умеренных различий в этом исходе.
Поскольку плохая долгосрочная приверженность назначенным лекарствам является распространенной проблемой у диализных пациентов [104, 109] и связана с более высокой заболеваемостью и смертностью, а также с увеличением затрат на лечение, особое значение имеют стратегии улучшения приверженности пациентов, находящихся на диализе. Одной из стратегий повышения приверженности может быть внутривенное введение лекарств, и такой подход стал возможным при применении ЭК. Надежда избежать желудочно-кишечные побочные эффекты и улучшить приверженность к лекарственным средствам при внутривенном введении была движущей силой в разработке кальцимиметического ЭК второго поколения [105].
Неуправляемый ВГПТ может приводить к ПТЭ с сопутствующими затратами на инвазивную хирургию, которая включает дополнительные осложнения и риск сердечно-сосудистых событий, также синдрома голодной кости у пациентов, находящихся на диализе [110, 111]. Хотя субтотальная ПТЭ по-прежнему остается вариантом лечения, показано, что терапия КМ уменьшает потребность в хирургическом вмешательстве [107, 112].
Нежелательные явления при применении кальцимиметиков
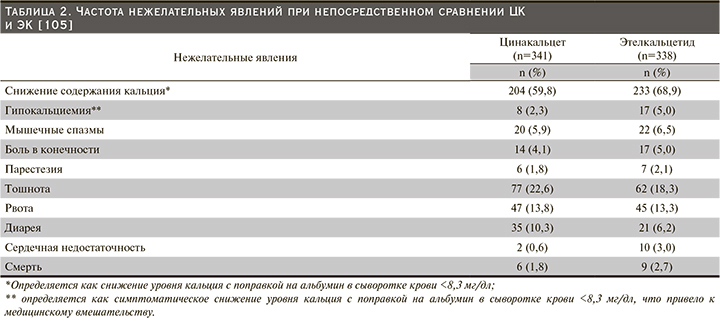
Причины прекращения приема лекарственных средств, вероятно, включают не только снижение приверженности, но и переносимость, и достижение цели ПТГ. Сообщалось, что непереносимость ЦК была результатом высокой частоты желудочно-кишечных побочных эффектов (наиболее часто тошнота и рвота) [83]. Частота нежелательных явлений (НЯ) при непосредственном сравнении цинакалцета и этелькальцетида представлена в табл. 2 [105].
Гипокальциемия
Как и предсказывалось в исследованиях фазы II, применение ЭК часто сопровождалось снижением концентрации Са в сыворотке крови (на основе общего Са с поправкой на альбумин), что отражает наличие бессимптомной гипокальциемии в исследованиях фазы III. Профиль безопасности ЭК, по-видимому, сопоставим с профилем безопасности ЦК. Согласно совсем недавней работе, объединившей данные двух исследований, наиболее часто регистрируемыми НЯ были вызванные изменениями параметров минерального обмена. Нежелательные явления, о которых сообщалось во время лечения ЭК в клинических испытаниях, по-видимому, по большей части коррелировали с механизмом действия кальцимиметических препаратов. Наиболее важным риском для ЭК является индукция гипокальциемии или событий, которые могут возникать как следствие снижения Са в сыворотке крови (например, судороги, удлинение интервала QTc, желудочковая аритмия). Частота этих НЯ, в частности гипокальциемии или снижения Са в сыворотке крови до уровней, которые не считаются истинной гипокальциемией, несколько выше, чем при ЦК. Вероятно, это связано с более высокой эффективностью нового препарата [71, 84, 113].
Гипокальциемия ниже 7,9 мг/дл (1,97 ммоль/л), т.е. той границы, за которой начинает повышаться смертность, не зафиксирована у 80% пациентов за все время исследования J.L. Fernández-Martín et al. [34], несмотря на то что никому из пациентов не повышались дозы VDRA или Са-содержащих ФСП. Клиническое значение гипокальциемии, вызванной КМ, остается неясным, поскольку она редко ассоциируется с клиническими симптомами [114].
D.A. Bushinsky et al. [84] в исследовании OLE проанализировали результаты трех исследований: двух рандомизированных двойных слепых плацебо-контролируемых и одного открытого одноцентрового исследования «переключения» с ЦК на ЭК, в которые были включены 682 пациента. Основной конечной точкой было изучение характера, частоты, тяжести и связи с лечением всех НЯ, о которых сообщалось на протяжении всех исследований и дополнительно в течение 52 недель. Все пациенты независимо от того, получали ли они плацебо, ЦК или ЭК во время участия в РКИ, далее получали только ЭК. Особое внимание в этом исследовании уделено отслеживанию НЯ, отмеченных у 89,8% пациентов. Побочные лекарственные реакции (т.е. события, которые считались связанными с ЭК) характеризовались желудочно-кишечными симптомами (диарея, тошнота и рвота) или в большинстве случаев (43,3%) бессимптомной гипокальциемией. Удлинение интервала QT, желудочковые аритмии, мышечные спазмы и миалгия наблюдались менее чем у 1% пациентов. Другими побочными лекарственными реакциями были гиперкалиемия, СН, гипофосфатемия и головная боль. Авторы отмечают, что, поскольку процессы реполяризации в сердечной мышце и влияние на калиевые каналы связаны с гипокальциемией, а не с прямым воздействием ЭК, мониторинг уровня Са является лучшей профилактикой нарушений проводимости и ритма. Сопутствовавшая терапия, направленная на поддержание уровня Са, состояла из КТ или неселективных VDRA у 81,8% пациентов, 67,5% дополнительно принимали Са-содержащие ФСП.
Практические рекомендации по МКН-ХБП KDIGO (2017) больше не рекомендуют поддерживать концентрацию Са в сыворотке крови в пределах нормального референтного диапазона у пациентов, находящихся на диализе; скорее они предлагают избегать гиперкальциемии и переносить легкую и бессимптомную гипокальциемию, связанную с КМ, чтобы избежать неадекватной нагрузки Са у этих пациентов [36]. Этот подход подтверждается анализом исследования EVOLVE, в котором была выявлена тяжелая гипокальциемия (общий Са сыворотки <7,5 мг/дл) в течение первых 16 недель после первой введенной дозы 78,4% пациентов в группе ЦК по сравнению с 4,4% в группе плацебо [115]. Это событие не зависело от дозы, но было связано с более высокими исходными значениями ПТГ, что отражает повышенную вероятность развития гипокальциемии с увеличением тяжести ВГПТ. У большинства пациентов гипокальциемия разрешилась в течение 14 дней без коррекции лечения (уменьшение/прекращение приема ЦК, начало/увеличение дозы VDRA, назначение Са-содержащего ФСП). Авторы пришли к следующему заключению: для определения влияния ЭК на здоровье сосудов и скелета с учетом гипокальциемического эффекта и связанных с ним изменений в терапии VDRA или добавках Са необходимы дальнейшие исследования. Тем не менее исходный уровень Са в сыворотке крови, скорректированный на альбумин, ≥8,3 мг/дл, в соответствии с испытаниями фазы III, был предварительным условием для начала применения ЭК.
Сердечная недостаточность
Хотя частота госпитализаций с СН была выше у пациентов в группе ЭК (2,2%) по сравнению с группой плацебо (1,2%), это наблюдение можно объяснить значительным дисбалансом в исходных характеристиках исследования NCT01785849 в области ишемической болезни сердца. Кроме того, большинство пациентов с подтвержденными случаями СН в обеих группах в плацебо-контролируемых исследованиях имели СН в анамнезе. Вместе с неклиническими токсикологическими исследованиями, которые не указывают на прямое влияние ЭК на функцию миокарда, которое могло бы привести к появлению или ухудшению ранее существовавшей СН [94], эти данные свидетельствуют: лечение ЭК вряд ли окажет какое-либо неблагоприятное влияние на частоту впервые возникшей СН. Возможно, что опосредованное ЭК снижение уровня Са может вызывать нестабильность гемодинамики и что быстрая или длительная гипокальциемия может потенциально снижать сократительную способность миокарда, особенно у пациентов с нарушенной функцией сердца; однако роль низкого уровня Са в сыворотке крови в развитии СН не установлена [94].
Удлинение интервала QT
В плацебо-контролируемых клинических исследованиях удлинение интервала QT (500 мс), вторичного по отношению к гипокальциемии, наблюдалось у 4,8% пациентов, получавших ЭК, и у 1,9% испытуемых, принимавших плацебо. Случаи желудочковой аритмии возникали с аналогичной частотой у пациентов, получавших ЭК или плацебо, не наблюдалось увеличения риска аритмий при более длительном воздействии ЭК. Результаты этого анализа согласуются с доклиническими данными исследований на собаках, свидетельствующими о том, что удлинение интервала QT, связанное с ЭК, является результатом снижения уровня Са в сыворотке крови, но не зависит напрямую от концентрации ЭК, таким образом, нет доказательств прямого влияния ЭК на реполяризацию сердца [94]. Следует иметь в виду, что удлинение интервала QT может возникать вторично по отношению к гипокалиемии, вызванной лекарственными средствами [68, 94].
Таким образом, тщательный мониторинг уровня Са необходим пациентам с такими факторами риска, как врожденный синдром удлиненного интервала QT, предыдущая история удлинения QT, семейный анамнез синдрома длительного интервала QT, внезапная сердечная смерть и другие медицинские условия (данные Европейского агентства по лекарственным средствам (EMA). Кроме того, следует проявлять осторожность в контексте потенциальных взаимодействий между лекарственными средствами, которые могут предрасполагать к удлинению интервала QT, вытеснять ЭК из связывания альбумина и потенциально ухудшать гипокальциемию или гипогликемию при введении ЭК пациентам с сахарным диабетом с ВГПТ [76, 113].
Желудочно-кишечные симптомы
Хотя внутривенное введение обходит желудочно-кишечный тракт, ЭК лишь частично уменьшает желудочно-кишечные НЯ, наблюдаемые при применении ЦК. Желудочно-кишечные события (диарея, тошнота и рвота) зарегистрированы у 46,7% пациентов, получавших ЦК, и 37,8% получавших ЭК. Отмечено, что в реальной клинической практике нежелательные гастроинтестинальные эффекты на ЭК возникают значительно реже, чем в РКИ (3–4% против 10–12%), и несравнимо реже, чем на терапии ЦК (3–4 против 53%) [70, 71]. Эти эффекты, вероятно, обусловлены системной активацией CaSR, а не на уровне слизистой оболочки желудочно-кишечного тракта. Тем не менее эти симптомы, как правило, мягкие по степени тяжести и улучшаются при снижении дозы ЭК или прерывании приема препарата [116].
Заключение
Вторичный гипепаратиреоз является частым тяжелым осложнением продвинутых стадий ХБП. Его клинические последствия включают внескелетную кальцификацию, изменения костного метаболизма, увеличение риска переломов, а также сердечно-сосудистой и общей смертности. Цинакальцет – первый кальцимиметик, одобренный к клиническому применению, эффективно снижает уровень ПТГ и положительно влияет на биохимические показатели при МКН у пациентов с ВГПТ. В крупных, тщательно проведенных РКИ показано, что новый кальцимиметик второго поколения ЭК превосходит ЦК в отношении снижения уровней ПТГ, Р, ФРФ-23, уменьшает ИМЛЖ у пациентов на ПГД.
Показано, что ЭК по сравнению с ЦК увеличивает частоту эпизодов бессимптомной гипокальциемии (эффект может быть более выражен в начале лечения). Возникновение в редких случаях клинических симптомов гипокальциемии контролируется снижением дозы препарата, применением сопутствующих методов лечения, таких как аналоги витамина D, пероральные ФСП на основе Са и иногда повышение концентрации Са в диализате. При введении ЭК может увеличиваться длительность электрокардиографического интервала QT. При назначении кальцимиметиков следует измерять концентрацию Са в сыворотке крови перед началом и во время лечения, и практикующие врачи должны знать о потенциальных эффектах удлинения интервала QT.
Этелкальцетид представляет собой перспективный терапевтический инструмент с точки зрения повышения эффективности контроля ПТГ, Ca, P, ФРФ-23, предупреждения сосудистой кальфификации, ГЛЖ, частоты переломов и ПТЭ с приемлемым уровнем безопасности и переносимости. Внутривенное введение ЭК в конце сеанса гемодиализа улучшает приверженность терапии, упрощает дозирование препарата, снижает количество принимаемых таблетированных препаратов.
Повышение приверженности и лучший контроль ВГПТ могут заложить основу для будущего крупного РКИ, чтобы продемонстрировать, что улучшенный контроль уровня ПТГ и минерального обмена с помощью ЭК приводит к доступным сердечно-сосудистым преимуществам, лучшему качеству жизни и могут помочь создать предпосылки к улучшению долгосрочных результатов у диализных пациентов с ВГПТ.



