Введение
Во всем мире наблюдается стремительный рост заболеваемости сахарным диабетом (СД). Самым опасным осложнением СД является диабетическая нефропатия (ДН), приводящая к развитию хронической почечной недостаточности (ХПН) и являющаяся одной из основных причин инвалидности и смертности данной категории больных [1]. В связи с этим раннее выявление нефропатии на этапе потенциально обратимых изменений в почках приобретает особую актуальность. Традиционно основной патологический процесс в почках определяют по концентрации креатинина в сыворотке крови, скорости клубочковой фильтрации (СКФ) и микро/ макроальбуминурии (МАУ) [2].
Однако, как показали морфологические исследования почек, изменения, характерные для СД, в их ткани уже выявляются у пациентов с нормальной экскрецией альбумина с мочой.
В дальнейшем оказалось, что появление МАУ свидетельствует о наличии склероза не менее чем у 20–25% нефронов, а прогрессирование до стадии протеинурии (ПУ) – о потере 50–70% клубочков [3].
Результатом активного поиска среди методов ранней диагностики повреждения почек стал мочевой биомаркер подоцитарной дисфункции нефрин, способный выявлять это повреждение раньше, чем традиционные показатели.
Нефрин – трансмембранный белок подоцитов с м.м. 160 кДА, продукт гена NPHS1, является основным структурным белком щелевой фильтрационной диафрагмы, относящийся к адгезивным белкам суперсемейства иммуноглобулинов [4, 5]. Он непосредственно участвует в формировании почечного фильтра. При повреждении почек возникает его усиленная экскреция с мочой.
Уточнение механизмов повреждения подоцитов при СД, их связи с метаболическими и гемодинамическими нарушениями, поиск биомаркеров, отражающих выраженность дисфункции подоцитов, в настоящее время являются предметом пристального внимания диабетологов и нефрологов. И если в немногочисленных исследованиях [4, 5] достоверно показана значимость нефрина для диагностики патологии почек в целом, то его роль с позиции ранней диагностики остается малоизученной.
Цель исследования: определить величину экскреции с мочой нефрина и уточнить его значение как раннего маркера повреждения почек при СД 2 типа (СД2).
Материал и методы
В исследование включены 97 пациентов (34 мужчины и 63 женщины) с СД2, находившихся на лечении в нейроэндокринологическом отделении Нижегородской областной клинической больницы им. Н.А. Семашко. Проведение исследования одобрено локальным этическим комитетом Нижегородской региональной медицинской ассоциации. Средний возраст больных составил 56 [51,7; 64] лет. По данным анамнеза, средняя длительность СД2 – 7,6 [1,5; 8,9] года, включая впервые выявленный СД2 у 30 пациентов. Диагноз СД2 установлен согласно Национальным стандартам по диагностике и лечению СД [6].
Всем больным были проведены клиническое и лабораторно-инструментальное обследования. Содержание гликозилированного гемоглобина (HbA1c) исследовали на анализаторе Д-10 производства Bio-Rad со стандартными наборами (France). Уровень креатинина определяли в плазме венозной крови по методу, основанному на реакции Яффе, с использованием диагностических систем ООО «Ольвекс Диагностикум», Санкт-Петербург (Россия), мочевины – с помощью диагностического набора «Диаком Н» на анализаторе «Статсфакс». СКФ рассчитывалась с помощью формул Cockcroft-Gault, стандартизированная на поверхность тела, MDRD (Modifi cation of Diet in Renal Disease) и уравнения CKD-EPI [6–8].
Для верификации диагноза диабетической нефропатии (ДН) исследовалась утренняя моча на МАУ турбометрическим методом на автоматическом анализаторе «Chem Well» с использованием диагностического набора «Microalbumin», США. Нормальным считался показатель ниже 30 мг/сут. Как МАУ нами расценивались результаты от 30 до 300 мг/сут [6, 9–12]. В случае превышения величины МАУ определяли содержание белка в суточной моче.
Согласно цели исследования, всем пациентам определяли нефрин в асептически собранной утренней порции мочи (средняя струя). Полученные образцы мочи центрифугировали 10 минут при 3000 об/мин с последующим немедленным анализом иммуноферментным способом в микропланшетном формате на автоматическом приборе EVOLIS Twin Plus BioRad (Франция). Иммуноферментный анализ (ИФА) включал следующие стадии: 1) образование иммунного комплекса; 2) стадия формирования связи конъюгата с иммунным комплексом или со свободными местами связывания; 3) стадия превращения ферментной метки в регистрируемый сигнал. Результаты ИФА регистрировали с помощью спектрофотометра, измеряя оптическую плотность в двухволновом режиме: основной фильтр – 450 нм, референс-фильтр – в диапазоне 620–650 нм. Допустимая регистрация результатов только с фильтром 450 нм [4]. Нормальные значения нефрина в моче – 0,118–20 нг/мл. Статистическая обработка результатов исследования проводилась с помощью Statistica 7.0. При анализе данных использованы методы непараметрической статистики, с выражением результатов в виде медианы, 25-го и 75-го перцентилей (Ме [25р; 75р]).
Достоверность отличий независимых групп по каждому признаку определили методом ANOVA по Краскелу– Уоллису. Анализ корреляционных взаимоотношений между исследуемыми показателями осуществлен с помощью критерия Спирмена с обязательным визуальным контролем диаграмм рассеяния и исключением выбросов. Различия считались достоверными при значениях р<0,05.
Результаты и их обсуждение
Согласно современным данным, клубочковый барьер состоит из трех слоев: сосудистого эндотелия, гломерулярной базальной мембраны и щелевой диафрагмы, расположенной между ножками подоцита. Если раньше основное значение в происхождении протеинурии придавалось состоянию базальных мембран клубочковых капилляров, то в последнее время становится все более очевидной роль белков подоцитов [2–4]. Заболевания клубочков сейчас признаны в большинстве случаев как патология подоцитов и частично вызваны изменением генов подоцитарных белков.
Щелевая диафрагма, играющая важную роль в поддержании структуры и функционирования фильтрационного барьера, представляет собой специализированный межклеточный контакт между соседними ножками подоцитов. Она состоит из сложного мультибелкового сигнального комплекса, который динамически контролирует архитектуру подоцитарной ножки посредством передачи сигнала на актин цитоскелета. Сигнальный комплекс щелевой диафрагмы содержит структурные белки, рецепторы, сигнальные адаптеры, ионные каналы и вспомогательные поддерживающие белки.
Кроме адекватного функционирования фильтрационного барьера комплекс необходим также для регуляции ряда биологических функций подоцита (организации цитоскелета, эндоцитоза, дифференцировки и подавления пролиферации, жизнеспособность подоцитов).
Нефрин, белок с м.м. 160 кДА, продукт гена NPHS1, является основным структурным белком щелевой фильтрационной диафрагмы и относится к адгезивным белкам суперсемейства иммуноглобулинов. Нарушения в структуре как самого нефрина, так и ассоциированного с ним белкового комплекса приводят к нарушениям архитектоники подоцитов, сглаживанию отростков ножек подоцитов и протеинурии [4].
По данным литературы, определение нефрина в моче при хроническом гломерулонефрите в качестве маркера подоцитарной дисфункции позволяет не только оценивать ее тяжесть, но и судить об активности заболевания, прогнозе эффекта иммуносупрессивной терапии [2, 3]. По данным нашего исследования, нефринурия присутствовала у 100% больных СД2 с микро- и МАУ, а также у пациентов с нормоальбуминурией. Клинико-лабораторные данные пациентов в зависимости от стадии ДН представлены в таблице. Следует подчеркнуть, что все пациенты были сопоставимыми по исходному уровню HbA1c и индексу массы тела (ИМТ).
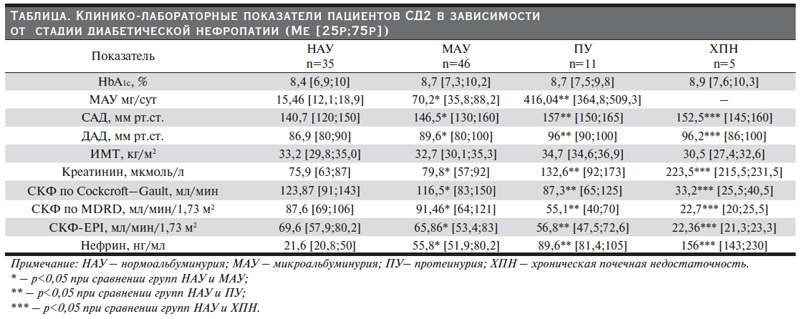
Статистически достоверные различия между группами пациентов с документированной ДН и нормоальбуминурией были достигнуты по следующим показателям: нефрину, суточной экскреции микроальбумина, содержанию мочевины, креатинина и СКФ (р<0,05). Группы также имели статистически значимую разницу по САД и ДАД, что еще раз подтверждает тот факт, что артериальная гипертензия является одним из ведущих факторов прогрессирования ДН [9, 11, 12].
Согласно цели настоящего исследования, мы попытались выявить зависимость между уровнем нефрина и другими лабораторными показателями. Были отмечены следующие статистически значимые положительные корреляционные связи с МАУ (r=0,72, р=0,001), HbA1c (r=0,54, р=0,001), креатинином (r=0,42, р=0,003), САД (r=0,56, р=0,002), ДАД (r=0,23, р=0,005) и СКФ (r=-0,42, р= 0,001).
Не установлено связей между нефрином и возрастом пациентов (r=0,18, р=0,05), ИМТ (r=0,11, р= 0,05).
Таким образом, нефринурия при ДН коррелирует с альбуминурией, уровнем креатинина, HbA1c, артериальным давлением и СКФ. При этом экскреция нефрина при СД увеличена еще до наличия альбуминурии и снижения СКФ, что имеет преимущество для раннего обнаружения повреждения почек у данной категории больных.
Заключение
Нефрин у больных СД2 в качестве биомаркера подоцитарной дисфункции является одним из ранних признаков повреждения почек. Экскреция с мочой нефрина при СД2 предшествует появлению альбуминурии, повышению уровня креатинина крови и снижению СКФ. Оценка уровня нефринурии способствует ранней диагностике ДН и своевременному назначению нефропротективной терапии.



