Введение
Снижение заболеваемости и смертности от хронической болезни почек (ХБП) стало одним из приоритетных направлений здравоохранения. Как и в других странах мира, в Кыргызской Республике (КР) число пациентов, находящихся на диализной терапии, увеличивается ежегодно и составляло на 2019 г. 1234 человека. Согласно постановлению правительства КР № 441 от 29.08.2019, финансирование гемодиализных услуг производится по линии ФОМС в 23 медицинских учреждениях. Что касается трансплантации почки, то число реципиентов с трансплантированной почкой на сегодня достигло 337 человек. Медико-социальные аспекты и бремя ХБП в КР заключается в том, что многие лица с ХБП в момент верификации диагноза уже имеют кардиоваскулярные осложнения (КВО). В последнее годы распространенность ХБП стала значительно больше, чем предполагалось ранее, и наблюдающийся в настоящее время прогрессивный рост числа пациентов с ХБП приобретает характер пандемии [1, 2]. Около 40% взрослого населения имеют повышенный риск развития ХБП [3]. В некоторых исследованиях установлено, что оценка концентрации фактора роста фибробластов-23 (FGF-23) может быть использована в качестве предиктора тяжести течения ХБП и развития ее осложнений [4]. В настоящее время активно исследуется роль фосфора и морфогенетических белков при ХБП [5, 6]. В частности, полученные данные по изучению FGF-23 как биологического маркера прогрессирования ХБП существенно изменили традиционный взгляд на механизм возникновения КВО [7]. FGF-23 – это белок, секретируемый из остеоцитов, главным образом из остеобластов, состоит из 251 аминокислоты и имеет молекулярную массу – 32 кДа [8]. FGF-23 относятся к семейству факторов роста, участвующих в ангиогенезе, заживлении ран, эмбриональном развитии, процессах пролиферации и дифференцировки остеоцитов [9]. Основная роль FGF-23 заключается в снижении плазменного уровня фосфата [9–11]. Секреция FGF-23 местно регулируется в костях при участии дентина-1 и фосфат-регулирующей эндопептидазы [12]. Период полураспада FGF-23 в крови у здоровых людей составляет 58 минут [13]. В проведенных исследованиях отмечено, что повышение продукции FGF-23 регистрируется на ранних стадиях ХБП [14, 15]. Вместе с тем высокие концентрации FGF-23 плазмы крови у лиц с ХБП, особенно на старте диализной терапии, ассоциируются с ростом смертности из-за структурно-функциональных изменений сосудистой стенки и миокарда [16, 17–20]. Эти данные получены в исследованиях, где в качестве объекта в основном выступали лица с терминальной стадией ХБП либо находящиеся на диализной терапии. Однако исследования по изучению роли фосфора и FGF-23 плазмы крови у пациентов на преддиализной стадии ХБП немногочисленны.
Цель исследования. Установить зависимость между концентрацией FGF-23 и показателями центральной гемодинамики у пациентов ХБП.
Материал и методы
В исследование включены 78 пациентов (45 женщин и 33 мужчины) в возрасте от 23 до 84 лет (средний возраст – 55,05±13,07 года). Клиническая характеристика пациентов представлена в табл. 1. По результатам анамнеза, инструментально-лабораторных обследований, а также из представленной медицинской документации установлена ХБП. У всех пациентов анализировалась частота сердечных сокращений (ЧСС, уд/мин), показатели систолического (САД, мм рт.ст.), диастолического (ДАД, мм рт.ст.) и центрального систолического (ЦСД, мм рт.ст.) артериального давления. Величину ЦСД определяли неинвазивным способом на приборе «Ангиоскан».
Проводили измерение роста и массы тела пациентов с расчетом индекса массы тела (ИМТ, кг/м2) по Кетле. Биохимический анализ крови включал исследование содержание фосфора (ммоль/л), С-реактивного белка (СРБ, МЕ/л) и креатинина (мкмоль/л) крови. Концентрация СРБ, превышавшая 5 МЕ/л, рассматривалась как повышенная. У всех пациентов оценивали показатели FGF-23 (C-terminal) в плазме крови с использованием набора фирмы Biomedica Medizinprodukte GmbH & Co KG (Вена, Австрия) методом иммуноферментного анализа. Забор крови для исследования осуществляли утром натощак с 07.00 до 08.00. За верхнюю границу нормы FGF-23 принята концентрация, равная 0,8 пмоль/л. Для расчета скорости клубочковой фильтрации (СКФ, мл/мин/1,73 м2) применялась формула CKD-EPI (Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration, 2011) [21]. Согласно рекомендациям KDIGO (Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes) от 2002 г., диагноз ХБП устанавливался на основании изменения мочевого осадка (протеинурия, гематурия) или снижения расчетной СКФ–рСКФ (менее 60 мл/мин), увеличения концентрации креатинина плазмы крови на протяжении более чем 3 месяцев [22]. В наше исследование не включены пациенты, находившиеся на программном гемодиализе, лица с трансплантированной почкой, беременные и кормящие женщины.
Полученные результаты обрабатывали методами статистического анализа с использованием пакета прикладных программ Statistica 10.0. Рассчитывались средние величины (М) и их стандартные ошибки (SD). В случае ненормального распределения количественного признака рассчитывали Me (Q25%;Q75%).
Значимость межгрупповых различий оценивалась с помощью t-критерия Стьюдента для переменных с нормальным распределением и Манна–Уитни U-test для переменных с непараметрическим распределением. Для установления связи между исследуемыми параметрами использован коэффициент корреляции Спирмена. Статистически значимыми различия считали достоверными при р<0,05.
Результаты исследования
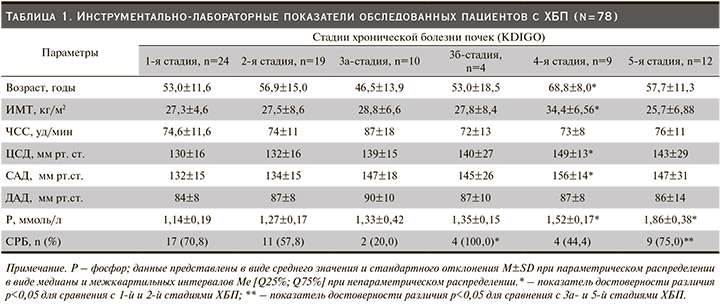
Настоящее исследование основано на анализе данных 78 пациентов с ХБП на разных стадиях заболевания. Как показано на рисунке, причиной синдрома ХБП служили артериальная гипертензия (АГ) – у 53,8%, коморбидное состояние – у 37,1%, хронический тубулоинтерстициальный нефрит – у 6,4%, хроническая обструктивная болезнь легких – у 7,6%, сахарный диабет 2 типа – у 19,2%, хронические гломерулонефриты – у 19,2%, ишемическая болезнь сердца – у 21,7%.
В исследовании 35 пациентов в 44,8% случаев имелись признаки хронической почечной недостаточности, т.е. у них величина рСКФ оказалась менее 60 мл/мин (табл. 1). Средний возраст обследованных пациентов отличался в зависимости от степени тяжести ХБП. Так, пациенты с 4-й стадией ХБП были старше, тогда как у лиц с 3а-стадией ХБП средний возраст был достоверно ниже (p<0,05). Различия по показателю ИМТ между стадиями ХБП отмечены не были, за исключением 4-й стадии заболевания, где величина ИМТ была существенно выше (p<0,05). Из представленных данных в табл. 1 видно, что у пациентов с ХБП 3а-стадии средняя ЧСС была значимо выше (p<0,05). Сравнительно более высокие уровни ЦСД и САД определены у лиц с ХБП 4-й и 5-й стадий (табл. 1). Клинически значимая разница в показателях ДАД отмечена у пациентов с ХБП 3а-стадии. Как и следовало ожидать, содержание фосфора плазмы крови нарастало от 1-й до 5-й стадии ХБП. Пациенты с высокой концентрацией СРБ плазмы крови чаще выявлены при 1-й, 3б- и 5-й стадиях ХБП.
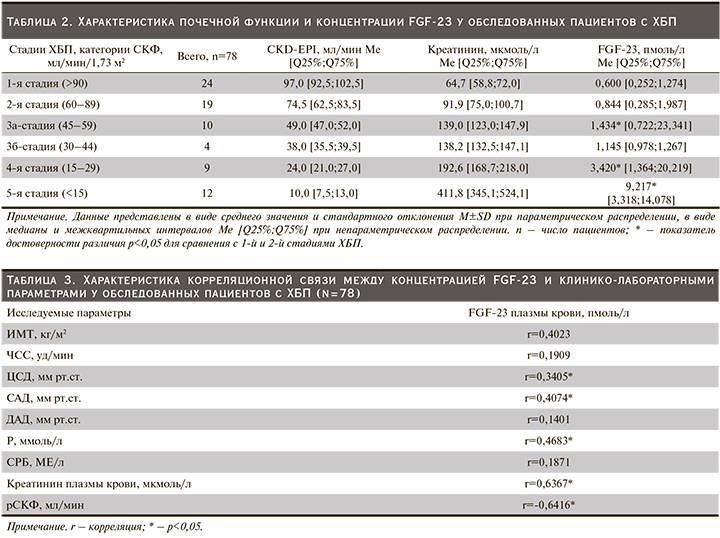
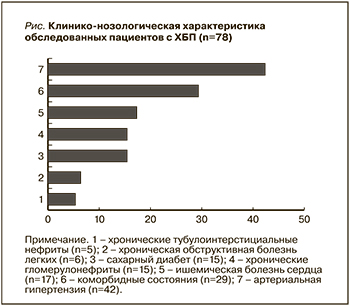
По мере снижения почечной функции медиана концентрации FGF-23 плазмы крови ощутимо повышалась и оказалась значимо выше на 4-й и 5-й стадиях ХБП. Полученные данные исследования послужили основанием проведения корреляционного анализа, целью которого стало установление двусторонних отношений между концентрацией FGF-23 и показателями центральной гемодинамики. Так, между концентрацией FGF-23 плазмы крови и уровнем ЦСД (r=0,3405; p<0,05), а также САД (r=0,4074; p<0,05) была установлена прямая корреляционная взаимосвязь (табл. 3).
Схожая связь получена между концентрациями фосфора (r=0,4683; p<0,05), креатинина (r=0,6367; p<0,05) и FGF-23 в крови. У обследованных нами пациентов выявлена отрицательная корреляция между снижением рСКФ и ростом концентрации FGF-23 в крови (r=-0,6416; p<0,05) (табл. 3).
Обсуждение
Избыточный синтез FGF-23 на ранних стадиях ХБП происходит в результате накопления фосфора и начального увеличения его внеклеточного пула [15]. В эпителиях проксимальных канальцев почек происходит реабсорбция фильтруемого фосфора с помощи натрийзависимых переносчиков – IIa, IIc и PIT2 [12, 23]. Ведущим гормоном, регулирующим гомеостаз фосфора в организме, является FGF-23 [15]. В нашей работе мы получили достоверную взаимосвязь (r=0,4683; p<0,05) между концентрацией фосфора и содержанием FGF-23 в крови (табл. 3). В работе O.M. Gutiérrez et al. (2011) с участием 1261 человека, где у большинства участников исследования была сохранная функция почек, установлено наличие прямой связи между потреблением фосфора с пищей и уровнем FGF-23 в крови [24]. Имеются сведения, согласно которым поступления фосфора для снижения уровня FGF-23 приводят к повышению реабсорбции фосфатов в почке и увеличению всасывания фосфора в кишечнике с увеличением синтеза витамина D [25, 26]. Кроме того, под воздействием FGF-23 происходит стимуляция почечной экскреции фосфора за счет прямого подавления натрийзависимых переносчиков типа IIa, IIc и PIT2 в проксимальных канальцах и подавления образования активной формы витамина D в почках [27, 28]. При потреблении пищи, богатой фосфором, высокий уровень FGF-23 приводит к фосфатурии и снижению образования кальцитриола [29]. Cо своей стороны низкий уровень кальцитриола снижает кишечную абсорбцию фосфора [30]. В случае диеты с низким содержанием фосфора, наоборот, сниженный уровень FGF-23 способствует накоплению фосфата в организме и усилению его всасывания в кишечнике посредством нарастания уровня кальцитриола [31]. Уменьшение выведения фосфора с мочой и повышение его концентрации в крови развиваются при снижении фильтрационной функции почек менее 30 мл/мин [29]. Полагается, что избыток фосфора индуцирует сосудистую кальцификацию независимо от уровня FGF-23 [16]. По мере снижения СКФ с уменьшением массы действующих нефронов происходит гиперпродукция FGF-23 [32]. В нашем исследовании мы установили тесную связь между снижением СКФ и ростом концентрации FGF-23 плазмы крови (r=-0,6416; p<0,05) (табл. 3). К тому же выявлена достоверная связь между ростом уровня креатинина плазмы крови и содержанием FGF-23 у участников исследования (табл. 3). Причем на более поздних стадиях ХБП уровень FGF-23 еще больше увеличивается, следовательно, высокие значения FGF-23 можно оценить как независимый предиктор быстрого прогрессирования ренальной дисфункции [10, 11]. Эти данные получены и в нашем исследовании (табл. 2). В частности, по мере ухудшения почечной функции достоверно нарастала концентрация FGF-23 плазмы крови. Вместе с тем при исследовании изменений уровня фосфора у пациентов в зависимости от тяжести ренальной функции обнаружено присутствие ХБП 4-й и 5-й стадий у большинства пациентов с гиперфосфатемией (табл. 1). Наличие повышенного уровня фосфора крови при ХБП ускоряет атеро- и артериосклеротические процессы в артериях с потерей эластичности сосудистой стенки, развитие гиперкинетического типа кровообращения и росту АД [29]. Гиперфосфатемия способствует не только прогрессированию ХБП, но и снижению нефропротективного действия блокаторов ренин-ангиотензин-альдестероновой системы (РААС) [33].
 При гиперфосфатемии у лиц с терминальной стадией ХБП наблюдается и высокий уровень FGF-23. Причем смертность среди пациентов на продвинутых стадиях ХБП прямо коррелирует с уровнем FGF-23 независимо от концентрации фосфора в крови. Достоверное повышение уровня FGF-23 плазмы крови на ранних стадиях ХБП выявлено в работе Ф.У. Дзгоевой и соавт. (2015), где уровень концентрации FGF-23 значимо коррелировал со структурными изменениями левого желудочка [16]. Негативное влияние FGF-23 на состояние кардиоваскулярной системы при ХБП объясняется тем, что он вызывает эндотелиальную дисфункцию и субклиническое воспаление [34, 35]. Стоит отметить, что повышение концентрации FGF-23 независимо от артериальной гипертензии вызывает гипертрофию левого желудочка [36, 37]. По результатам данных нашей работы, между концентрацией FGF-23 плазмы крови и уровнями ЦАД и САД установлена прямая корреляционная взаимосвязь, что вполне согласуется с результатами ранее проведенных исследований [7]. Одним из объяснений повышения АД у пациентов с ХБП при высоком уровне FGF-23 могут служить кальцификация сосудов, изменение оксидативного стресса и увеличение экспрессии супероксиддисмутазы [38, 39]. Следует также отметить, что системные эффекты FGF-23 реализуются через СРБ, повышенное содержание которого при ХБП рассматривается как маркер субклинического атеросклероза. По современным данным, СРБ подавляет продукцию оксида азота эндотелием и оказывает влияние на экспрессию рецепторов гладкомышечных клеток к ангиотензину типа I, тем самым усугубляя дисфункцию эндотелия, развитие системной вазоконстрикции, что является механизмом повышения АД [40, 41]. Сочетание повышенного уровня FGF-23 и СРБ ведут к воспалению, нестабильности атеромы, вазоконстрикции и тромбообразованию, особенно у популяции диализных пациентов. Другим системным последствием изменений в системе FGF-23 является дополнительная активация РААС, что безусловно поддерживает развитие КВО при ХБП.
При гиперфосфатемии у лиц с терминальной стадией ХБП наблюдается и высокий уровень FGF-23. Причем смертность среди пациентов на продвинутых стадиях ХБП прямо коррелирует с уровнем FGF-23 независимо от концентрации фосфора в крови. Достоверное повышение уровня FGF-23 плазмы крови на ранних стадиях ХБП выявлено в работе Ф.У. Дзгоевой и соавт. (2015), где уровень концентрации FGF-23 значимо коррелировал со структурными изменениями левого желудочка [16]. Негативное влияние FGF-23 на состояние кардиоваскулярной системы при ХБП объясняется тем, что он вызывает эндотелиальную дисфункцию и субклиническое воспаление [34, 35]. Стоит отметить, что повышение концентрации FGF-23 независимо от артериальной гипертензии вызывает гипертрофию левого желудочка [36, 37]. По результатам данных нашей работы, между концентрацией FGF-23 плазмы крови и уровнями ЦАД и САД установлена прямая корреляционная взаимосвязь, что вполне согласуется с результатами ранее проведенных исследований [7]. Одним из объяснений повышения АД у пациентов с ХБП при высоком уровне FGF-23 могут служить кальцификация сосудов, изменение оксидативного стресса и увеличение экспрессии супероксиддисмутазы [38, 39]. Следует также отметить, что системные эффекты FGF-23 реализуются через СРБ, повышенное содержание которого при ХБП рассматривается как маркер субклинического атеросклероза. По современным данным, СРБ подавляет продукцию оксида азота эндотелием и оказывает влияние на экспрессию рецепторов гладкомышечных клеток к ангиотензину типа I, тем самым усугубляя дисфункцию эндотелия, развитие системной вазоконстрикции, что является механизмом повышения АД [40, 41]. Сочетание повышенного уровня FGF-23 и СРБ ведут к воспалению, нестабильности атеромы, вазоконстрикции и тромбообразованию, особенно у популяции диализных пациентов. Другим системным последствием изменений в системе FGF-23 является дополнительная активация РААС, что безусловно поддерживает развитие КВО при ХБП.
Заключение
Таким образом, результаты настоящего исследования подтверждают, что у пациентов с ХБП концентрация FGF-23 плазмы крови начинает повышаться еще на додиализной стадии. При этом на 4-й стадии ХБП высокие уровни FGF-23 плазмы крови ассоциируются с ростом ЦАД и САД, ИМТ и гиперфосфатемией.
Необходимость определения FGF-23 плазмы крови на додиализной стадии ХБП продиктовано тем, что разработки новых критериев оценки риска для своевременной диагностики и профилактики развития осложнений сердечно-сосудистой системы.



