Введение
Калий является наиболее распространенным катионом во внутриклеточной жидкости, и поддержание его правильного распределения по обеим сторонам клеточной мембраны важно для нормальной работы клетки. Почти все клетки обладают Na+/K+-АТФ-азой, которая переносит Na+ из клетки, а K+ в клетку, что создает градиент концентрации K+ (K+ внутри >K+ снаружи) и поддержание разности потенциалов на клеточной мембране. Почки отвечают за гомеостаз K+ в организме, обеспечивая баланс между поступлением K+ и его экскрецией. Уровни K+ могут повышаться при нормальных (физическая активность) и патологических состояниях (метаболический ацидоз и хроническая болезнь почек – ХБП). На его почечную секрецию особенно влияет увеличение концентрации альдостерона в плазме, скорость реабсорбции Na+ и воды в дистальных и собирательных канальцах нефрона.
Гиперкалиемия (ГК) – патологическое состояние, характеризующееся мышечной слабостью, гипотонией, одышкой, нарушениями ритма сердца и как следствие – увеличением летальности [1–5]. ГК в основном является симптомом ухудшения функции почек, при котором уменьшается выведение калия с мочой и повышается его концентрация в сыворотке крови [6, 7]. Помимо почечной недостаточности сердечная недостаточность, сахарный диабет, артериальная гипертензия и прием лекарственных препаратов служат ключевым фактором риска развития ГК [8]. Использование ингибиторов ренин-ангиотензин-альдостероновой системы (РААС), таких как антагонисты рецепторов альдостерона, ингибиторы ангиотензинпревращающего фермента (иАПФ), блокаторы рецепторов ангиотензина (БРА) и прямые ингибиторы ренина, приводит к увеличению частоты и тяжести проявлений ГК. К ГК также приводят чрезмерное потребление калия с пищей, ацидоз и нарушение экскреции калия почками [9, 10]. Повышение уровня калия в сыворотке крови связано с высокой смертностью, особенно среди пожилых пациентов и пациентов с сопутствующими заболеваниями [11–15]. Различные исследования показали, что у пациентов с сердечно-сосудистыми заболеваниями и/или ХБП ГК служит значительным фактором риска смертности от всех причин [11, 13, 15].
Дать определение ГК сложно, т.к. значения уровней калия в плазме крови варьируются не только у разных людей, но и у одного и того же человека в течение дня. Нормальным считается уровень калия в сыворотке крови, как правило, от 3,5 до 5,0 мг-экв/л [16]. Гипокалиемия возникает при снижении уровня калия в сыворотке ниже нижнего, а ГК – при превышении верхнего предела нормального диапазона [17, 18]. ГК по степени тяжести может быть легкой, умеренной или тяжелой [19]. Увеличение уровня K+ выше 6,0 ммоль/л ассоциировано с расширением комплекса QRS, остроконечным зубцом Т, развитием брадикардии, желудочковой аритмии и внезапной смертью [20, 21].
Отмечают исключительную важность ГК у пациентов, получающих заместительную почечную терапию гемодиализом (ГД). Так, внезапная смерть служит основной причиной смерти этих пациентов, а 27% всех смертей обусловлены нарушениями сердечного ритма [22]. При стандартном режиме ГД 3 раза в неделю эти осложнения наиболее часто возникают после 2-дневного перерыва, когда перегрузка жидкостью и концентрации уремических токсинов и К+ наиболее высокие [23–25].
На сегодняшний день практически нет исследований, включивших пациентов с ХБП и ответивших на вопрос: являются ли умеренные отклонения от нормы уровня K+ в крови клинически значимыми и если да, то какие значения ГК ассоциированы с клиническими проявлениями? Насколько нам известно, было выполнено только одно исследование большой группы пациентов с ХБП, которое показало, что уровень К+ в сыворотке ≤4,0 ммоль/л был связан с более высоким риском смерти по сравнению с уровнем K+ в диапазоне 4,1–5,5 ммоль/л. Эти результаты имеют большое клиническое значение, поскольку большинство врачей считают, что значения K+ в диапазоне 3,5–3,9 ммоль/л находятся в «нормальных пределах», а уровни K+ выше 5 ммоль/л требуют немедленной терапии для больных ХБП. Кроме того, отмечалось, что самый низкий риск смерти среди этих пациентов был в диапазоне уровня K+ от 4,1 до 5,5 ммоль/л [26].
ГК является абсолютным показанием к проведению ГД. Так, 24% экстренных процедур ГД проводятся из-за ГК [27]. Длительное время в отсутствие возможности проведения ГД единственным методом лечения ГК было введение растворов глюкозы в сочетании с инсулином, бикарбоната натрия и кальция. Однако подобные методы имеют нестабильный и краткосрочный эффект.
Снизить уровень калия и повысить выведение его из организма в долгосрочной перспективе помогает применение катионообменных смол. В настоящее время в России в продаже доступен препарат Калимейт (Р-Фарм АО, Россия); производитель Ортат АО (Россия). Это средство представляет собой катионообменную смолу полистиролсульфонат кальция. После перорального введения в желудочно-кишечном тракте катион кальция смолы высвобождается в кровь, замещаясь катионом калия из крови пациента (преимущественно в толстом кишечнике), чем объясняется терапевтический эффект препарата при ГК.
Целью работы было исследование безопасности и эффективности приема препарата Калимейт пациентами, находящимися на заместительной почечной терапии ГД, в междиализные дни при двух режимах приема – 4 и 2 дня в неделю.
Материал и методы
Исследование было открытым проспективным контролируемым когортным, выполнено на базе 12-го отделения гемодиализа ГКБ им. С.П. Боткина (Москва) в 2018 г. В исследовании участвовали 33 пациента с ХБП-5, получавших заместительную почечную терапию методом ГД более 6 месяцев (табл. 1, 2).
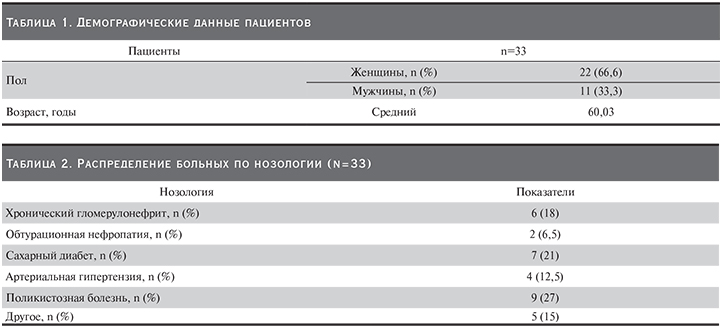
Включались пациенты старше 18 лет с адекватным сосудистым доступом, стандартным режимом ГД 3 раза в неделю, скоростью кровотока не менее 300 мл/мин, диализным Kt/V более 1,2 за процедуру, использованием диализирующего раствора с концентрацией K+ 3,0 ммоль/л и додиализной концентрацией K+ в сыворотке крови более 5,5 ммоль/л после 2-дневного междиализного интервала. Параметры и режим процедур ГД за время исследования не изменялись.
Из исследования были исключены пациенты с тяжелой ГК (K+ более 7 ммоль/л на момент скрининга), гипокалиемией (уровень K+ менее 3,5 ммоль/л), ГК (уровень Ca2+ более 2,5 ммоль/л), гипомагниемией (уровень Mg2+ менее 1,7 мг/дл), тяжелым ацидозом (уровень бикарбоната натрия менее 16 мэкв/л), анемией (уровень гемоглобина менее 90 г/л), имевшие в анамнезе сердечно-сосудистые осложнения менее чем за 12 недель до начала исследования; тяжелым лейкоцитозом (уровень лейкоцитов более 20×109/л) или тромбоцитозом (уровень тромбоцитов более 450×109/л) на момент скрининга. Также исключались пациенты с гематологическими и онкологическими заболеваниями, саркоидозом, заболеваниями желудочно-кишечного тракта, нарушениями сердечного ритма, требовавшими немедленного лечения; ожидаемой продолжительностью жизни менее 6 месяцев, неспособные принимать пероральную смесь лекарственных препаратов.
После начала исследования из него выбыли 6 пациентов: 3 больных в связи с выполненной аллотрансплантацией трупной почки, 3 – в результате развития побочных эффектов.
Дизайн исследования: скрининг, 1-й этап – прием препарата в междиализные дни, т.е. 4 раза в неделю с последующим периодом выведения препарата в течение 1 месяца; 2-й этап – прием препарата в длительный междиализный промежуток, т.е. 2 раза в неделю. Во время каждого этапа исследования проводилось титрование дозы препарата в течение 4 недель с последующими периодом лечения и оценкой – 4 и 4 недели соответственно.
Во время скрининга у всех предварительно отобранных в исследование пациентов определялся додиализный уровень K+ сыворотки крови после 2-дневного интервала, а также оценивался общий и биохимический анализ крови, ЭКГ. В исследование включались пациенты с концентрацией K+ более 5,5 ммоль/л, отсутствием грубой патологии в лабораторных анализах и ЭКГ.
Во время титрации дозы, лечения и оценки лечения каждого из двух этапов исследования выполнялись в динамике: 1) общий и биохимический анализы крови, включившие общий белок, альбумин, общий билирубин, аланинаминотрансферазу, аспартатаминотрансферазу, щелочную фосфатазу, глюкозу крови, общий кальций, фосфор, показатели обмена железа, С-реактивный белок – 1 раз в месяц; 2) определение показателей кислотно-щелочного состояния (КЩС) и электролитов крови – еженедельно; 3) ЭКГ с определением длительности интервала QTс (коррекция на частоту проводилась по формуле Fredericia:QTc (FridericiaCorrection)=QT/(RR interval)⅓) – 1Т раз в неделю.
Период титрования дозы препарата Калимейт составил 4 недели. Титрация была начата с дозы 10 мг/сут с последующим повышением дозы (максимальная доза – 30 мг/сут) до достижения и поддержания уровня K+ сыворотки перед процедурой ГД в диапазоне между 4 и 5,5 ммоль/л. В дальнейшем во время лечения подобранная доза препарата Калимейт не изменялась.
После титрования дозы у трех пациентов развились побочные эффекты в виде желудочно-кишечных расстройств, которые регрессировали после отмены препарата. Эти больные были исключены из исследования.
Дозы других препаратов, принимаемых больными до исследования, не изменялись.
Оценка безопасности:
- серьезные и все побочные эффекты, случаи смерти;
- показатели жизнедеятельности оценивались при каждом визите 3 раза в неделю (жалобы, частота сердечных сокращений);
- ЭКГ (1 раз в неделю);
- мониторирование артериального давления 3 раза в неделю во время процедуры ГД;
- Статистический анализ. Непараметрические методы, компьютерное ПО SPSS 18.0.
Результаты исследования
Динамика изменений показателей уровня K+ представлена в табл. 3.
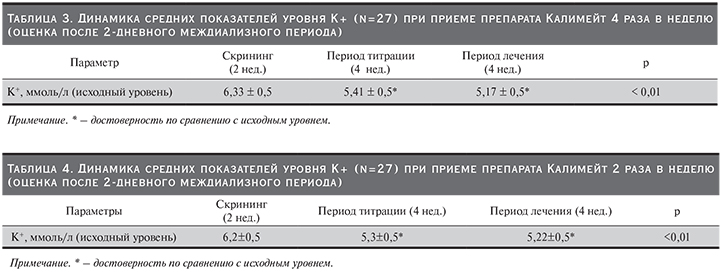
Как видно из табл. 3, уровень K+ существенно снизился на фоне приема препарата в междиализные дни. Средняя доза препарата составила 89±21 г/нед.
Нами была проведена также оценка уровня K+ в сыворотке крови изучаемой группы после 1-го дневного промежутка между диализами без лечения препаратом. Уровень K+ оказался равным5 ,4±0,6ммоль/л и достоверно не отличался от уровня K+ на фоне лечения препаратом.
С учетом вышеизложенного в изучаемой группе через месяц было повторно исследовано влияние препарата на уровень K+ при приеме препарата только 2 дня в неделю в период большого промежутка времени между процедурами ГД. Результаты представлены в табл. 4.
Оценка результатов приема препарата 2 раза в неделю в длительный междиализный промежуток показала его эффективность. Средняя доза препарата составила при приеме 2 раза в неделю 43,05±7,5 г/нед.
Анализ результатов исходного уровня K+ перед процедурой ГД (после 2-дневного перерыва) при приеме препарата 2 раза в неделю и при приеме препарата 4 раза в неделю показал, что они достоверно не различались (5,17 против 5,22 ммоль/л). Количество препарата для достижения цели различалось в двух группах в 2 раза. Оценка в динамике интервала QTc на этапе скрининга и в период лечения достоверно показала его снижение с 0,392±0,062 до 0,327±0,027 мс (р<0,01), что не выходило за рамки допустимой нормы. Однако у 7 (25,9%) пациентов из 27 на этапе скрининга длительность интервала QTc была выше нормальных значений. На фоне приема препарата у всех пациентов длительность интервала QTc была в пределах допустимых границ.
На фоне лечения препаратом Калимейт были отмечены побочные эффекты у 3 пациентов, принимавших препарат 4 раза в неделю, в виде нарушений со стороны желудочно-кишечного тракт (запоры, тошнота), что заставило прекратить лечение этих пациентов. Серьезных побочных эффектов у больных, принимавших препарат Калимейт, зарегистрировано не было.
Обсуждение
Применение катионообменных смол для снижения уровня K+ началось еще в 1958 г. (одобрены к применению FDA в США), однако до сегодняшнего дня было проведено только 3 контролируемых рандомизированных исследования (КРИ) по оценке эффективности и наличию побочных эффектов у этих препаратов [28–30]. Но эти исследования не могут рассматриваться в полной мере достаточными: так, в исследовании Gruy-Kapral (1998) выборка составила всего 6 больных. В исследовании K. Nasir и A. Ahmad сравнивались две группы пациентов, получавших два разных вида катионообменных смол (полистиролсульфонат кальция и натрия) без групп сравнения. В исследовании L. Lepage оценка проводилась всего в течение 7 дней у пациентов с легкой степенью ГК – 5,0–5,5 ммоль/л.
В нашем исследовании впервые получен достоверный результат снижения уровня K+до целевых значений <5,5 ммоль/л в большой группе больных ХБП на программном ГД. Однако кроме этого дизайн исследования был составлен так, чтобы минимизировать побочные эффекты препарата с достижением максимума эффективности. Известно, что применение катионообменных смол ассоциируется со значительными желудочно-кишечными и другими побочными эффектами, что в сочетании с плохой вкусовой привлекательностью вызывает беспокойство и препятствует их применению в плане длительного поддержания оптимального уровня K+ [31–33].
В проведенном исследовании у троих пациентов, получавших препарат Калимейт 4 раза в неделю, были зарегистрированы побочные эффекты (запоры, тошнота), что заставило прекратить использование препарата. В то же время у больных, получавших препарат 2 раза в неделю, побочных эффектов зарегистрировано не было. Нагрузка препаратом у больных, принимавших препарат 2 раза в неделю, была, соответственно, в 2 раза ниже, чем в группе с 4-дневным приемом препарата, – 43,05±7,5 против 89±21 г/нед.
Другим немаловажным аспектом исследования было изучение длительности интервала QTc в группе. На этапе скрининга у каждого четвертого пациента длительность интервала QTc выходила за пределы референсных значений, что свидетельствовало о повышенном риске внезапной сердечной смерти и аритмии у этих больных. На фоне лечения препаратом Калимейт у всех больных средняя длительность интервала QTc достоверно уменьшилась и была в пределах нормальных значений.
Кроме положительных аспектов в плане достижения целевых значений K+ и уменьшения риска аритмий и внезапной сердечной смерти, представляет интерес и оценка экономической стороны лечения больных ГК. В недавно опубликованном исследовании [34] на большой выборке пациентов (n=40 000) был проведен сравнительный анализ пациентов с ГК и больных контрольных групп, сопоставимых по основным и сопутствующим заболеваниям (лечению ГД, стадиям ХБП, сердечной недостаточности и использованию препаратов иАПФ, возрасту) по стоимости их лечения. В этом ретроспективном исследовании пациенты с ГК имели значительно более высокие затраты на медицинское обслуживание по сравнению с подобранными контролями. Эти различия были больше у пациентов с ХБП на программном ГД и/или сердечной недостаточностью. Пациенты с ГК чаще госпитализировались, обращались в отделение неотложной помощи и к врачу в амбулаторных условиях. Кроме того, при госпитализации пациенты с ГК имели более длительные сроки пребывания и чаще имели повторные госпитализации в течение 30, 60 или 90 дней после выписки. Таким образом, ГК связана со значительным экономическим бременем, затраты на этих больных отличаются в разы от таковых на пациентов с нормокалиемией, а стоимость катионообменных смол несопоставимо мала по сравнению с этими затратами.
Выводы
В результате проведенного клинического исследования у больных ХБП, получавших лечение программным ГД, впервые был продемонстрирован хороший терапевтический эффект применения катионообменной смолы Калимейт с целью снижения уровня K+ до целевых значений и достигнуто достоверное уменьшение интервала QTc до нормальных значений при приеме препарата как через день в междиализные дни, так и в 2-дневный междиализный промежуток. Отмечена равная эффективность препарата при 4- и 2-дневном приеме, но при приеме 2 дня в неделю существенно снизилась нагрузка препарата на пациента (в 2 раза), что уменьшает риск развития побочных эффектов.
Таким образом, препарат Калимейт может быть рекомендован к применению 2 дня в неделю в длительный междиализный промежуток с минимальным риском развития побочных эффектов для снижения уровня K+ до целевых значений с целью снижения риска внезапной смерти.



