Введение
Хроническая болезнь почек (ХБП) является глобальной проблемой общественного здравоохранения во всем мире, затрагивающей более 750 млн человек во всем мире [1]. Маркерами ХБП являются снижение скорости клубочковой фильтрации (СКФ) 60 мл/мин/1,73 м2 в течение 3 месяцев и более и/или наличие структурных или функциональных повреждений почек [2–5].
Распространенность ХБП 1–5-й стадий в мире составляет 13,4%, в т.ч. 3-й стадии – 7,6% [6], среди взрослого населения США распространенность ХБП – 14,8%, из них ХБП 3-й стадии – 6,4% [1]. Заболеваемость ХБП существенно различается по всему миру [1]. Так, распространенность ХБП в Канаде составляет 71,9 на 1000 человек [7], в странах Южной Азии от 10,6 до 23,3% [8]. Выявлены значительные различия в распространенности ХБП среди европейских исследуемых групп населения, которая варьировалась от 3,31% в Норвегии до 17,3% в северо-восточной Германии [9].
Основными причинами нарушения функции почек в настоящее время являются не только первичные заболевания почек, но и артериальная гипертензия (АГ), и сахарный диабет 2 типа (СД2) [10, 14]. Среди населения увеличивается распространенность сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний, ожирения, СД2 [12], при этом за 2013–2016 гг. частота регистрации новых случаев ХБП у больных СД2 возросла в 3,7 раза (190,4 против 51,8/10 тыс. взрослых) [12]. ХБП и сердечно-сосудистые заболевания имеют сходные факторы риска [13]. По данным наблюдательных регистров, общая распространенность сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний вдвое выше среди больных ХБП по сравнению с таковыми без ХБП [6], при этом нарастание тяжести ХБП ассоциируется с увеличением числа сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний [14]. Снижение СКФ и появление альбуминурии независимо друг от друга и других факторов сердечно-сосудистого риска ассоциируются с увеличением риска сердечно-сосудистой и общей смертности, ухудшением исходов инфаркта миокарда [15–17]. Следует подчеркнуть особую значимость негативного влияния на функцию почек факторов, связанных с образом жизни: курения [18], употребления алкоголя [19–21], наличия ожирения [22, 23], неправильного питания, избыточного употребления соли.
Распространенность этих факторов риска в Республике Коми высока. Так, по данным Роспотребнадзора, Республика Коми вошла в число лидеров по уровню потребления алкоголя в России: в 2016 г. в Коми продажи алкоголя составили 117,86 л/человека в год [24], показатель потребления алкоголя превысил 13 л чистого спирта на душу населения, при среднем потреблении алкоголя в Российской Федерации, по разным оценкам, от 5,9 до 10 л на душу населения [25]. По данным Федеральной службы статистики, число курящих в Коми составило 32,4% , в то время как в среднем по России это показатель был 22,5% [26, 27]. По данным популяционного исследования ЭССЕ РФ, ожирением страдают 29,7% населения России [28], в т.ч. и в Республике Коми.
ХБП протекает бессимптомно до развития терминальной стадии, в связи с чем пациенты зачастую недостаточно осведомлены о наличии у них ХБП [29, 30], что приводит к поздней ее диагностике. В Российской Федерации и в мире растет обеспеченность заместительной почечной терапией пациентов терминальной ХБП. По данным Федерального регистра ХБП, в России обеспеченность диализом выросла с 2010 по 2019 г. с 25 тыс. до 54 953 больных, в т.ч. в Северо-Западном Федеральном округе этот показатель составляет 373,3 на 1 млн населения [31]. При этом диализ не может решить всех проблем пациентов с ХБП, смертность среди диализных больных выше, чем в общей популяции [32, 33]. Поэтому раннее выявление ХБП, своевременное назначение пациентам нефропротективной терапии и проведение профилактических мероприятий среди лиц, входящих в группу риска, приобретают особое значение [34–36].
С учетом выраженных различий распространенности ХБП в разных странах и регионах, а также различных темпов ее прогрессирования среди пациентов актуально ведение региональных регистров ХБП, позволяющих выявлять особенности течения ХБП в конкретном регионе. Во многих странах и регионах ведутся регистры ХБП [6, 37, 38]. В Республике Коми с 2015 г. ведется регистр пациентов с ХБП, госпитализированных в нефрологическое отделение [39].
Цель – выявить региональные особенности хронической болезни почек в Республике Коми по данным регистра республиканской больницы.
Материал и методы
Использованы данные регистра 484 пациентов отделения нефрологии ГБУЗ РК «Коми республиканская клиническая больница» за 2015–2018 гг., из них 231 (47,7%) мужчина, 253 (52,3%) женщины. Средний возраст составил 58,8±15,8 года.
Пациенты включались в регистр по мере их поступления в отделение на госпитализацию. В регистре регистрировались паспортные данные, диагноз, статус пациента, дата обследования, артериальное (АД), лечение, а также вносились результаты клинических и биохимических анализов.
Создание и обработку базы данных проводили при помощи электронных таблиц MicrosoftExcel-2016, статистический анализ – с использованием пакетов программ Statistika и XLSTAT-2018. Характер распределения данных оценивали с помощью теста Колмогорова–Смирнова. Количественные значения исследуемых признаков, подчиняющиеся закону нормального распределения, представлялись в виде (М±σ), где М – среднее арифметическое значение, σ – стандартное отклонение, непараметрические значения представлялись в виде X (a; b), где X – медиана, a и b – 25 и 75 процентили. Оценку достоверности различий между парными независимыми выборками проводили с использованием t-критерия Стьюдента. При характере распределения результатов, отличном от нормального, оценку различий между группами проводили с помощью методов непараметрической статистики с использованием критериев Манна–Уитни и χ2-критерия. Для определения линейной зависимости между двумя величинами использовали коэффициент корреляции Спирмена. Вероятность «р» вычисляли из уравнения регрессии. Результаты сравнения рассматривали как статистически значимые при p<0,05.
Результаты
Число пациентов, включенных в регистр за годы наблюдения, было следующим: 2015 г. – 190 больных, 2016 г. – 127, 2017 г. – 71, 2018 г. – 97 (рис. 1).
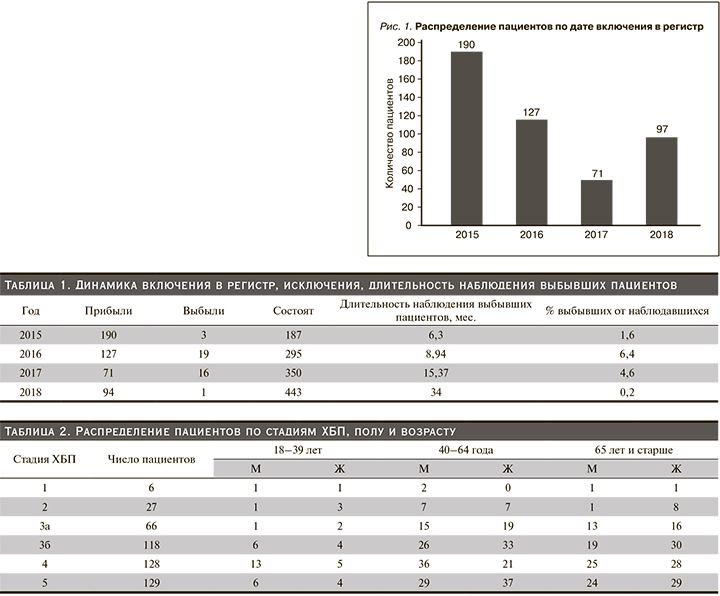
Наибольшее число пациентов включено в регистр в 2015 г., т.к. это был год начала регистра, вследствие чего все пациенты были впервые включены в регистр. В последующие годы часть этих пациентов поступали в отделение повторно, поэтому число первично зарегистрированных пациентов уменьшилось. Число пациентов с одним визитом составило 314 (64,9%). Всего за время наблюдения повторно были госпитализированы 170 (35,1%) пациентов, из них только 2 визита совершили 97 (18,6%) человек, 3 визита – 41 (8,5%), 4 – 3,9% и 5 – 1,7%.
Средний возраст пациентов составил 58,8±15,8 года. Наибольшая часть пациентов, включенных в регистр, находились в возрастном диапазоне 40–64 года – 232 (47,9%) человек, 65 лет и старше – 196 (40,5%). Средняя СКФ у пациентов, включенных в регистр, составила 30,1±19,3 мл/мин/1,73 м2. Распределение пациентов по стадиям ХБП, полу и возрасту представлено в табл. 2.
Распределение пациентов по стадиям ХБП было следующим: 1-я стадия ХБП – 1,2%, 2-я – 5,6%, 3а-стадия – 13,6%, 3б – 24,4%, 4-я стадия – 26,4%, 5-я – 26,6% от числа пациентов в регистре. Чаще всего среди пациентов встречалась ХБП 3-й стадии.
Распределение пациентов по нозологическим формам, явившимся причиной ХБП, представлено в табл. 3.
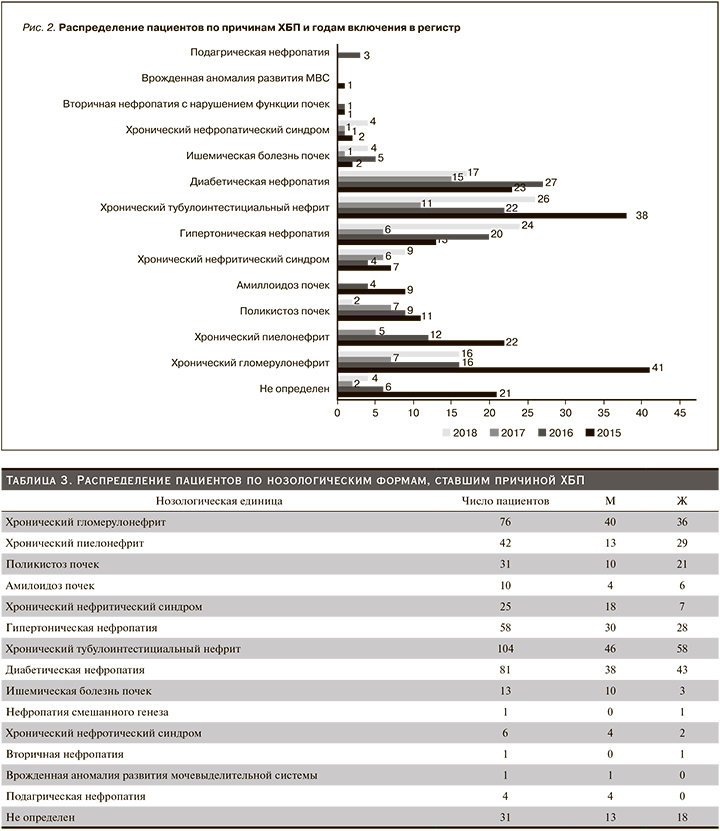
Основные причины ХБП: тубулоинтерстициальный нефрит (ТИН) – 21,5%, хронический гломерулонефрит – ХГН (20,8%), диабетическая нефропатия (ДН) – 16,9%, гипертоническая нефропатия – (12,0%), диагноз не определен – 12,8%. Наиболее частой причиной ХБП у женщин являлся ТИН, у мужчин – ХГН. У женщин чаще, чем у мужчин, встречались такие заболевания, как хронический пиелонефрит, поликистоз почек, ДН, в то время как у мужчин чаще, чем у женщин, были ХГН, гипертоническая нефропатия, ишемическая болезнь почек. Распределение пациентов по годам и нозологическим формам представлено на рис. 2.
Проанализирован ряд лабораторных данных, имевшихся на момент включения пациентов в регистр. Корреляция результатов лабораторных исследований, отражавших активность почечного заболевания (протеинурия), нарушения фосфорно-кальциевого обмена, тяжесть анемии, с показателями СКФ представлена в табл. 4.
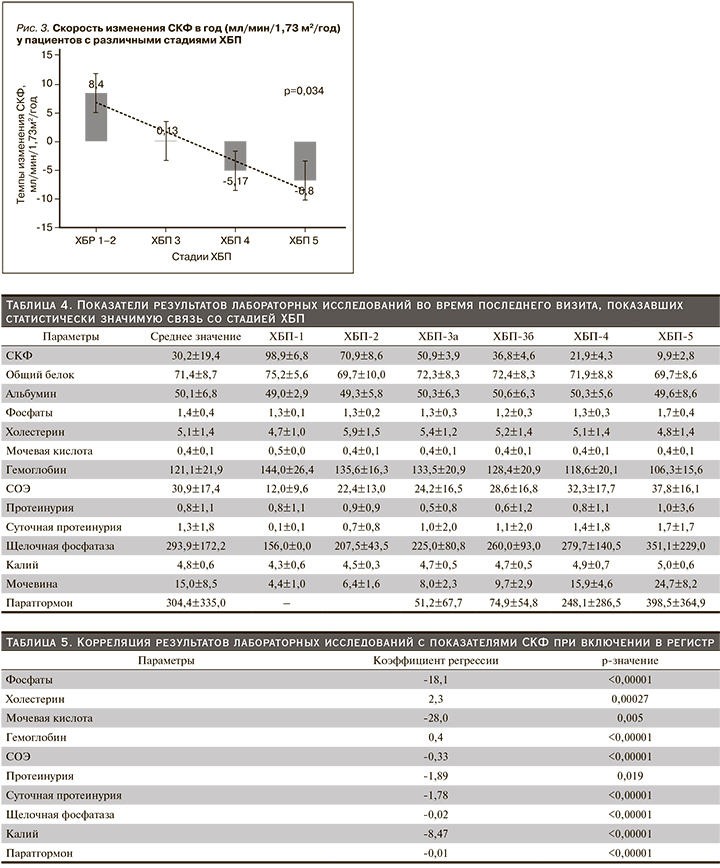
Выявлена обратная корреляция значения СКФ с уровнем фосфатов, мочевой кислоты, СОЭ, протеинурии, щелочной фосфатазы, калия, паратгормона; прямая корреляционная связь с уровнями гемоглобина.
На основании показателей СКФ, оцениваемых при каждом обращении пациентов, рассчитана скорость изменения СКФ за год у каждого пациента, имевшего 2 и более визита. Проанализирована динамика показателей СКФ у 130 пациентов, отвечавших данным требованиям. Среднее снижение СКФ составило 3,99±2,7 мл/мин/1,73 м2 за год наблюдения, при этом у 29 пациентов СКФ увеличилась, у 101 – снизилась.
Результаты сравнения основных лабораторных показателей пациентов со сниженной и увеличенной в динамике СКФ представлены в табл. 5.
Пациенты со снижавшейся СКФ отличались от группы пациентов с увеличивашейся или стабильной СКФ более низкими показателями изначальной СКФ (19,8±12,6 мл/мин/1,73 м2), гемоглобина и более высокими уровнями фосфатов (р=0,018), мочевины и паратиреоидного гормона.
Темпы изменения СКФ в год у пациентов с различными стадиями ХБП представлены на рис. 3. Темпы снижения СКФ значительно различались у пациентов в зависимости от стадии ХБП. Так, у пациентов с ХБП 2-й стадии средняя СКФ увеличивалась на 8,4±3,6 мл/мин/1,73 м2 в год, в то время как у пациентов с 3-й стадией ХБП средние показатели СКФ практически не изменялись, у пациентов с 4-й и 5-й стадиями ХБП темпы снижения СКФ составили 5,17±2,4 и 6,8±2,6 мл/ мин/1,73 м2 в год соответственно. Таким образом, чем ниже у пациента была СКФ при постановке на учет, тем быстрее она снижалась в дальнейшем (р=0,034). Установлена прямая корреляция темпов ухудшения функции почек с исходными уровнями фосфатов, мочевины, калия сыворотки, протеинурии, СОЭ, а также обратная корреляция с исходными показателями гемоглобина и СКФ. Прослеживалась тенденция связи ускорения темпов ухудшения функции почек с мужским полом, однако без статистической значимости этих взаимосвязей (табл. 6).
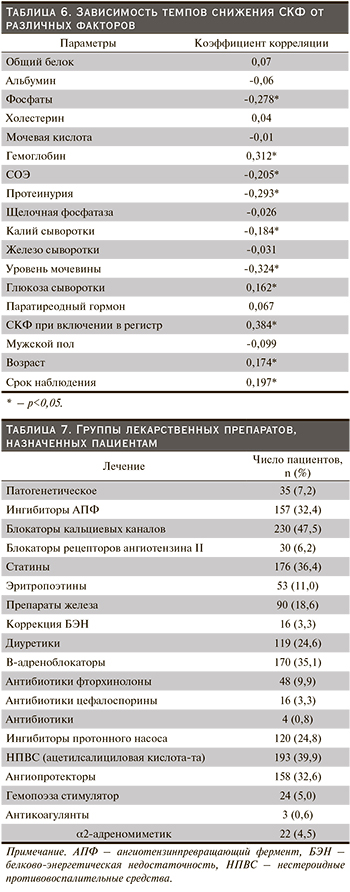
Все пациенты на момент исследования получали медикаментозную терапию. Группы лекарственных препаратов, назначенных пациентам, представлены в табл. 7.
Пациенты получали адекватную нефропротективную терапию, в частности ингибиторы АПФ (32,4%), блокаторы кальциевых каналов (47,5%), статины (36,4%). Диализ получали 8,8% пациентов в возрасте до 75 лет и 1,6% в возрасте старше 75 лет.
Обсуждение
В представленной работе сделана попытка проанализировать причины ХБП и оценить, насколько это было возможно, темпы прогрессирования ХБП у пациентов, проживающих в отдельном регионе на севере России. За основу анализа взят регистр госпитализированных пациентов с ХБП, ведущийся в отделении нефрологии с 2015 г. В исследуемый регистр были включены больные, госпитализированные в отделение нефрологии, т.е. пациенты с более тяжелым течением ХБП, средняя СКФ которых составляла 30,1±19,3 мл/мин/1,73 м2, в связи с чем состав стадий ХБП у данных пациентов не полностью отражает популяционные данные.
Число пациентов с 1 визитом составило 314 больных, с 2 и более – 170. Средний возраст пациентов, включенных в регистр, составил 58,8±15,8 года.
Несмотря на то что в регистр были включены пациенты с продвинутыми стадиями ХБП, в исследуемом регистре пациенты с ХБП моложе, чем в аналогичном Санкт-Петербургском городском регистре ХБП и в ряде других клинических исследований ХБП [38, 40], что может свидетельствовать о большей распространенности факторов риска или о более высоких темпах прогрессирования ХБП в северном регионе, также не исключается вероятность поздней диагностики ХБП у пациентов. В то же время в литературе сообщается и о более молодом среднем возрасте пациентов с впервые выявленной ХБП, в частности у пациентов из Камеруна [41] и у больных СД из Эфиопии [42]. В настоящем исследовании выявлены основные причины ХБП: ТИН, ХГН, ДН, гипертоническая нефропатия. Полученные в настоящем исследовании результаты несколько отличаются от структуры ХБП в других регистрах. Так, по данным последнего отчета регистра ERAEDTA за 2017 г. [43], в структуре причин ХБП лидируют СД (23%), ХГН (17%), гипертоническая болезнь (12%), неизвестные причины (20%). По данным регистра ХБП Санкт-Петербургского городского регистра ХБП, основной причиной терминальной ХБП были хронический пиелонефрит (26%), гипертоническая болезнь (22%), ХГН (20%), СД (15%) [38]. Большую распространенность ТИН, по данным исследуемого регистра, предположительно возможно объяснить распространенностью факторов риска повреждения почек, в частности тубулоинтерстициальной ткани. Так, согласно литературным данным, причиной ТИН могут быть не только лекарственные повреждения, инфекции или обструкция мочевых путей [44, 45], но и токсическое воздействие алкоголя [46–48], курения [49–51], избыточного потребления соли [53, 54], наличия ожирения [53,
56, 57], СД [58, 59] и ряд других факторов. Так, курение вызывает эндотелиальную дисфункцию [49], повреждение почек и фиброз, что сопровождается прогрессированием альбуминурии и нарушением функции почек [50, 51]. Курение ухудшает прогноз со стороны почек при сопутствующей артериальной гипертензии [52], а также в 3,59 раза повышает риск повреждения почек и развития протеинурии у людей, не имеющих факторов риска [52]. Негативное влияние злоупотребления алкоголем на функцию почек нарушает метаболические и обменные процессы в почках, что связано с повышенным риском развития ХБП [46, 47]. Так, потребление более двух алкогольных напитков в день было связано с повышенным риском почечной недостаточности среди населения в целом, у пациентов в группе злоупотребляющих алкоголем было больше множественных сопутствовавших заболеваний (p<0,001), повышена заболеваемость ХБП изначально (отношение рисков – ОР=1,62) и более высокая частота новой заболеваемости ХБП в течение периода наблюдения (ОР=1,68) [48]. Совместное воздействие курения и пьянства было связано почти с пятикратной вероятностью развития ХБП по сравнению с их отсутствием [20]. Наличие метаболического синдрома и ожирения также способствует повреждению почек, в конечном счете – к развитию и прогрессированию ХБП [56, 57]. Повышение индекса массы тела (ИМТ)≥25 кг/м2 способствует 3-кратному избыточному риску развития ХБП для людей с избыточной массой тела для ХБП по сравнению с лицами с ИМТ≤25, при этом риск терминальной ХПН составил 3,57 для людей с ожирением I степени, 6,12 – II степени и 7,07 – для лиц с сильным ожирением (ИМТ> или =40 кг/м2). [58]. Покольку указанные неблагоприятные факторы вызывают в т.ч. повреждение тубулоинтерстициального аппарата почек, они могли быть в числе возможных причин ТИН в регионе. Как уже отмечалось, распространенность указанных вредных факторов среди населения Республики Коми очень высока.
В динамике за исследуемый период наблюдается увеличение числа включенных в регистр пациентов с диагнозами ТИН, пиелонефрит, гломерулонефрит, а также существенно увеличилось число пациентов с впервые выявленной ХБП без определенной видимой причины. Нельзя исключить, что одной из возможных причин ухудшения функции почек у пациентов с ХБП без определенной нозологической формы могли послужить перечисленные выше вредные факторы.
При анализе лабораторных данных на момент включения пациентов в регистр выявлено, что снижение СКФ влечет за собой снижение уровня гемоглобина и повышение уровня фосфатов, мочевой кислоты, СОЭ, протеинурии, щелочной фосфатазы, калия, паратгормона. Данная закономерность ожидаема, т.к. она отражает естественную динамику развития уремических осложнений ХБП при ее прогрессировании.
Оценкой динамики изменения СКФ за период наблюдения у пациентов с 2 и более визитами установлено, что среднее снижение СКФ составило 3,99±2,7 мл/мин/1,73 м2 за год наблюдения. Скорость прогрессирования ХБП, установленная по данным настоящего регистра, была более высокой по сравнению с данными Санкт-Петербургского городского регистра, где она составила -3,71±0,20 и -2,89±0,24 мл/мин/1,73 м2 за год у мужчин и женщин соответственно [38]. При этом следует учесть, что в Санкт-Петербургский городской регистр включены все пациенты города, имевшие ХБП, в то время как в анализируемом регистре представлены в основном пациенты с более продвинутыми стадиями ХБП, нуждавшиеся в госпитализации, чем, возможно, и объясняются более ускоренные темпы прогрессирования ХБП у данных больных.
У 22% пациентов в динамике наблюдалось увеличение СКФ. Возможность улучшения показателя СКФ за время наблюдения у пациентов с ХБП выявлена также и в других наблюдательных регистрах [38, 60]. Пациенты с улучшением функции почек за время наблюдения отличались более высоким уровнем СКФ (39,3±20,5 мл/мин/1,73 м2) и менее выраженными сдвигами в лабораторных показателях, характеризующих ХБП. Это свидетельствует о том, что пациенты с ХБП 1–3-й стадии имеют потенциальную возможность улучшения функции почек, чего, к сожалению, не приходится ожидать у пациентов с 4-й и 5-й стадиями ХБП. Полученные результаты соответствуют литературным данным, согласно которым регресс ХБП встречается примерно у четверти пациентов, госпитализированных в нефрологические отделения, и коррелирует с низкой протеинурией и АД. Это состояние предвещает лучший прогноз, в основном на ранних стадиях ХБП, без избыточного риска смертности [60]. Наше исследование показывает, что чем ниже уровень СКФ, соответственно, хуже показатели, характеризующие состояние уремической интоксикации (анемия, гиперфосфатемия, протеинурия, гиперкалиемия, азотемия), тем выше темпы прогрессирования ХБП. Темп снижения СКФ значительно ускоряется при увеличении стадии ХБП и составляет на 3-й стадии 0,13 мл/ мин/1,73 м2 в год, а на 4-й и 5-й стадиях 5,2 и 6,8 мл/мин/1,73 м2 в год соответственно. По данным настоящего исследования, темпы прогрессирования ХБП были выше, чем в аналогичных регистрах, где они составили -3,35±4,45 мл/мин/год у больных ХБП 4-й и 5-й стадий [61]. Ускорение темпов прогрессирования ХБП на 4-й и 5-й стадиях продемонстрировано и другими авторами на большей когорте больных (n=3682), показано, что на стадии 3a пациенты проводят в среднем 7,9 года (от 2,3 до >12 лет), на 5-й – до 0,8 года (0,3–1,6) [62]. Полученные нами данные совпадают с результатами других наблюдательных исследований [61, 63, 64]. Кроме того, в аналогичных исследованиях установлена связь темпов снижения СКФ с низким уровнем альбумина, дефицитом железа [38], полиморбидностью пациента [63], уровнем систолического АД, применением двойной блокады ренин-ангиотензиновой системы, курением, наличием сердечной недостаточности [64, 66], диабета, с принадлежностью к мужскому полу [66–68]. По данным литературы, пожилой возраст был связан с более медленным прогрессированием ХБП на поздних стадиях [69]. В нашем исследовании эти факторы не учитывались или не показали значимых результатов.
Все пациенты получали адекватную нефропротективную медикаментозную терапию: ИАПФ, антагонисты кальциевых каналов, статины, β-адреноблокаторы, дезагреганты. Полученные данные совпадают с результатами аналогичных исследований, указывающими на частое назначение ингибиторов АПФ, β-адреноблокаторов и ацетилсалициловой кислоты при лечении сопутствующих сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний у пациентов с ХБП. Сообщается, что нефропротективная терапия позволяет увеличивать длительность додиализного периода на 1,5–2,0 года при условии снижения систолического АД на 5 мм рт.ст. и протеинурии на 0,3 г/сут. [69]. В то же время исследования показывают, что только 61,3% больных ХБП привержены режимам лечения. Предикторы несоблюдения: ХБП 4-й и 5-й стадий, низкий доход, увеличенное количество прописанных лекарств [70]. В нашем исследовании эти вопросы не исследовались. Получали диализ 8,8% пациентов в возрасте до 75 лет, в то время как в группе больных старше 75 лет – только 1,6%, что может быть оправданным. Так, результаты отдельных клинических наблюдений позволяют предположить, что диализ не обеспечивает выживания для пожилых людей с низкой подвижностью и высоким уровнем сопутствующей патологии [71]. Консервативная помощь как вариант лечения для пациентов с ХБП стадии 5 в возрасте 75 лет и старше хорошо известна и реализуется во многих странах [72]. Система междисциплинарной помощи может снижать частоту сердечно-сосудистых исходов и терминальной ХБП у пациентов с ХБП на 64% [73].
Таким образом, по результатам анализа регистра больных ХБП в регионе с высоким уровнем распространения вредных факторов среди населения выявлены некоторые особенности течения заболевания. Они включают более молодой средний возраст пациентов, значительную долю ТИН в структуре причин ХБП, а также более ускоренное прогрессирование ХБП, особенно на продвинутых стадиях. Для более детальной интерпретации полученных данных требуются дальнейшие исследования.
Ограничения
Результаты анализа настоящего регистра имеют ограничения, связанные с тем, что в регистре представлены пациенты, госпитализированные в отделение нефрологии, имевшие ХБП 3–5-й стадий, поэтому состав стадий ХБП может не отражать популяционные данные, т.к. в больницу попадают более тяжелые пациенты. По той же причине в указанном регистре пациенты не имеют большого числа визитов. Относительно небольшое число пациентов, прошедших повторное обследование, не позволило с точностью выявить факторы, способствующие прогрессированию или замедлению нарастания стадии ХБП.
Заключение
Полученные результаты позволили выявить региональные особенности течения ХБП в популяции пациентов отделения нефрологии в Республике Коми. Формирование регистра больных ХБП необходимо в настоящее время, поскольку позволяет знать реальное число больных и причины развития ХБП, оценивать темпы прогрессирования ХБП и выявлять модифицируемые факторы прогрессирования в конкретном регионе. Для выяснения причин региональных особенностей течения ХБП требуются дальнейшие исследования.

