Введение
За последние годы отмечен рост распространенности хронической болезни почек (ХБП) с высоким риском сердечно-сосудистых осложнений (ССО), что является основной причиной смерти [1–3]. ССО при ХБП связаны с минерально-костными нарушениями (МКН-ХБП). В исследованиях показано влияние регуляторов кальцификации и минерально-костного обмена на формирование сердечно-сосудистой кальцификации (ССК) [4–7], выявлены противовоспалительные свойства препаратов, контролирующих МКН [8–10]. Роль провоспалительных цитокинов в развитии ССК активно изучается. Им принадлежит ключевая роль и в развитии воспаления, но и в прогрессировании ХБП [11, 12]. Активация процессов воспаления происходит параллельно со снижением функции почек. Значительное повышение уровней провоспалительных факторов наблюдается начиная уже с 3-й стадии ХБП. Установлено, что увеличение уровней интерлейкина-3 (ИЛ-3) и ИЛ-6 коррелирует со снижением скорости клубочковой фильтрации [13, 14]. Патогенетические механизмы формирования ССК с участием провоспалительных цитокинов, оценка риска развития требуют дальнейшего изучения.
Цель исследования: изучить участие провоспалительных цитокинов в формировании сердечно-сосудистой кальцификации, выявить взаимосвязь с риском его развития у больных ХБП, получающих заместительную почечную терапию (ЗПТ).
Материал и методы
Проведено одномоментное когортное исследование 85 больных ХБПС 5Д-стадии, которые получали лечение программным гемодиализом [15]. Средний возраст пациентов составил 56,6±14,9 года. Лечение гемодиализом продолжалось в среднем 11,7±6,9 года.
Всем пациентам проведены общеклинические исследования в соответствии с протоколом, а также определены уровни провоспалительных цитокинов: ИЛ-3 и -6 с помощью иммуноферментного анализа с применением наборов (Bioscience, Bender MedSystems).
Для комплексной оценки на основании значений уровней С-реактивного белка и альбумина крови рассчитан индекс риска системного воспаления по шкале Glasgow Prognostic Score (GPS). При значении шкалы GPS, равном 2, больного относили к группе высокого риска воспаления, при значении 1 – умеренного, при значении 0 – низкого риска [15]. Также рассчитан индекс сдвига лейкоцитов крови (ИСЛК), который в норме составляет 1,99±0,15 у.е. [16].
Наличие клапанной кальцификации определяли при эхокардиографии с применением допплеровского режима. Наличие кальцификации брюшного отдела аорты определяли при обзорной рентгенографии брюшной полости в левой боковой проекции с регистрацией кальцинатов в зоне I–IV поясничных позвонков, передней и задней стенки аорты. ССК разделена на кальцификацию стенки аорты (КСА), клапанов сердца (ККС), любую кальцификацию (КСА и/ или ККС) или содружественную кальцификацию клапанов сердца и аорты (КСА+ККС) [15]. Статистический анализ проводили с применением набора инструментов программы Statistica 12.6. Для оценки удельного веса наличия признака в группах и межгруппового сравнения использовали метод Пирсона с определением χ2-критерия. Влияние признаков на риск обнаружения другого проводили с применением однои двухфакторного логит-регрессионного анализа с определением критериев F и р [15].
Результаты
Средние значения уровней ИЛ-3, ИЛ-6, а также ИСЛК и GPS составили: ИЛ-6 – 60,9±13,1 пг/мл, ИЛ-3 – 33,6±10,6 пг/мл, ИСЛК – 1,8±0,98 к.е., GPS – 0,38±0,62 балла [15]. С целью выявления взаимосвязи уровней ИЛ-3 и -6, а также ИСЛК, GPS с формированием ССК и оценки риска его развития проведен логит-регрессионный анализ (табл. 1).
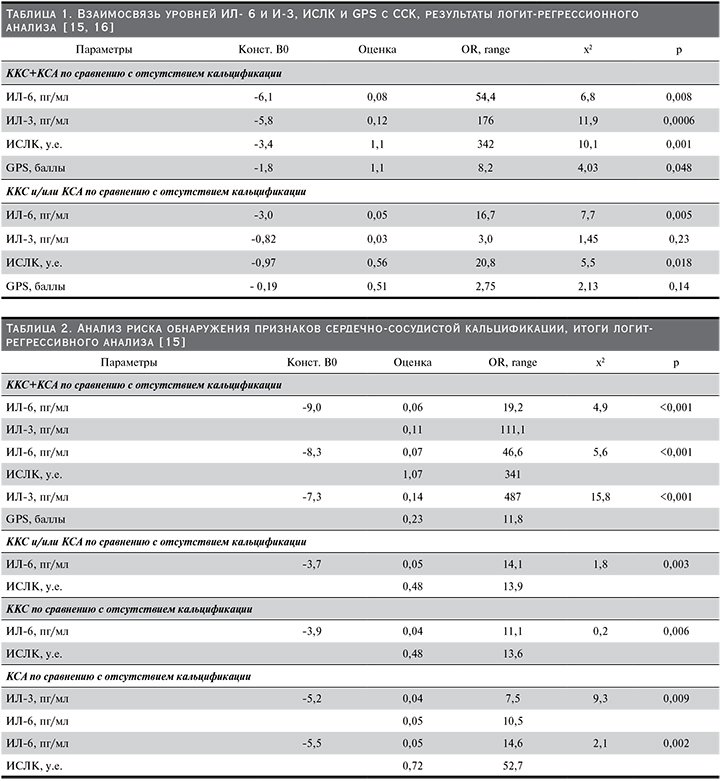
Установлена достоверная связь риска обнаружения кальцификации аорты и клапанов сердца (ККС+КСА) с уровнем ИЛ-3 и ИЛ-6 [15] (табл. 1). Выявлено, что при значениях ИЛ-6 более 55 пг/мл риск ККС+КСА возрастает и достигает максимума при значениях 80 пг/мл. По мере повышения уровня ИЛ-3 (более 35 пг/мл) также отмечено наиболее выраженное повышение риска содружественной кальцификации аорты и клапанов сердца. Прогностическая значимость ИЛ-3 снижается, а ИЛ-6 сохраняется при наличии какой-либо составной части кальцификации аорты и клапанов сердца: ККС или КСА [15,16]. Отмечено преодоление 20%-ного порога риска развития ССК уже при значениях ИЛ-6 более 33 пг/мл. Логит-регрессивный анализ также подтвердил связь ИСЛК с развитием как содружественной, так и изолированной кальцификации аорты или клапанов. Связь GPS установлена в отношении содружественной кальцификации [15, 16] (табл. 1).
Для достижения поставленной цели из числа выявленных статистически значимых параметров проведены расчеты с построением модели двуфакторного анализа (табл. 2).
Как видно из табл. 2, повышение значений ИЛ-3 и ИЛ-6, ИЛ-6 и ИСЛК, ИЛ-3 и GPS сопровождается повышением риска выявления содружественной ККС сердца и КСА.
Повышение значений ИЛ-6 и ИСЛК сопровождается повышением риска изолированной кальцификации – ККС или КСА, а повышение значений ИЛ-3 и ИЛ-6 – риска КСА [15]. Методом двуфакторного логит-регрессионного анализа проведен анализ оценки распределения ранговых признаков в подгруппах с определением распределения по методу Пирсон χ2 в отношении пар признаков [15]. Значения количественных признаков преобразованы в ранговые путем разделения их по медиане. Содружественное повышение значений признаков более медианы принималось за 1, снижение – за 0. Анализ проведен в группе повышенных значений уровней ИЛ-3 и ИЛ-6. Установлено, что кроме изолированной ККС все остальные виды кальцификации статистически значимо чаще встречались в группе больных с повышенными уровнями ИЛ-3 и ИЛ-6 (χ2-критерий=7,9, p=0,005; χ2-критерий= 4,3, p=0,039, χ2-критерий=2,53, p=0,11; χ2-критерий=7,8, p=0,006 соответственно) [15].
Обсуждение
Широкая распространенность ХБП и его осложнений делает актуальным дальнейшее изучение этой проблемы. Практическая значимость вопроса заключается в необходимости комплексной оценки сердечно-сосудистого риска [3]. Роль провоспалительных цитокинов в формировании ССК активно изучается. В результате проведенного исследования установлено повышение уровней ИЛ-3 и ИЛ-6, продемонстрирована отчетливая связь с развитием ССК у больных ХБП.
Провоспалительные цитокины – это большая группа белковых цитокинов, объединенная связью с лейкоцитами, участвующая в пролиферации и дифференцировке Bи T-клеток, а также в лейкопоэзе [17–19]. Во взаимосвязи с ИЛ-3 и ИЛ-6 показана статистическая значимость ИСЛК и GPS в прогнозировании риска ССК у диализируемых больных.
Заключение
ССК – сложный процесс, в реализации которого принимает участие много факторов, одним из которых является воспаление, возникающее за счет дисбаланса цитокинового статуса. Определение уровня провоспалительных цитокинов у больных ХБП актуально для выявления больных, угрожаемых по ССК, и определения терапевтической тактики.



