Глобальная распространенность хронической болезни почек (ХБП), по оценкам, составляет около 7% у людей в возрасте ≥30 лет с более высокой распространенностью (23–36%) среди людей в возрасте ≥64 лет [1]. ХБП сегодня является одним из ключевых факторов, определяющим состояние здоровья у пациентов с основными неинфекционными болезнями [2]. Повышенный уровень сывороточного фосфата (гиперфосфатемия) является неизбежным следствием поздних стадий ХБП [3, 4]. Гиперфосфатемия связана с рядом серьезных клинических осложнений, в т.ч. сосудистой кальцификацией [5] и гипертрофией левого желудочка [6], а также увеличением сердечно-сосудистой смертности и смертности от всех причин [7, 8]. Крупные наблюдательные исследования показали четкую связь между уровнями сывороточного фосфата и смертностью от всех причин у пациентов, находившихся на диализе [7–11]. Учитывая вышеизложенное, одной из главных целей в лечении пациентов, находящихся на гемодиализе является коррекция гиперфосфатемии.
Достижение рекомендуемых уровней фосфатов в сыворотке крови представляется достаточно сложной задачей. В исследовании DOPPS II сывороточные уровни фосфора оставались неконтролируемыми у 54% больных ХБП на гемодиализе, у 9 и 47% пациентов определялись уровни сывороточного фосфата <1,13 ммоль/л (3,5 мг/дл ) и >1,78 ммоль/л (5,5 мг/дл) соответственно [12].
Коррекция гиперфосфатемии, безусловно, требует комплексного подхода, включающего диетические ограничения потребления фосфатов, их удаление с помощью интенсивных режимов диализа (ночной продолжительный диализ или короткий ежедневный) и/или фармакологическую коррекцию. Фармакологические вмешательства включают снижение кишечной абсорбции фосфата при назначении ФСП.
Адекватная коррекция гиперфосфатемии не возможна без взаимодействия врача и пациента. Последний должен отчетливо понимать последствия гиперфосфатемии и соблюдать гипофосфатную диету, назначенную врачом.
Возможности нефармакологических воздействий для достижения нормального уровня фосфатов
У пациентов с ХБП со сниженной почечной экскрецией фосфатов для коррекции уровня сывороточного фосфата используются ограничение потребления и/или экстраренальное удаление фосфата.
Диетические вмешательства по снижению потребления фосфата пациентами на поздних стадиях ХБП часто основываются на рекомендациях поддержания адекватного потребления белка [7]. Диетическое ограничение потребления фосфатов рекомендуется в основных руководствах по лечению пациентов [13, 14]. Значение ограничения потребления фосфатов с пищей подтверждено данными наблюдательного исследования, в котором использовали опросники для оценки диетического потребления фосфора и белка у 224 больных на гемодиализе в течение 5 лет наблюдения. Результаты исследования: более высокие уровни диетического потребления продуктов с высоким белково-фосфатным коэффициентом были связаны с повышенным риском смерти [15]. Однако, несмотря на то что диетическое ограничение потребления белка может снизить уровни сывороточного фосфата, недостатком такого подхода является риск развития белково-энергетической недостаточности, которая сама по себе является независимым фактором риска заболеваемости и смертности у диализных пациентов [16]. Действительно, риск, связанный с контролем сывороточного фосфата путем ограничения диетического потребления белка, может перевесить преимущества улучшенного контроля сывороточного фосфата [17]. Это подтверждается данными ретроспективного исследования 1751 пациентов, находящихся на гемодиализе, которым было назначено ограничение ежедневного потребления фосфатов. Результаты показали, что предписанное диетическое ограничение фосфатов не было связано с пользой для выживания [18]. Еще одной проблемой при ограничении диетического потребление фосфора является то, что, если пациент может относительно легко ограничить потребление продуктов с высоким содержанием органических фосфатов, сложнее ограничить потребление переработанных продуктов с высоким содержанием неорганических фосфатов в виде добавок. Эти добавки содержат фосфат в форме, которая легче усваивается, чем содержащийся естественный фосфат в пищевых продуктах [19, 20]. В последние годы образовательные программы для пациентов пополнились новыми данными о различиях в биодоступности органических и неорганических соединений фосфора, позволяющих больному лучше ориентироваться в вопросе, в каких продуктах содержится больше всего фосфатов.
Диализное удаление фосфата может быть повышено за счет увеличения частоты и длительности диализа, использования высокообьемной онлайн-гемодиафильтрации [21–26].
В частности, короткий ежедневный или длительный ночной диализ может обеспечить отмену ФСП [22]. У больных, получающих перитонеальный диализ, лучший контроль над уровнем сывороточного фосфата по сравнению с гемодиализом, достигается в основном благодаря наличию остаточной функции почек.
Значение ФСП в лечении пациентов с ХБП
Фосфат-связывающие препараты – группа лекарственных средств с различной химической структурой, используемых для предотвращения или лечения гиперфосфатемии у пациентов с ХБП за счет уменьшения всасывания фосфатов пищи в желудочно-кишечном тракте.
Связь между нарушением фосфатного гомеостаза и повышенной смертностью и заболеваемостью была продемонстрирована в ряде исследований. Например, оценка данных 40 538 пациентов показала ступенчатое увеличение относительного риска смертности, связанной с увеличением концентрации фосфора в сыворотке крови выше 5 мг/дл [10]. В ретроспективных исследованиях, включивших 14 829 пациентов, находившихся на гемодиализе, была установлена зависимость между концентрациями сывороточного фосфора в пределах 4,5–5,3 мг/дл и смертностью от сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний. Повышение концентрации фосфора в крови выше 6,4 мг/дл было связано с повышением риска смертности от всех причин [11]. Данные проспективного двухлетнего наблюдения 58 058 больных на гемодиализе также показали, что гиперфосфатемия (более 6 мг/дл) связана с повышенным риском смерти [27].
В систематическом обзоре, включившем 27 исследований, установлена взаимосвязь между нарушениями минерального обмена и показателями смертности от всех причин и сердечно-сосудистой смертности, а также частоты развития сердечно-сосудистых осложнений у больных ХБП [28].
Данные трех наблюдательных исследований свидетельствуют об увеличении выживаемости пациентов на диализе, связанном с ранним назначением ФСП [12, 29, 30]. В исследовании DOPPS упоминаемом выше, которое включили 23 894 пациента на гемодиализе, с периодом наблюдения 1,92 года наблюдалось 6283 смерти. У пациентов, получавших лечение ФСП, наблюдалось снижение риска смерти на 25% по сравнению с теми, кто не принимал ФСП (HR: 0,75; 95% ДИ: 0,68–0,83); в моделях с поправкой на факторы питания снижение риска составило 12% (HR: 0,88; 95% ДИ: 0,80–0,97) [12].
В исследовании 8610 пациентов на гемодиализе установлено, что смертность от всех причин в течение 1 года убольных, которым были назначены ФСП в течение 90 дней после начала гемодиализа (n=3555), была значительно ниже, чем у тех, кто не получал препараты (n=5055; относительный риск: 0,58; 95% ДИ: 0,52–0,66, p<0,0001) [29].
Данные исследования COSMOS, включившего 6321 пациента, находившегося на гемодиализе, также показывают, что применение ФСП было связано со значительно меньшим риском смертности от всех причин [30].
Фосфат-связывающие препараты были внедрены в клиническую практику в 1970-е гг. для лечения гиперфосфатемии у пациентов на диализе после того, как было обнаружено, что пероральное применение гидроксида алюминия в качестве антацидного средства сопровождается снижением уровня сывороточного фосфора. Спустя 40 лет алюминий стал реже использоваться в качестве ФСП в связи с появлением новых безопасных препаратов для контроля над гиперфосфатемией.
Фосфат-связывающие препараты на основе кальция (карбонат и ацетат кальция) становятся препаратами выбора в 1980-х и 1990-х гг. Содержащие кальций ФСП были высокоэффективными и не приводили к развитию энцефалопатии и костной патологии, в отличие от ФСП, содержащих алюминий. Однако в последние годы их использование стало ограничиваться в связи с выявленными негативными эффектами гиперкальциемии [31–36].
В 2001 г. появляется первый ФСП на основе не содержащего металлы невсасывающегося анионообменного полимера – севеламера гидрохлорид (Renagel) [37], преимуществом которого стало отсутстиве риска индукции гиперкальциемии. Однако освободившийся в результате ионного обмена гидрохлорид (HCl) приводил к увеличению кислотной нагрузки и развитию метаболического ацидоза, нежелательного для пациентов с ХБП.
В 2004 г. внедряется лантана карбонат (Phosrenol) – первый не содержащий кальция ФСП в форме жевательной таблетки [38].
В течение последнего десятилетия появились новые ФСП: первая жидкая лекарственная форма ФСП на основе ацетата кальция – Phoslyra [39], севеламера карбонат (Renvela) [40], зарегистрированный в Японии новый ФСП на основе не содержащего металлы ионообмненного полимера – биксаломер (Kiklin) [41]. В числе недавно зарегистрированных препаратов – первый, не содержащий кальция ФСП на основе железа – полинуклеарный комплекс Fe (III) оксигидроксида, сахарозы и крахмала (PA 21; Velphoro®) [42] и препараты на основе цитрата трехвалентного железа (Auryxia) [43].
Все ФСП обеспечивают уменьшение всасывания фосфатов пищи в желудочно-кишечном тракте (ЖКТ). В основу их эффектов положен ионный обмен аниона PO4 с активным катионом с образованием невсасывающихся соединений, которые выводятся из организма с фекалиями [38–43]. Соли кальция, лантана и новые соединения железа обмениваются анионами, карбоната, ацетата, оксигидроксида и цитрата, связывая фосфаты. Севеламер является неселективным анионообменником, который связывается не только с фосфатами, но и с солями желчных кислот, а также с другими лекарственными препаратами [37, 40].
В связи с внедрением в клиническую практику новых ФСП важной задачей является оптимизация индивидуального выбора лекасрственного средства в соответствии с потребностями каждого пациента. В идеале препарат выбора должен эффективно связывать диетический фосфат независимо от рН, при минимуме системной абсорбции и побочных эффектов, обеспечивать удобство применения, снижение лекарственной нагрузки и стоимости проводимой терапии. Появление новых возможностей фосфат-связывающей терапии требует от специалиста понимания специфики применения ФСП, начиная с подбора адекватной дозы, оценки эффективности и переносимости, доступности и экономической целесообразности, которые должны учитываться при выборе того или иного ФСП.
Относительные фосфат-связывающие коэффициенты и эквивалентные дозы ФСП
При лечении пациентов с хроническими заболеваниями часто возникает вопрос об эквивалентности доз лекарственных препаратов при переходе с одного варианта терапии на другой с сохранением стабильного терапевтического эффекта. Группа исследователей Frequent Hemodialysis Network Trial [44] столкнулась с проблемой сравнительной оценки эффективности ФСП при попытке интерпретировать изменения уровня фосфатов в сыворотке крови. В ходе исследования возник вопрос, насколько эти изменения были связаны с увеличением частоты диализа и в какой степени с использованием различных ФСП. Daugirdas и соавт. [44] оценивали фосфат-связывающую способность (ФСС) по изменениям уровня фосфатов in vivo в кале и в моче в группах лиц с ХБП и без заболеваний почек.
Результатом этих исследований стала разработка новых инструментов для сравнительной оценки эффективности ФСП: «относительный коэффициент связывания фосфатов» (ОКСФ) и «эквивалентная фосфат-связывающая доза» (ЭФСД) (ЭФСД=ОКСФ × дозу соответствующего ФСП). Для сравнения фосфат-связывающей способности использовали показатель количества фосфатов (мг), связываемых 1 г соединения или 1 г активного ингредиента (лантан, железа оксигидроксид, севеламер и трехвалентного железа цитрат). В качестве стандарта был выбран 1 г карбоната кальция. Исходя из результатов исследований, показавших, что пациентам с ХБП, получающим обычный гемодиализ три раза в неделю, требуется в среднем 6 г карбоната кальция/сут для контроля над уровнем сывороточного фосфата, были рассчитаны эквивалентные количества таблеток ФСП [44–46].
В табл. 1 представлены ОКСФ, ЭФСД и количество таблеток различных ФСП, необходимых для достижения эффекта карбоната кальция в суточной дозе 6 г.
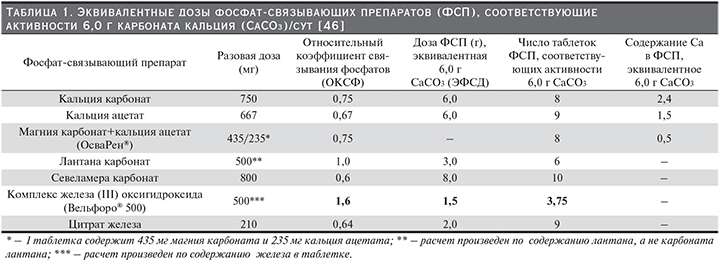
Daugirdas и соавт. предупреждают, что ОКСФ и ЭФСД являются оценочными показателями.
ОКСФ является полезным инструментом для расчета начальной суточной дозы при переключении с одного ФСП на другой. Безусловно, при этом необходим контроль уровня фосфатов в сыворотке крови и подбор дозы должен осуществляться в соответствии с инструкцией по применению ФСП.
ФСП на основе кальция
ФСП на основе кальция являются наиболее широко применяемыми в мире средствами для контроля сывороточного фосфора, несмотря на многочисленные исследования, в которых демонстрируется их влияние на прогрессирование сосудистой кальцификациии [31–36].
Руководства KDIGO и KDOQI рекомендуют ограничить или избегать назначение кальций-содержащих ФСП у пациентов, имеющих повышенный уровень кальция или низкий уровень паратиреоидного гормона в сыворотке крови, а также при наличии у них признаков сосудистой кальцификации [13, 14]. В ряде исследований показано, что у многих пациентов имеются признаки кальцификации еще до начала диализа. В такой ситуации стоит вопрос целесообразности назначения кальций-содержащих ФСП даже на ранних стадиях ХБП [47, 48]. Карбонат и ацетат кальция в большинстве стран являются безрецептурными, недорогими, а значит, легкодоступными лекарственными средствами. Существует несколько исследований, сравнивающих эффективность карбоната кальция с ацетатом кальция в качестве ФСП [49–51]. В этих работах ацетат кальция показал столь же высокую или большую эффективность в снижении уровней фосфатов в сыворотке по сравнению с карбонатом кальция. При этом влияние на процессы кальцификации у пациентов, получавших ацетат кальция, было менее выраженным.
В Российской Федерации зарегистрирован в качестве лекарственного средства единственный ФСП на основе кальция: комбинированный препарат, содержащий в своем составе кальция ацетат и магния гидроксикарбонат (ОсваРен) [52]. В составе одной таблетки ОсваРена содержится 435 мг кальция ацетата и 235 мг магния гидроксикарбоната. Эффективность и безопасность препарата оценивались в рандомизированном контролируемом слепом многоцентровом исследовании (CALMAG) [53].
В исследование были включены 255 пациентов, которые были рандомизированы в 2 группы в соотношении 1: 1. Первая группа получала кальциево-магниевый ФСП (CaMg), вторая – севеламера гидрохлорид (Sev-HCl). Пациенты обеих групп получали препараты в течение 24 недель. Двести четыре пациента завершили исследование в соответствии с протоколом (CaMg, n=105; выбыли n=18; Sev-HCl, n=99; выбыли n=34). Исходные характеристики пациентов были одинаковыми в обеих группах. В результате проводимой терапии уровни сывороточного фосфора уменьшилось значительно у пациентов обеих групп на 25-й неделе. Была подтверждена исследовательская гипотеза о том, что CaMg не уступает по эффективности севеламеру. Площадь под кривой сывороточного фосфора (p=0,0042) и число пациентов с превышением уровней сывороточного фосфора в соответствии с рекомендациями KDOQI (≤1,78 ммоль/л, р=0,0198) и KDIGO (≤1,45 ммоль/л, p=0,0067) были значительно ниже при назначении CaMg. Количество ионизированного кальция в сыворотке крови не отличались между группами; общий кальций в сыворотке крови повышался в группе, получавшей CaMg (разница между группами: 0,0477 ммоль/л, p=0,0032), что сопровождалось повышением риска гиперкальциемии. Не было значимой разницы в количестве пациентов с побочными эффектами. Выводами исследования стали: ОсваРен является эффективным ФСП, не вызывающим в терапевтических дозах опасной гиперкальциемии с хорошим профилем переносимости и, таким образом, может успешно использоваться с целью коррекции гиперфосфатемии у пациентов с ХБП [53]. Препарат назначается в суточной дозе от 3 до 10 таблеток, разделенных в соответствии с приемом пищи. Максимальная суточная доза составляет 12 таблеток. Поскольку скорость и/или степень абсорбции других пероральных лекарственных препаратов может варьироваться при одновременном использовании с ОсваРеном, не следует принимать никаких других пероральных лекарственных препаратов в пределах 2 часов до и 3 часов после приема ОсваРена. Препарат противопоказан пациентам со следующими состояниями и заболеваниями: гипофосфатемия; гиперкальцемия с клиническими симптомами или без таковых, например, как результат передозировки витамина D, паранеопластический синдром (бронхиальная карцинома, рак молочной железы, почечно-клеточная карцинома, плазмоцитома), костные метастазы, саркоидоз или иммобилизационный остеопороз;повышенные уровни магния сыворотки, более чем 2 ммоль/л, и/или симптомы гипермагниемии; атриовентрикулярная блокада III степени; миастения гравис [52].
ФСС карбоната кальция составляет 39 мг/г [45]. В связи с тем, что ФСС 1 г карбоната кальция использовалась в качестве эталонного стандарта, ЭФСД препарата составляет 1,0. При этом ЭФСД таблеток карбоната кальция по 750 мг составляет 0,75 (750 мг/1000 мг), т.е. необходимо назначить 8 таблеток для достижения суточной дозы, эквивалентной 6 г карбоната кальция [44]. Кальций, содержащийся в ацетате кальция, меньше всасывается (21%) с пищей и имеет немного более высокую ФСС: 45 мг/ г кальция ацетата [49]. ОКСФ кальция ацетата равен 1,0, а это означает, что активность ацетата кальция подобна связывающей способности карбоната кальция, однако ЭФСД ацетата соответствует 0,67 (т.к. в таблетке содержится 0,667 г препарата), т.е. необходим прием 9 таблеток, чтобы получить дозу, эквивалентную 6 г карбоната кальция [45]. ОКСФ кальция ацетата/магния карбоната соответствует 0,75, т.е. 8 таблеток кальция ацетата/магния карбоната будут эквивалентны 6 г карбоната кальция [46]. При сопоставлении содержания кальция в суточной дозе кальций-содержащих ФСП в пересчете на 6 г карбоната кальция, у кальция ацетата/магния карбоната этот показатель самый низкий – 0,5 г (табл. 1)
Нежелательные явления, связанные с использованием кальций-содержащих ФСП, включают запоры, гиперкальциемию и гипопаратиреоз. Кроме того, существуют доказательства того, что перегрузка кальцием при назначении таких доз может способствовать развитию метастатической кальцификации [13, 50, 54]. Основные нежелательные побочные эффекты кальция ацетата/магния карбоната приведены в табл. 2.

ФСП, не содержащие кальций
Севеламера гидрохлорид и карбонат являются препаратами, доступными в настоящее время в этом классе. Севеламер является невсасывающимся полимером, HCl или HCO3 которого обмениваются на фосфаты в ЖКТ [37, 40]. Соляная кислота и карбонат всасываются, в то время как связавшиеся с полимером фосфаты через желудочно-кишечный тракт выводятся из организма. В двух основных исследованиях, в которых изучалась эффективность севеламера гидрохлорида, сывороточные уровни фосфатов снизились без увеличения уровней кальция сыворотки [55, 56].
После 2-недельного отмывочного периода в первом исследовании уровень сывороточного фосфата снизился с 9,1±2,4 мг/дл до 6,6±1,9 мг/дл у 144 пациентов, получавших препарат в средней дозе 5,4 г в течение 8 недель [55]. Второе исследование севеламера гидрохлорида и ацетата кальция у 84 больных по изучению их эффективности было открытым сравнительным и перекрестным. После 2-недельного отмывочного периода, пациенты были рандомизированы для получения либо севеламера гидрохлорида, либо кальция ацетата в течение 8 недель. После завершения этого этапа и нового 2-недельного отмывочного периода пациенты переводились на назначение другого ФСП. Эффективность терапии в обеих группах была сопоставимой (снижение сывороточного фосфата составило -2,0±2.3 мг/дл в группе, получавшей севеламер, vs 2,1±1,9 мг/дл в группе, получавшей ацетат кальция). Однако в группе больных, получавших ацетат кальция, у 22% участников сывороточный уровень кальция были выше 11,0 мг/дл и прекращение приема препарата не привело к его снижению [56].
Кроме того, помимо связывания фосфатов севеламер также связывает соли желчных кислот (от 15% до 31%), что в результате приводит к снижению общего холестерина и липопротеинов низкой плотности сыворотки крови [40]. С другой стороны, связывание солей желчных кислот сопровождается уменьшением всасывания липидов и жирорастворимых витаминов (А, D, Е и К). В этой связи рекомендован мониторинг концентраций жирорастворимых витаминов и фолиевой кислоты при назначении севеламера.
Севеламер противопоказан пациентам с риском развития непроходимости кишечника. В ходе применения препарата были зарегистрированы случаи задержки таблеток в пищеводе у пациентов с дисфагией, перфорации кишечника и кишечной непроходимости, потребовавшие госпитализации. Менее серьезные побочные реакции, связанные с приемом севеламер, включают рвоту (22%), тошноту (20%), диарею (19%), диспепсию (16%), боли в брюшной полости (9%), метеоризм (8%), запоры (8%) [40] (табл. 2).
При сочетанном назначении с севеламером других лекарственных средств было установлено, что препарат не влияет на биодоступность дигоксина, варфарина, эналаприла, метопролола и сульфата железа. При этом севеламер уменьшает биодоступность ципрофлоксацина примерно на 50%, отмечается снижение концентрации циклоспорина, микофенолята, мофетила и такролимуса. Рекомендуется мониторинг тиреотропного гормона при совместном назначении препарата с левотироксином [37, 40].
Рекомендуемые начальные дозы для севеламера гидрохлорида и карбоната колеблются в диапазоне от 800 до 1600 мг на один прием пищи в зависимости от уровня фосфатов в сыворотке крови. Средняя суточная доза по результатам клинических исследований составляет 7,0 г (9 табл./сут [37].
Изучение ФСС севеламера проводилось на здоровых добровольцах: после промывания желудка 31 человек получил рацион, содержавший 380 мг фосфата и севеламер в разовой дозе 2400 мг. После оценки содержания фосфатов в кале была рассчитана ФСС севеламера, составившая 26 мг на 1 таблетку препарата или 21 мг/г севеламера карбоната [44]. В других исследованиях оценивалась ФСС севеламера гидрохлорида. Участники первого исследования (24 здоровых добровольца) получали пищевой рацион, содержавший 1200 мг фосфатов в течение 18 дней. В течение 5 дней 9 пациентам давали либо плацебо, либо севеламера гидрохлорид в разделенных дозах по 3, 7,5 или 15 г. Анализ полученных данных показал обратную зависимость между суточной дозой севеламера и его ФСС (36 мг/г; 33 мг/г; 23 мг/г соответственно). Аналогичная ситуация наблюдалась и по результатам двух других исследований, в которых изучалась ФСС севеламера: в дозе 1,6 г ФСС составила 50 мг/г, а в дозе 6,4 г – 32 мг/г [44].
ОКСФ для севеламера при назначении в стандартной дозе 800 мг составляет 0,75, а ЭФСД – 0,60, таким образом, 9 таблеток севеламера будут эквивалентны 6 г карбоната кальция [46].
Биксаломер (Киклин) является еще одним невсасывающимся полимером, который в настоящее время доступен только в Японии [41]. Механизм действия сходен с севеламером, однако он меньше сорбирует воду и набухает, обладая большей текучестью, чем севеламер [41].
В рандомизированном клиническом исследовании 3-й фазы, проведенном в Японии, биксаломер показал более высокую эффективность в сравнении с севеламером. Среди пациентов, получавших биксаломер, 72,2% достигли целевых уровней сывороточного фосфора от 3,5 до 6,0 мг/дл, в то время как в группе, получавшей севеламер, этот эффект отмечался в 68% случаев. Кроме того, процент неблагоприятных побочных эффектов со стороны ЖКТ был достоверно ниже в группе больных, получавших биксаломер (29,1%) [41]. Поскольку севеламера карбонат не доступен в Японии, биксаломер стал хорошей альтернативой не содержащего кальций ФСП, не увеличивающего кислотную нагрузку.
Лантана карбонат является первым соединением на основе металлического лантана для связывания фосфата. Каждая жевательная таблетка лантана карбоната содержит по 500, 750 или 1000 мг элементарного лантана. В желудочно-кишечном тракте лантан связывает фосфаты с образованием невсасывающегося комплекса фосфата лантана. Исследования in vitro показали, что лантан связывает фосфаты в диапазоне рН от 3 до 7. Наибольшее связывание фосфата с лантаном происходит при рН от 3 до 5 ( 97%), в то время как при рН 7 связывается только 67% пищевого фосфора [38].
В клинических исследованиях 2-й и 3-й фаз назначение лантана карбоната сопровождалось снижением и удержанием концентраций сывороточного фосфата в пределах целевых значений в диапазоне от 4,03 до 5,58 мг/дл. Эффективность лантана карбоната была сопоставимой при сравнении с ацетатом кальция и севеламером. Однако при назначении лантана поддержание целевых уровней сывороточного фосфора достигалось при существенном снижении числа таблеток [57–59]. Рекомендуемая начальная доза составляет 1500 мг, которая равномерно распределяется во время приемов пищи. Коррекция дозы проводится каждые 2–3 недели до достижения целевых уровней сывороточного фосфора, максимальная суточная доза – 4500 мг.
В регистрационных клинических исследованиях наиболее распространенными побочными реакциями лантана карбоната были тошнота (11%), рвота (9%), а также боли в животе (5%). Дальнейший опыт клинического применения лантана выявил дополнительные неблагоприятные реакции, включавшие запоры, диспепсию, кожные аллергические реакции при повторном применении, гипофосфатемию и повреждение зубов при разжевывании таблеток [38].
При назначении лантана наблюдались серьезные осложнения со стороны ЖКТ. Следует соблюдать осторожность при назначении лантана пациентам с анатомическими изменениями ЖКТ. Препарат противопоказан больным, имевшим непроходимость кишечника в анамнезе. Некоторым из них в связи с развитием острой обструкции кишечника потребовались госпитализация и/или хирургическое вмешательство. Кроме того, лантан является тяжелым металлом и он обладает рентген-контрастными свойствами, что может приводить к искажению изображений брюшной полости при проведении рентгенологических процедур [38, 59].
При совместном назначении лантана снижается биодоступность тетрациклинов, фторхинолонов и хинолонов. Биодоступность левотироксина в сочетании с лантаном уменьшается примерно на 40%. В такой ситуации препараты, назначаемые совместно с лантаном, необходимо принимать за 2 часа до или через 2 часа после приема лантана. Содержащие алюминий, магний и кальций антациды также не следует принимать в течение 2 часов до или после назначения лантана [38].
В систематическом обзоре и мета-анализе 16 рандомизированных контролируемых исследований с участием 3789 пациентов оценивалась эффективность и безопасность лантана. Чжан и соавт. обобщили материал 10 исследований, в которых собраны данные о накоплении лантана в костной ткани и крови. Большинство результатов показало небольшое увеличение уровней лантана в сыворотке. Однако это увеличение не было статистически достоверным [60].
В трех клинических исследованиях использовались гистологические методы для оценки накопления лантана в костной ткани при назначении препарата 85 пациентам в течение от 1 до 2 лет. Биопсия кости проводилась в начале исследования, а затем ежегодно. Отмечалось накопление лантана в костной ткани, которое было незначительным (5,5 мкг/г). Только в одном случае лечение было прекращено в связи с кумуляцией лантана в костной ткани [61–63].
Исследование фосфат-связывающей активности лантана in vivo проводилось с участием здоровых добровольцев. В исследовании приняли участие тридцать один доброволец, которые получали однократно 1000 мг лантана и рацион, содержащий 375 мг фосфатов. Оценка выведения фосфатов с калом показала, что лантан снижает их поглощение на 45%. Таким образом, было установлено, что 1000 мг лантана может связывать 135,1±12,3 мг фосфатов [44]. Daugirdas и соавт. рассчитали, что лантан имеет ОКСФ, равный 2, а ЭФСД – 1 таблетки, содержащей 500 мг лантана, соответствует 1, т.е. 6 таблеток лантана по 0,5 г эквивалентны 6 таблеткам карбоната кальция [45, 46].
Железо-содержащие ФСП
Полинуклеарный комплекс железа (III) оксигидроксида, сахарозы и крахмала (Вельфоро® 500) является первым ФСП, не содержащим кальций, на основе железа. Каждая жевательная таблетка 2500 мг содержит 500 мг железа. Связывание с фосфатом происходит путем обмена лигандами между гидроксильными группами и/или водой и фосфат ионами во всем интервале физиологических значений рН в желудочно-кишечном тракте (ЖКТ) [64].
В условия эксперимента с аденин-индуцированной ХБП у животных комплекс железа оксигидроксида был столь же эффективен, как лантан или cевеламер в контроле над уровнями фосфатов, ПТГ и FGF-23 в сыворотке крови, а также в предотвращении развития сосудистой кальцификации [65].
Эффективность и безопасность применения комплекса оксигидроксида железа у пациентов на диализе оценивались в исследованиях 3-й фазы, относящихся к числу самых крупных РКИ, посвященных изучению фосфат-связывающих препаратов.
Первое исследование: 6-недельное рандомизированное открытое с активным контролем, ставило целью выбор оптимальной дозы. В 50 диализных центрах Европы и США были отобраны пациенты, которым назначали комплекс окигидроксида железа (Вельфоро®) или севеламера карбонат (Ренвелла®) в качестве активного контроля. Пациенты были рандомизированы в группы, получавших комплекс оксигидроксида железа в суточных дозах 1,25; 5; 7,5; 10 и 12,5 г. Во всех группах, за исключением получавших препарат в дозе 1,25 г/сут, отмечали снижение уровней сывороточного фосфора, которое составило -1,08; -1,25; -2,0 и -1,69 мг/дл соответственно [66].
Второе исследование: 52-недельное двухступенчатое рандомизированное контролируемое открытое, было посвящено изучению эффективности и безопасности комплекса оксигидроксида железа [67, 68]. После 2-недельного отмывочного периода 1059 пациентов на диализе были рандомизированы в группы, получавшие в ходе первой стадии данного исследования либо комплекс оксигидроксида железа, или севеламера карбонат в течение 24 недель. Стартовыми дозами для каждого препарата были 1000 мг и 4800 мг соответственно, с титрованием до достижения и поддержания уровней сывороточного фосфата не выше 5,5 мг/дл. В конце 24 недели пациенты, достигшие целевых уровней сывороточного фосфора, были рандомизированы для участия во второй (расширенной) стадии исследования. Участники продолжали получать комплекс оксигидроксида железа или севеламера карбоната в дозах, соответствующих их первоначальной рандомизации [68]. Во второй стадии исследования приняли участие 658 диализных пациентов, получавших лечение в течение 28 недель.
В конце 12-й недели уровни сывороточного фосфата снижались на 2,2 и 2,4 мг/дл в группах, получавших комплекс оксигидроксида железа или севеламера карбонат соответственно. Таким образом, комплекс оксигидроксида железа был столь же эффективным в коррекции гиперфосфатемии как и севеламера карбонат. Однако достижение целевых уровней сывороточного фосфата в группе, получавших комплекс оксигидроксида железа, сопровождалось трехкратным снижением лекарственной нагрузки (3 таблетки в сутки против 9 таблеток севеламера карбоната) [68]. Снижение лекарственной нагрузки при применении комплексом оксигидроксида железа обеспечило повышение приверженности пациентов проводимой терапии.
В исследовании в условиях реальной практики, изучавшем эффективность фосфат-связывающей терапии при переходе с традиционно назначаемых ФСП (препараты кальция, севеламер, лантан) в диализных центрах США на комплекс оксигидроксида железа, было установлено что при переходе на прием Вельфоро число пациентов, достигших целевых уровней сывороточного фосфора (<5,5 мг/дл), увеличилось в 2 раза. Например, при переходе с севеламера на комплекс оксигидроксида железа этот показатель увеличился на 119% при наблюдении в течение 1 года [69].
Кроме того, при совместном назначении с комплексом оксигидроксида железа других лекарственных средств отмечается меньшее количество межлекарственных взаимодействий, чем при назначении севеламера [68]. Лекарственные препараты, наиболее часто принимаемые пациентами на диализе, могут назначаться одновременно с комплексом окигидроксида железа. Важным преимуществом комплекса оксигидроксида железа, в отличие от севеламера, является отсутствие влияния на активность пероральных агонистов рецепторов витамина D в снижении иПТГ при назначении в течение 1 года [70].
Исследования комплекса оксигидроксида железа не выявили клинически значимых изменений параметров метаболизма железа при назначении препарата. После 6-недельного приема различных доз комплекса оксигидроксида железа сывороточные уровни ферритина и насыщения трансферрина оставались стабильными [67]. Аналогичные результаты были получены и в ходе 52-недельного исследования [68].
Наиболее распространенными побочными реакциями комплекса оксигидроксида железа являются диарея (24%), потемнение стула (16%) и тошнота (10%) [68]. Диарея при назначении комплекса оксигидроксида железа в большинстве случаев протекает в мягкой или умеренной форме в первые дни назначения препарата и, как правило, в дальнейшем исчезает, не требуя дополнительной терапии или отмены препарата. Потемнение стула является предсказуемой реакцией, связанной с наличием в препарате железа. В числе противопоказаний к назначению комплекса оксигидроксида железа: гемохроматоз, или другие расстройства накопления железа, а также наследственная непереносимость фруктозы, глюкозо-галактозная мальабсорбция или сахаразо-изомальтазная недостаточность [42].
Рекомендуемая начальная доза Вельфоро®500: 500 мг (1 таблетка) с каждым приемом пищи с титрованием 1 раз в 2 недели до достижения уровня сывороточного фосфата не более 5,5 мг/дл. Максимальная суточная доза препарата составляет 3000 мг (6 таблеток) [42].
Установлено, что ФСС комплекса железа оксигидроксида не изменяется в диапазоне физиологических значений рН ЖКТ (от 1,2 до 7,5) и составляет 130 мг на 1 таблетку, что соответствует 260 мг/г железа [64, 70, 71]. Этот показатель комплекса железа оксигидроксида является самым высоким среди имеющихся в арсенале нефрологов ФСП [71].
Daugirdas и соавт., исходя из оценки эффективности комплекса оксигидроксида железа в достижении и поддержании уровня сывороточного фосфора в диапазоне от 3,5 до 5,5 мг /дл [68], рассчитали, что ЭФСД 500 мг Fe в таблетке равна 1,5; т.е. ФСС 3,75 таблетки Вельфоро будет эквивалентна 6 г кальция карбоната [46].
Вторым ФСП на основе железа является препарат цитрата трехвалентного Fe, вызывающий, в отличие от комплекса оксигидроксида, изменения параметров метаболизма железа. Препарат зарегистрирован недавно несколькими производителями в разных странах под различными коммерческими наименованиями (Auryxia, Riona, Nephroxil). В составе 1 таблетки по 1000 мг содержится 210 мг железа. В ЖКТ железо связывается с фосфатами, образуя нерастворимый фосфат железа, который выводится через кишечник [43].
Изначально было проведено 4-недельное плацебо контролируемое исследование для определения эффективности цитрата трехвалентного железа в достижении целевых уровней сывороточного фосфора (3,5–5,5 мг/дл) [72]. В дальнейшем в 52-недельное рандомизированное контролируемое многоцентровое открытое исследование 3-й фазы был включен 441 пациент на диализе. После завершения 2-недельного отмывочного периода больные были рандомизированы группы, получавшие либо цитрат трехвалентного железа, или препараты активного контроля (ацетат кальция и/или севеламера карбонат). У пациентов, получавших цитрат железа, начальная доза составила 6 г в сутки (по 2 таблетки при 3-разовом питании) с еженедельным титрованием до достижения целевого уровня сывороточного фосфора.
В конце 52-й недели пациенты, получавшие цитрат трехвалентного железа, были перерандомизированы для продолжения текущей терапии или приема плацебо.
Средние исходные уровни сывороточного фосфата составили 7,41±0,1 мг/дл в группе, получавшей цитрат трехвалентного железа, и 7,56±0,14 мг/дл в группе активного контроля. Снижение фосфатов до целевых уровней от 3,5 до 5,5 мг/дл достигалось через 12 недель в обеих группах и поддерживалось в течение 52 недель со средними уровнями 5,2 (4,4–6,1) мг/дл и 5,1 (4,4–6,2) мг/дл соответственно. Кроме того, в сравнении с плацебо цитрат трехвалентного железа снижал уровень фосфата в сыворотке крови на 2,2±0,2 мг/дл (р<0,001) [73].
Результаты исследования показали, что для достижения и поддержания целевых уровней сывороточного фосфора (от 3,5 до 5,5 мг/дл) было необходимо назначение 8 таблеток (8 г) цитрата трехвалентного железа. Суточные дозы для достижения и поддержания тех же целевых уровней сывороточного фосфора в группах активного контроля составили: 7,7 табл./сут (5,14 г) для ацетата кальция и 9,0 табл./сут (7,2 г) для севеламера карбоната [72].
В ходе проведения исследования было продемонстрировано увеличение показателей метаболизма железа при назначении в качестве ФСП цитрата трехвалентного железа. В долгосрочном исследовании сывороточные уровни ферритина увеличились со среднего исходного уровня 593±18 нг/мл до 899±31 нг/мл при назначении с цитрата трехвалентного железа, в то время как в группе активного контроля наблюдались незначительные изменения по сравнению с исходным уровнем (609±26 нг/мл), на 52-й неделе -628±31 нг/мл.
Кроме того, к концу 52-й недели у пациентов, получавших цитрат трехвалентного железа, снижалась потребность в препаратах внутривенного железа (в среднем 12,9 мг/нед в группе, получавшей цитрат трехвалентного железа и 26,8 мг/нед в группе активного контроля (p<001),а также эритропоэтинов (средняя доза эпоэтин-эквивалентных единиц: 5,303 ЕД/нед для цитрата железа и 6,954 ЕД/нед в группе активного контроля) [73].
Наиболее распространенными побочными реакциями, связанными с использованием цитрата трехвалентного железа, были диарея (21%), тошнота (11%), запор (8%), рвота (7%), и кашель (6%), потемнение стула, связанное с наличием в препарате железа.
Пациентам, получающим доксициклин, следует принимать препарат за 1 час перед, а ципрофолоксацин за 2 часа перед или после приема цитрата трехвалентного железа [43]. Рекомендуемая начальная доза препарата составляет 2 таблетки с каждым приемом пищи с титрованием к дозы каждые 1–2 недели в зависимости от уровня сывороточного фосфата до достижения целевых уровней вплоть до максимальной дозы 12 таблеток в сутки. Цитрат железа противопоказан пациентам с гемохроматозом или другими расстройствами накопления железа [43]. Кроме того, необходим мониторинг параметров метаболизм железа, т.к. при сочетанном применении цитрата с препаратами внутривенного железа может наблюдаться увеличение концентраций выше терапевтического диапазона [43].
В исследовании ФСС in vitro в диапазоне рН от 2 до 7 препарат показал способность связывать 46±2 мг фосфата/г цитрата трехвалентного железа [69]. Daugirdas и соавт. рассчитали ЭФСД для 1 таблетки препарата (0,64), таким образом, 9 таблеток цитрата трехвалентного железа необходимы для получения дозы эквивалентной доза 6 г карбоната кальция [45].
Новые подходы к контролю гиперфосфатемии
В числе новых способов контроля уровня сывороточного фосфора, используемых в течение последних нескольких лет, является использование ниацина и хитозан-содержащей жевательной резинки.
Никотиновая кислота и никотинамид уменьшают всасывание фосфатов путем ингибирования кишечного натрия-фосфат ко-транспортера-2b. В рамках 8-недельного исследования с использованием никотинамида в дополнении к принимаемому пациентами ФСП, уровень сывороточного фосфата снизился с 6,45 мг/дл до 5,28 мг/дл [74].
Использование этих препаратов в дополнение к ФСП может приносить пользу, т.к. установлено, что диетические ограничения приема фосфатов и применение ФСП могут вызывать повышение активности натрия-фосфатного ко-транспортера-2b, и соответственно, всасывания фосфатов, особенно в ситуации пропуска приема или применения неадекватной дозы ФСП [75].
Связывание фосфатов в слюне представляет собой новый подход в контроле над уровнем сывороточного фосфата у пациентов с ХБП [76]. Хитин – целлюлозо-подобный биополимер, который встречается в природе в основном в экзоскелете ракообразных и применяется в водоочистке (поглощение жиров, масел, металлов и токсичных веществ). Исследования с использованием жевательной резинки с хитозаном для связывания фосфата в слюне показали смешанные результаты в плане контроля над сывороточным фосфором [76]. В целом хитозан не является эффективным ФСП, но может улучшить контроль над уровнем фосфора, контролируя жажду.
Заключение
Коррекция повышенного уровня сывороточного фосфора остается одной из главных задач в терапии пациентов с ХБП на диализе. Несколько стратегий используются для контроля уровней сывороточного фосфата, включая ФСП, диетические ограничения потребления фосфатов и адекватную диализную терапию. Количество ФСП увеличилось за последние 10 лет, предоставив практикующим врачам различные препараты и лекарственные формы (порошки, жидкости, жевательные таблетки). В настоящее время имеется широкий арсенал средств, позволяющий осуществлять индивидуальный выбор схемы лечения гиперфосфатемии с учетом предпочтений пациента, переносимости препарата, фосфатной нагрузки, наличия сопутствующих заболеваний и противопоказаний к применению ФСП. Безусловными преимуществами новых ФСП являются высокая ФСС и снижение лекарственной нагрузки, позволяющие повысить приверженность пациентов к назначенной терапии. Использование понятий относительного коэффициента связывания фосфатов и эквивалентной фосфат-связывающей дозы позволяет облегчить задачу сравнительной оценки и выбора оптимальной дозы ФСП.



