Сегодня в Кыргызской Республике эпидемиологическая ситуация по хронической болезни почек (ХБП) остается неблагоприятной, несмотря на тенденцию к снижению показателей заболеваемости и смертности от осложнений почечной недостаточности [1, 2]. Решение данной проблемы требует всевозрастающих финансовых затрат со стороны государства. Среди многообразия причин, приводящих к этой ситуации, лидирующие позиции занимает, как и прежде, рост идиопатических и вторичных гломерулопатий (ГП) [3]. Данная обстановка обусловлена различными факторами. В первую очередь это отсутствие полноценной профилактики и своевременной диагностики ГП. Большинство клиницистов верифицируют ГП, опираясь на клинико-лабораторные данные без нефробиопсии [4]. Однако эти результаты истинную картину патологического процесса в паренхиме почек отражают не полностью [5]. Известные клинико-морфологические исследования показали, что нефропатии сопровождаются повреждением не только гломерулярного аппарата, но и других отделов нефрона [6, 7]. Безусловно, внедрение нефробиопсии в клиническую практику значительно обогатило представление об особенностях патоморфоза ГП [4–9]. Нефробиопсия имеет решающее значение в тактике ведения больных ХБП [8]. При однотипной клинической картине ГП наблюдаются различные морфологические изменения в ренальной паренхиме, что определяет в дальнейшем лечение и прогноз заболеваний [9]. Благодаря этим данным в перспективе изменется трактовка течения и прогноза ХБП [8]. Однако в настоящее время в этой области остается много нерешенных вопросов. Работа над установлением четкой связи между клиническими данными и морфологическими проявлениями ГП в Кыргызской Республике далека от завершения.
Цель работы: изучить клинико-морфологическую характеристику ГП в Кыргызской Республике.
Материал и методы
В исследование были включены 245 больных, которым было выполнено исследование образцов почечной ткани, полученной путем прижизненной чрескожной биопсии. Скорость клубочковой фильтрации (рСКФ) рассчитывали по рCKD-EPI (2013), а стадии ХБП диагностированы согласно NKF K/DOQI (Guidelines, 2002) [10]. Для сравнительного анализа клинических особенностей течения ГП пациенты были разделены на две группы. В первую вошли 98 больных детского возраста, у них медиана возраста дебюта заболеваний оказалась равной 11,9 года (1,0–18,0). Вторая группа состояла из 147 взрослых больных ГП, медиана возраста – 35,7 года (18,1–70,0). Гендерное соотношение среди исследуемых пациентов: в детской группе преобладали девочки 1:1,4, во взрослой, наоборот, – мужчины 1,6:1. На момент исследования все больные получали стационарное лечение в специализированных нефрологических клинических отделениях. Всем пациентам проводился комплекс общеклинических, биохимических, иммунологических, инструментальных и морфологических исследований.
Гистопатологический анализ. При исследовании нефробиоптата использованы гистологический, иммунофлуоресцентный и электронномикроскопический методы. Для диагностики форм ГН использовали общепринятые морфологические критерии [10]. Заключение по изучению ткани из почек устанавливалось согласно единой терминологии при описании патологического процесса и морфологической классификации Международной классификации болезней 10-го пересмотра.
При морфологическом анализе гломерулярных изменений определялись размеры клубочка, наличие (степень) или отсутствие пролиферации мезангиальных клеток и эпителия капсулы, состояние мезангиального матрикса и структуры базальной мембраны (утолщение, неровность контуров, расщепление) клубочков. Алгоритм исследования биоптата почки включал также информацию об интерстициальной ткани (фиброз, отек, инфильтрация) и о наличии в канальцах атрофии, дистрофии, некрозов и спаек. Морфологические признаки активности процесса включали такие экссудативные процессы, как белковые выделения в просвете капсулы, полнокровие капилляров, плазморрагия, фиксация на базальной мембранах капилляров и в мезангиуме клубочков иммуноглобулинов, фракций комплемента, фибриногена и амилоида.
Результаты
В первой группе наблюдался 41 (41,8%) пациент с гематурией в сочетании с нефротической протеинурией, что явилось максимальным количеством от всех обследованных детей (табл. 1). На втором месте с одинаковой частотой встречались пациенты с нефритическим и нефротическим синдромами – 27 (27,5%) и 22 (22,4%) пациентов соответственно. Изолированный мочевой синдром выявлен лишь у 8 (8,16%) больных.
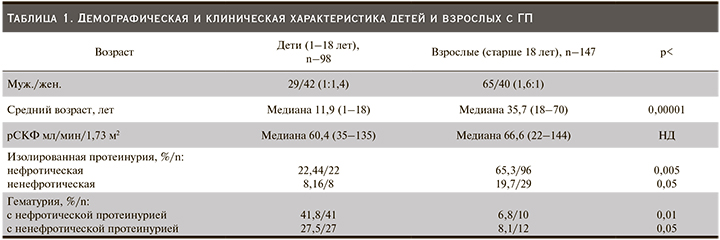
Во взрослой когорте чаще фиксировалась протеинурия нефротического уровня – 96 (65,3%) пациентов. Изолированный мочевой синдром отмечен у 30 (20,4%) больных. Следует подчеркнуть, что встречаемость всех клинических проявлений (протеинурия с и без гематурии) по сравнению с детьми различалась.
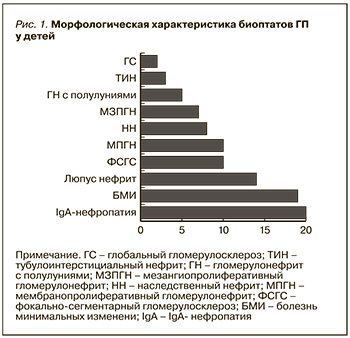 Всем 245 больным ГП было выполнено морфологическое исследование образцов почечной ткани, полученных путем прижизненной биопсии. Частоту обнаружения отдельных морфологических вариантов у пациентов с ГП сравнивали в двух группах. Наиболее распространенными вариантами поражения клубочков в детской группе были IgAН и болезнь минимальных изменений (БМИ), отмеченная у 20,4% и 19,3% пациентов соответственно. Следующими по частоте обнаружены люпус нефриты (ЛН) – 14,2%, фокально-сегментарный гломерулосклероз (ФСГС) и мембранопролиферативный гломерулонефрит (МПГН) по 10,2% соответственно. Среди других вариантов ГП почти с одинаковым удельным весом зафиксированы наследственный нефрит (НН) и мезангиопролиферативный гломерулонефрит (МЗПГН) – 8,16 и 7,14% соответственно (рис. 1).
Всем 245 больным ГП было выполнено морфологическое исследование образцов почечной ткани, полученных путем прижизненной биопсии. Частоту обнаружения отдельных морфологических вариантов у пациентов с ГП сравнивали в двух группах. Наиболее распространенными вариантами поражения клубочков в детской группе были IgAН и болезнь минимальных изменений (БМИ), отмеченная у 20,4% и 19,3% пациентов соответственно. Следующими по частоте обнаружены люпус нефриты (ЛН) – 14,2%, фокально-сегментарный гломерулосклероз (ФСГС) и мембранопролиферативный гломерулонефрит (МПГН) по 10,2% соответственно. Среди других вариантов ГП почти с одинаковым удельным весом зафиксированы наследственный нефрит (НН) и мезангиопролиферативный гломерулонефрит (МЗПГН) – 8,16 и 7,14% соответственно (рис. 1).
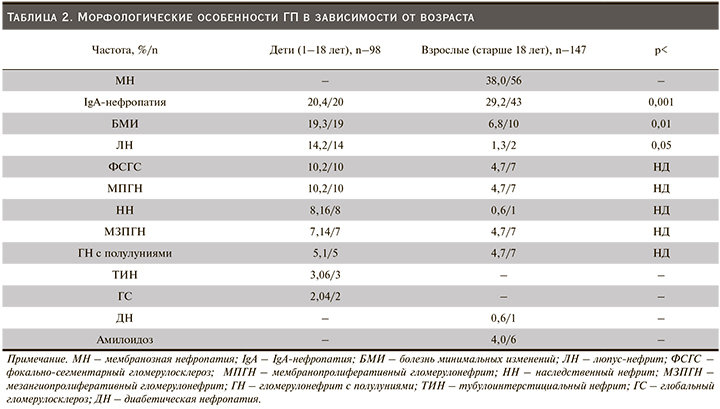
По сравнению с детьми взрослая когорта характеризовалась высокой распространенностью мембранозного нефрита (МН) – 38%, чуть менее – IgA-нефропатией, 29,2% случаев. Далее в порядке убывания частоты следовали БМИ – 6,8%, ФСГС, МЗПГН, МПГН, ГН с полулуниями – 4,7%, амилоидоз – 4,0% соответственно (рис. 2). В целом мы обнаружили значимую статистическую разницу в возрастных группах по определенным морфологическим формам ГП (табл. 2).
 Обсуждение
Обсуждение
ХБП является одним из неинфекционных заболеваний, приводящих к потере трудоспособности, высоким затратам на лечение и одной из причин смертности из-за кардиоваскулярных осложнений [11]. Следовательно, раннее выявление заболевания почек и проведение соответствующей терапии должны рассматриваться как инструмент, необходимый для снижения риска развития осложнений ХБП. Изучение встречаемости морфологических вариантов ГП служит ключевым элементом планирования диагностики и успешного лечения. Сложность почечного повреждения у лиц с ГП обычно смазывает клиническую картину. Без нефробиопсии установление правильного диагноза невозможно [12–14]. Не существует возрастных ограничений для нефробиопсии. Bomback et al. предложили проводить нефробиопсию всем, у кого есть хотя бы два из следующих показателей: гематурия, протеинурия ≥1 г/сут, снижение СКФ и/или положительная серология для системных заболеваний [15]. Такая стратегия предусматривает разработку правильного подхода к ведению пациента. У изученных нами пациентов наиболее частым клиническим проявлением ХБП был нефротический синдром (68,3%) с гематурией или без нее (21,5 и 46,8% соответственно), что соответствовало наблюдениям других исследователей [16–19]. Ряд исследователей считают, что даже острое почечное повреждение (ОПП) служит ведущим показанием к проведению биопсии нативной почки [20].
Наше исследование охватывает период с 2015 по 2019 г., клинические данные были предоставлены двумя нефрологическими отделениями. Описания течения болезни были единымии достаточно точными в разделении ОПП, ОПП при ХБП и ХБП.
Проанализировав частоту морфологических видов ГП, мы обнаружили, что спектр заболеваний, затронувших детей, почти такой же, как и у взрослого населения. Однако имелись и некоторые четкие различия в частоте определенных нефропатий между этими возрастными группами. Например, в нашем исследовании с высокой частотой у взрослых выявлялась МН – 56 (38%), чего мы не наблюдали у детей. Эти данные согласуются с другими сообщениями [20–24]. Патологическая картина гломерулярных изменений была представлена диффузным утолщением базальных мембран капилляров клубочков. При иммунофлуоресцентном исследовании на базальной мембране выявлены иммунные комплексы, содержащие IgG-, M- и С3-фракцию комплемента, фибрин. При этом наиболее часто обнаруживали гранулярное распределение иммуноглобулинов, реже линейного типа. Клинически МН представлен в виде нефротического синдрома (табл. 3). Гистологическая верификация МН обеспечило важное обоснование применения иммуносупрессивной или биологической терапии.
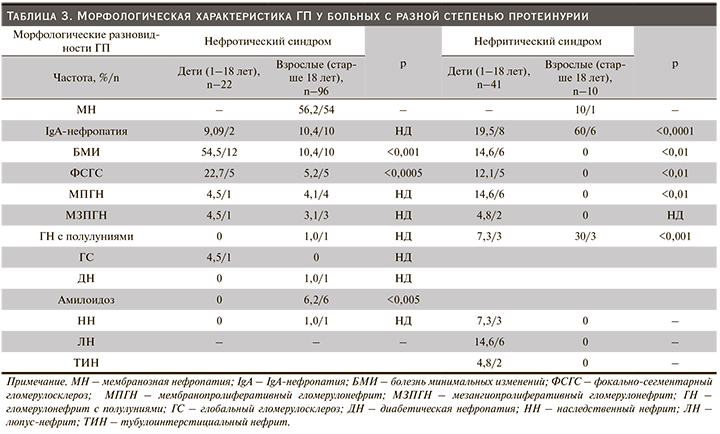
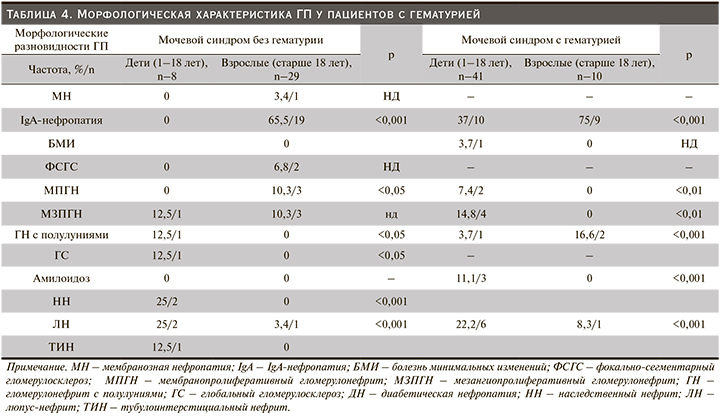
В нашем реестре IgA-нефропатия признана наиболее выявляемым гистологическим диагнозом у детей (20,4%). В то же время у взрослой когорты данная патология была на втором месте по частоте встречаемости 43 (29,2%). По данным литературного анализа, распространенность упомянутого варианта варьируется по всему миру, чаще всего встречается у жителей Азии – в 30–40% случаев. В Японии примерно треть всех пациентов, которым проведена нефробиопсия, имели диагноз IgA-нефропатии [25–27]. Обнаруженные нами особенности частоты отдельных клинических характеристик согласуются с данными аналогичных исследований из стран Европы и Азии [25, 28]. Большинство наших обследуемых (35%) с IgA-нефропатией имели гематурию с незначительной протеинурией, а нефротический синдром был диагностирован лишь у 10,4 взрослых и у 9,02% детей соответственно (табл. 3, 4). Идентификация по четырем гистологическим признакам MEST по Оксфордской классификации производилась всем. Морфологически IgA-нефропатия неоднородна. При гистологическом исследовании почечных биоптатов в клубочках выявлены незначительные изменения мезангиума – 2 (3,1%), очаговая или диффузная пролиферация мезангиальных клеток – 43 (67,1%), ФСГС – 13 (20,3%), а также ГН с полулуниями – 6 (9,3%). Структура отложений IgA при иммуногистохимическом исследовании в большинстве случаев была гранулярной (+++).
БМИ служит основной причиной идиопатического нефротического синдрома в детской популяции. Исследования в США показали, что в возрасте от 2 до 8 лет 90% детей с нефротическим синдромом имели БМИ. В нашей работе БМИ у детей встречалась чуть реже (19,3%), чем IgAН. Это объясняется тем, что процедура нефробиопсии производилась избирательно – только детям со стероидрезистентным нефротическим синдромом. Согласно педиатрической практике, если нефротический синдром отвечал на пероральную кортикостеродную терапию в рекомендуемых дозах, идентификации морфологии не требовалось. Следовательно, эти стероидчувствительные случаи можно было считать как БМИ. Некоторые авторы утверждают, что эта болезнь несколько чаще встречается в Азии, преимущественно болеют мальчики (приблизительно 2:1) [29, 30]. Что касается взрослых, данная патология имела место у 6,4%. Клинически БМИ проявилась классическим нефротическим синдромом как у детей, так и у взрослых. Диагностическим критерием БМИ стали изменения, выявленные с помощью электронной микроскопии, где патология подоцитов и эндотелия выявлялась при интактной базальной мембране капилляров клубочков, а также в отсутствие Ig и комплемента.
Морфологическая картина ЛН мало чем отличается от таковой при других ГП. Принципиальным отличием в этих наблюдениях считается специфическая находка – наличие иммунных депозитов различного вида на субэндотелиальной и субэпителиальной сторонах базальных мембран капилляров, реже в мезангиуме. Частота поражений почек при системной красной волчанке (СКВ), по данным различных авторов, колеблется в пределах от 2,9 до 38% [31–33]. Приведенные цифры со всей определенностью указывают на значимое влияние нефрита на течение СКВ. По результатам пункционной биопсии, среди исследованных нами пациентов частота ЛН составила 14,2 у детей и 1,3% у взрослых. Низкая частота встречаемости ЛН у взрослых объясняется тем, что биопсия больным СКВ производилась редко.
ФСГС – гетерогенная группа гломерулярных поражений, вошла в пятерку лидирующих патологий ГП, который диагностировался у 10,2 детей и у 4,7% взрослых. В подавляющем большинстве изученных нами случаев морфологические и клинические признаки свидетельствовали о вторичной природе гломерулярного склероза. Клинически в этих наблюдениях превалировал нефротический синдром (табл. 3). Подобные изменения описывают в своих работах и другие авторы [34].
МПГН характеризуется гиперплазией мезангиума и интерпозицией его в базальную мембрану. Опираясь на перекликающиеся данные наших исследований и мировой литературы, можно с уверенностью сделать заключение, согласно которому МПГН статистически является наименее распространенным видом ГП. На его долю приходится примерно 10,2 и 4,7% у детей и взрослых соответственно [35]. В нашей работе мы указываем на то, что МПГН обнаруживался у детей в 10,2 и взрослых 4,7%.
Следующим по частоте вариантом ГП является МЗПГН. Гистологически группа характеризуется диффузной пролиферацией преимущественно мезангиальных клеток, увеличением мезангиального матрикса, неравномерным утолщением стенок капилляров. По данным пункционной биопсии почек, частота выявления МЗПГН составила 7,14% в детской и 4,7% во взрослой группах. Эти показатели схожи со сведениями из регистров других стран. МЗПГН без IgA не редкость и очень часто демонстрируется во многих исследованиях [36–38]. Подобные результаты были получены в Южной Индии, где МЗПГН без IgA составил 11,3 и 7,3% всех подтвержденных биопсией ГП у детей и взрослых соответственно [38].
Системный амилоидоз – нередкое заболевание. Частота амилоидоза почек среди амилоидоза внутренних органов занимает одно из первых мест. У больных молодого возраста амилоидоз встречается изредка. Так, Agnieszka Perkowska-Ptasinska et al., изучив биоптаты нативной почки в группе пациентов в возрасте от 18 до 64 лет, диагностировали амилоидоз в 3,2% случаев из 9394 пациентов [39]. У больных старше 65 лет амилоидоз верифицирован у 12,8% [31, 40, 41]. В последние годы отмечается некоторое учащение случаев обнаружения амилоидоза, что связано с рядом причин. Одна из них – улучшение диагностики в связи с внедрением в клиническую практику пункционной биопсии почки. В нашей работе приведено 6 (4%) случаев амилоидоза почек во взрослой группе, наиболее частой клинической картиной которого был нефротический синдром. Полученные результаты подтверждают данные, согласно которым с возрастом частота встречаемости амилоидоза увеличивается.
Диабетическая нефропатия (ДН) – наиболее значимое осложнение сахарного диабета, который определяет его прогноз. Приведенные цифры Национального норвежского регистра диабета у детей свидетельствуют о возрастающей частоте развития терминальной почечной недостаточности: 0,7% – при длительности заболевания 20 лет, 2,9% – 30 лет, 5,3% – 40 лет соответственно [42]. Начало изучения морфологии ДН положила начало новому витку нефробиопсии [43, 44]. В Европе частота морфологически верифицированных ДН составила 17,5% среди других ГП [36–38]. В нашей работе ДН была выявлена только у 1 (0,6%) пациента. У двух обследуемых с сахарным диабетом диагностированы другие виды ГП, что позволило исключить ДН.
На сегодня существует много эпидемиологических реестров с расширенными клинико-морфологическими анализами. Результаты исследования нефробиопсии 245 пациентов (2015–2019) легли в основу создания регистра почечных биопсий Кыргызской Республики. Малое количество биоптатов обусловлено нежеланием пациентов подвергаться нефробиопсии.
Выводы
Наш анализ подтвердил различия в распространенности некоторых заболеваний почек у детей и взрослых лиц. Основным клиническим проявлением у пациентов, перенесших биопсию почки, была протеинурия, чаще всего нефротического уровня. Полученные сведения о характере морфологических изменений, по данным нефробиопсии при ГП, почти схожи с таковыми в других работах.
Однако все-таки следует отметить, что встречаемость морфологических видов ГП у жителей Средней Азии имеет свои особенности. Относительно высокая распространенность потенциально излечимых заболеваний почек у больных указывает на важность нефробиопсии.



