Введение
Хронический пиелонефрит (ХПН) является одним из частых осложнений сахарного диабета, который характеризуется прогрессирующим гломерулосклерозом, сосудистым склерозом и тубулоинтерстициальным воспалением бактериального генеза в условиях патологической глюкозурии [1, 2]. Одна из ведущих ролей в его возникновении отводится токсическому влиянию на элементы нефрона гликированного гемоглобина (HbA1c), который является важным индексом состояния клеточного метаболизма не только на диабетическом, но и недиабетическом уровне, т.к. по своей повреждающей значимости занимает второе место после действия свободных радикалов [3]. Недавно установлено, что процессу гликирования подвержены все тканевые белки человека, включая клеточные структуры паренхимы почки [4]. Некоторые из гликированных белков в процессе межклеточных контактов в качестве медиаторов специфических взаимодействий могут формировать ковалентные связи (сшивки) и участвовать в процессах клеточной адгезии [4]. Биохимически связанные молекулы глюкозы обладают способностью самопроизвольно окисляться с выработкой липоперекисей, провоцирующих поражение мембранных фосфолипидов, и разрушением различных белковых структур клетки [5–11].
Канальцевая эритроцитурия (КЭ) является малоизученным морфологическим проявлением ХПН. В специальных электронно-микроскопических исследованиях показана возможность прохождения эритроцитов через неповрежденную базальную мембрану клубочковых капилляров [12]. Эритроциты, поступившие в канальцевую жидкость, связываются с белками Тамма–Хорсфолла и образуют мочевые цилиндры, содержащие как непосредственно эритроциты, так и продукты их деградации [13]. Поступая в почечные канальцы, гемоглобин адсорбируется клетками почечного эпителия, которые при этом слущиваются и удаляются током мочи [14]. Физиологическая целесообразность этого процесса и его возможная роль в нарушении структурно-функциональной состоятельности нефрона не совсем понятны и нуждаются в специальном углубленном исследовании [15–17].
У больных сахарным диабетом уровень гликемии более 7 ммоль/л считается «почечным порогом», выше которого избытки глюкозы выводятся с мочой. Не связанная с гипергликемией клинически значимая почечная глюкозурия может быть следствием редкого врожденного нарушения канальцевой реадсорбции – почечного диабета. Однако и у здоровых людей допустимым уровнем обнаружения глюкозы в моче считается показатель в 0,8 ммоль/л, хотя механизм этого явления и его возможная патогенетическая значимость также не совсем ясны [7, 8, 18].
Ранее проведенные и опубликованные нами работы в этом направлении показали, что в нефробиоптатах пациентов с различными нозологическими проявлениями хронической болезни почек, неотягощенных сахарным диабетом, в 18% случаев наблюдалась КЭ, совпадающая со слабовыраженной глюкозурией [19, 20]. Исходя из этого высказано предположение, согласно которому фиксированные в канальцах эритроциты и продукты из деградации могли оказаться одним из недиабетических предикторов микробно-воспалительного поражения нефрона.
Удобную модель для исследования этого вопроса представляют лабораторные и морфологические проявления первичного ХПН, который развивается в интактных почках без аномалии развития и нарушений уродинамики. Патологический процесс, как правило, имеет скрытое течение и случайно выявляется по результатам лабораторного исследования мочи [1, 2, 21].
Цель исследования: изучить лабораторные и морфологические проявления недиабетической глюкозурии, сочетанной с канальцевой эритроциурией, у пациентов с первичным ХПН.
Материал и методы
В рамках настоящей работы проведено исследование уровня глюкозы в сыворотке крови, недиабетической глюкозурии у 40 пациентов (20 мужчин и 20 женщин в возрасте 35–55 лет) с первичным ХПН, находившихся на лечении в отделении урологии ГБУЗ ТО «Областная клиническая больница № 2» в 2017–2021 гг. Группу сравнения составили 20 медицинских работников аналогичного возраста и пола, прошедших текущую диспансеризацию и признанных здоровыми (диспансерная группа Д1). Морфологические исследования состояния клубочкового аппарата и тубулоинтерстициальной зоны по результатам нефробиопсии проведены 20 пациентам с ХПН на базе патологоанатомического бюро ГАУЗ ТО МК МЦ «Медицинский город» (Тюмень). Препараты окрашивались эозин-токсилином и реактивом Шиффа с визуальным анализом при увеличении х20. Статистическая обработка полученных данных выполнена согласно международным требованиям, предъявляемым к обработке данных научных исследований, при помощи программы для персональных компьютеров Statistica for Windows (версия 11.5). Непрерывные переменные представлены в виде M±m (среднее±стандартная ошибка среднего). Достоверность выявленных различий оценивалась по t-критерию Стьюдента.
Результаты
Результаты сравнительного исследования проявлений глюкозурии, гликемии и мочевого синдрома у здоровых лиц и пациентов с первичным ХПН представлены в таблице.
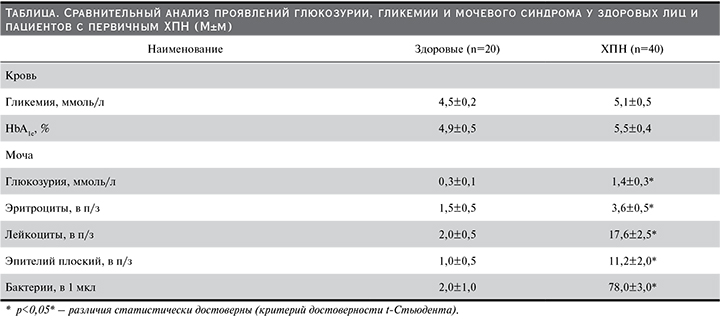
Из представленных данных видно, что уровень утренней гликемии и процентное содержание эритроцитов с HbA1c у пациентов с ХПН не имели статистических отличий от показателей здоровых лиц, наблюдалась только некоторая тенденция к их нарастанию. При стандартном компьютеризированном исследовании мочевого осадка здоровых лиц биохимический показатель глюкозурии число форменных элементов крови, эпителиальных и бактериальных клеток в моче не превышал общепринятых референтных показателей. У пациентов в стадии латентного течения первичного ХПН, проявлявшегося изолированным мочевым синдромом, наблюдалось статистически значимое увеличение в мочевом осадке клеточных и бактериальных включений, а также интенсивности глюкозурии, показатели которой при этом оставались в пределах допустимой нормы.
В качестве морфологического сравнения в изучении особенностей КЭ нами рассмотрены результаты исследования состояния клубочного аппарата и тубулоинтестициального пространства у пациентов с криптогенным сепсисом и септической нефропатией, в нефробиоптате которых часто обнаруживалось много кровяных телец как в мочевом пространстве клубочках, так и в просвете канальцев при минимальных изменениях элементов нефрона (рис. 1).

При анализе биопсийного материала пациентов с ХПН и изолированным мочевым синдромом кровяные тельца, а также продукты их распада визуализировались только в просвете дистальных канальцев (рис. 2).
Использование специальной окраски препаратов реактивом Шиффа у 11 (36,7%) пациентов с ХПН и изолированным мочевым синдромом позволило визуализировать ШИКпозитивные белковые цилиндры в просвете расширенных канальцев, эпителий которых был значительно истончен, что соответствовало картине выраженной атрофии элементов нефрона (рис. 3).
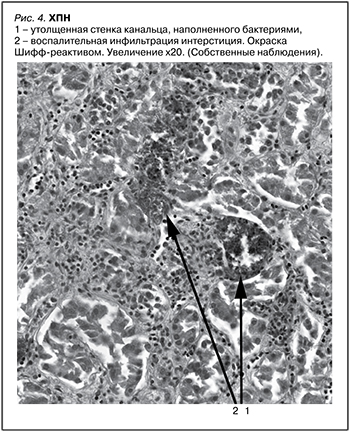
У 18 (63,3%) пациентов с изолированным мочевым синдромом на фоне ХПН в нефробипотатах обнаружено значительное утолщение стенок канальцев с большим скоплением бактерий в просвете и лимфоцитарно-лейкоцитарной инфильтрацией окружающего интерстиция (рис. 4).
Проведенное в рамках настоящей работы исследование показало, что уровень утренней гликемии и процентное содержание эритроцитов с HbA1c у здоровых людей и пациентов с ХПН не имели статистических различий. При этом нарастающая по интенсивности недиабетическая глюкозурия совпадала со статистически значимым увеличением клеточных и бактериальных включений мочевого осадка. В отличие от транзиторной канальцевой гематурии токсического генеза у пациентов с изолированным мочевым синдромом на фоне ХПН в нефробиоптах наряду с неизмененными кровяными тельцами в просвете дистальных канальцев наблюдалась фиксация выщелоченных эритроцитов и продуктов их деградации. Использование специальной окраски позволило в 36,7% наблюдений визуализировать ШИК-позитивные белковые цилиндры в просвете канальцев с выраженной атрофией их эпителия, и в 63,3% случаев имело место значительное утолщение стенок канальцев с большим скоплением в их просвете бактерий и лимфоцитарно-лейкоцитарной инфильтрацией окружающего интерстиция.
Заключение
ХПН с изолированным мочевым синдромом – одно из самых труднодиагностируемых проявлений микробно-воспалительной нефропатии. Патология протекает скрытно, а клиническая манифестация болезни знаменует необратимость начатого патологического процесса в почках, при этом КЭ в сочетании с недиабетической глюкозурией может оказаться одним из факторов, инициирующих формирование первичного ХПН.



