Введение
Экспертами KDIGO предложено определение острой болезни почек (ОБП) – «острое почечное расстройство» (AKD – acute kidney diseases and disorders) – для ситуаций, которые не соответствуют критериям ни хронической болезни почек (ХБП), ни острого повреждения почек (ОПП). При этом ОБП включает и ОПП [1]. По мнению А.В. Смирнова и соавт. (2016), если учесть, что диагноз ОБП в т.ч. может быть обоснован только по уровню маркеров структурного повреждения (без изменений уровня сывороточного креатинина [сКр] или скорости клубочковой фильтрации [СКФ]), то концепция острой патологии почек обретает необходимую стройность [2, 3].
В последнее время все большее внимание уделяется липокалину, ассоциированному с желатиназой нейтрофилов (NGAL – Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipoca-lin), который рассматривается в качестве информативного биомаркера ОПП и ХБП [2, 4]. NGAL может быть полезным в диагностике как наиболее ранний маркер структурного (тубулярного) повреждения.
В результате анализа объединенных данных от 2322 критически больных пациентов (с преимущественно кардиоренальным синдромом) из 10 проспективных обсервационных исследований показано, что пациенты с повышенным уровнем NGAL (в крови и моче), но без диагностического повышения уровня сКр имели вероятное субклиническое ОПП.
У этих больных был отмечен повышенный риск неблагоприятных исходов, кроме этого они длительнее находились в отделении интенсивной терапии и стационаре. В связи с этим авторы указали, что концепция ОПП, возможно, нуждается в пересмотре [5]. Позднее в небольшом отечественном исследовании больных артериальной гипертензией авторы также указали на возможность выявления пациентов с вероятным субклиническим ОПП по уровню NGAL (в крови) [6].
ОПП – частое осложнение острого коронарного синдрома (ОКС) (инфаркта миокарда – ИМ), и, по данным ряда авторов, его частота составляет 9–55% [7]. При этом ОПП ухудшает течение сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний, в т.ч. ИМ, и увеличивает летальность в госпитальном и отдаленном периодах (1, 3, 5 и 10 лет после ИМ) [8, 9].
Цель: оценить функциональное состояние почек и значимость уровней NGAL в качестве маркера субклинического повреждения почек у больных ОКС.
Материал и методы
Обследованы 111 больных (80 мужчин и 31 женщина, средний возраст – 59,5±10 лет), экстренно госпитализированных в городские стационары с инвазивной и неинвазивной стратегией лечения с диагнозом ОКС с подъемом сегмента ST (ОКСпST) у 58 (52,3%) и без подъема сегмента ST (ОКСбпST) у 53 (47,7%) больных.
В период госпитализации у 82 (73,9%) больных диагностирован ИМ, у 29 (26,1%) – нестабильная стенокардия (НС). Заболевания почек (пиелонефрит, мочекаменная болезнь, кисты) имели 28 (25,2%) пациентов. Диагноз ОКС и ОПП установлен в соответствии с национальными рекомендациями. В исследование не включили лиц старше 75 лет, а также имевших тяжелую сопутствующую патологию. Контраст-индуцированная нефропатия выявлена у 1 пациента с ОКС (не включен в последующий анализ). 41 (69,5%) больному ОКСпST проведена тромболитическая терапия (ТЛТ); 18 (30,5%) пациентам ТЛТ не проводилась ввиду поздней доставки в стационар; 26 (63,4%) больным ТЛТ выполнена на догоспитальном и 15 (36,6%) – госпитальном этапе.
При этом 39 (66,1%) больным ОКС было проведено чрескожное коронарное вмешательство (ЧКВ) (коронарная баллонная ангиопластика и/или стентирование) 28 (71,8%) пациентам – в остром, 11 (28,2%) – в подостром периоде. При этом первичное ЧКВ выполнено лишь у 4 (6,9%) пациентов, вторичное – у 25 (43,1%) больных ОКСпST.
Медикаментозное лечение больных в стационаре проводили в соответствии с действующими рекомендациями в стандартных дозировках с учетом имеющейся коморбидной патологии. Почти все больные ОКС получали аспирин (у 1 пациента был противопоказан ввиду обострения язвенной болезни желудка). Более 90% пациентов ОКС получали низкомолекулярный гепарин (эноксапарин, фраксипарин), блокаторы P2Y12 рецепторов тромбоцитов (клопидогрель – 81,4%, тикагрелор – 8,9%), β-адреноблокаторы (метопролол, бисопролол) и статины (симвастатин, аторвастатин). 88,5% больных ОКС получали двойную антитромбоцитарную терапию. Более 2/3 больных получали ингибиторы АПФ (каптоприл, эналоприл, рамиприл, лизиноприл), нитраты (нитроглицерин, изосорбида моно- и динитрат) и несколько реже назначали нефракционированный гепарин (72,6%) (сначала внутривенно болюсно 60–70 МЕ/кг (не более 5000 МЕ) с дальнейшей инфузией со скоростью 12–15 МЕ/кг/ч (не более 1000 ЕД/ч). Частота назначения блокаторов гликопротеиновых рецепторов IIb/IIIа тромбоцитов (эптифибатид, руциромаб), блокаторов рецепторов к ангиотензину II (валсартан, лозартан) и антагонистов минералокортикоидных рецепторов (спиронолактон) составляла менее 10%. По показаниям пациентам ОКС назначали диуретики (фуросемид, торасемид, индапамид) (26,5%).
У всех пациентов в 1–3-й день госпитализации (до проведения селективной коронарографии) определено содержание NGAL в крови (s-NGAL) и моче (u-NGAL) в нг/мл иммуноферментным методом (Human Lipocalin-2/NGAL Quantikine ELISA, R&D Systems, США). В те же сроки в крови определена концентрация сКр (мкмоль/л) колориметрическим методом (кинетика). Наличие и уровень альбуминурии (n=79) определены в суточной моче иммунотурбидиметрическим методом в отсутствие белка в общем анализе мочи. Уровни отсечения (верхние границы референсных значений), указанные в инструкции фирмой производителем реактивов, для s-NGAL и u-NGAL составили 177 и 72 нг/мл соответственно; нормальное содержание сКр составило у мужчин 64–104, у женщин – 49–90 мкмоль/л. СКФ рассчитана по формуле CKD-EPI (2009, модификация 2011). Клиренс креатинина (КлКр) рассчитан по формуле Кокрофта–Голта (1976).
Все пациенты с ОКС (n=111) в нашей выборке были разделены на 4 подгруппы по величине NGAL (s-NGAL и u-NGAL) и сКр: 1) NGAL-/сКр-; 2) NGAL-/сКр+; 3) NGAL+/сКр- (субклиническое ОПП); 4) NGAL+/сКр+. При этом NGAL«+» соответствовал величине >177 (s-NGAL) и >72 нг/мл (u-NGAL), NGAL«-» считали при значениях ≤ соответствовавших величин для s-NGAL и u-NGAL; сКр«+» соответствовал величине > 104 мкмоль/л для мужчин и >90 – для женщин, сКр«-» – величинам ≤ соответствовавших значений для мужчин и женщин. Ультразвуковое исследование органов брюшной полости и почек до госпитализации выполнено 17 (15,3%), в стационаре – 39 (35,1%) больным ОКС.
В стационаре у больных ОКС оценивали частоту развития различных кардиоваскулярных осложнений (далее – осложнений): острая левожелудочковая недостаточность (9,0%), кардиогенный шок (1,8%), атриовентрикулярная блокада III степени (0,9%), острая аневризма левого желудочка (9,9%), рецидив острого ИМ (0,9%), инсульт (1,8%, ургентные); пароксизм наджелудочковой тахикардии или фибрилляция предсердий (7,2%), желудочковая экстрасистолия высоких градаций по Lown (16,2%), синдром слабости синусового узла (4,5%), атриовентрикулярная блокада II степени (1,8%), ранняя постинфарктная стенокардия (14,4%, неургентные). Me развития осложнений составила – 5 суток [3,7]. Также оценен исход через 6 месяцев после выписки из стационара (конечные точки: смерть (1,9%), повторный ИМ (1,9%), повторная госпитализация с ОКС (11,5%), острая левожелудочковая недостаточность (1,0%), инсульт (1,0%), проведение чрескожного коронарного вмешательства в рамках ОКС (6,7%), аортокоронарного шунтирования (3,8%), формирование хронической аневризмы левого желудочка (2,9%)).
Статистический анализ полученных результатов проведен с использованием специализированного пакета прикладных программ Statistica v. 10.0 (StatSoft. Ins., 2011). При приближенно нормальном распределении данные представлены в виде среднего арифметического (М) и стандартного отклонений (±SD). При распределении, отличном от нормального, результаты представлены в виде медианы (Ме) и квартилей (Р25; Р75) в %. Для сравнения количественных данных использован U-тест Манна–Уитни. При сравнении трех независимых групп и более по количественному признаку использован метод Краскела–Уоллиса. Для сравнения качественных данных применен точный критерий Фишера. Оценка силы связи между признаками проведена с помощью рангового коэффициента корреляции (R) Спирмена и γ-корреляции. Различия считали статистически значимыми при р<0,05.
Результаты
Уровни s-NGAL и u-NGAL у больных ОКС составили 198,3 (143,6–375,8) и 4,2 (1,8–9,7), при этом Ме s-NGAL была выше референсных значений. Уровень сКр в исследуемой группе не превышал нормальных показателей 77,7 (67,6–92,2). Значения рСКФ и КлКр составили 88,0 (71,0–103,0) и 95,3 (73,0–120,0) соответственно. У 55 (78,4%) выявлена оптимальная или незначительно повышенная альбуминурия, у 16 (14,4%) – высокая, у 8 (7,2%) – очень высокая. При этом Ме альбуминурии у больных ОКС соответствовала оптимальному или незначительно повышенному уровню 5,1 (2,2–51,0)].
Выявлена значимая прямая связь величины альбуминурии с уровнем сКр (R=0,31; p=0,02) и обратная – с величиной рСКФ (R=-0,37; p=0,006). Снижение рСКФ менее 60 мл/ мин при ОКС ассоциировалось с более высокой величиной альбуминурии (γ=0,41; р=0,03).
Получена достоверная обратная корреляция уровней u-NGAL с величиной КлКр (R=-0,23; p=0,01) и прямая связь с величиной альбуминурии (R=0,23; p=0,04).
Проанализированы уровни s-NGAL, u-NGAL и показатели функционального состояния почек у больных разными формами ОКС (табл. 1). Уровень u-NGAL у больных ОКСпST был в 2 раза достоверно выше, чем при ОКСбпST.
При этом у пациентов с ОКСбпST выявлена тенденция к более высоким значениям сКр, альбуминурии и более низкой величине рСКФ и КлКр по сравнению с ОКСпST. Полученные результаты, по-видимому, связаны с тем, что в анамнезе у пациентов с ОКСбпST чаще были ишемическая болезнь сердца (р=0,02) и перенесенный ИМ (р=0,004) по сравнению с больными ОКСпST.
У 53 (47,7%) больных течение ОКС было осложненным.
У 34 (64,2%) больных диагностировали одно, у 19 (35,8%) – 2 осложнения и более. При осложненном течении ОКС выявлен более высокий уровень s-NGAL (266,0; 144,39–508,2) по сравнению с пациентами без развития осложнений – 172,61 (132,3–262,68; р=0,02). По остальным исследуемым показателям больные ОКС в зависимости от течения госпитального периода были сопоставимыми (р<0,05).
В отдаленном периоде (6 месяцев) исход был оценен у 104 из 111 больных ОКС (1 умер в госпитальный период, связь с 6 пациентами была утеряна). При этом у 25 (24%) исход расценен как неблагоприятный: НС (n=5) и ИМ (n=20).
У 20 (64,5%) больных отмечено развитие 1 конечной точки, у 5 (35,5%) – 2 и более. Благоприятный исход был у 79 (76%) пациентов с НС (n=22) и ИМ (n=57).
У больных с развитием конечных точек отмечена тенденция к более высоким значениям s-NGAL: 271,6 (225,4–350,6), по сравнению с пациентами с благоприятным течением заболевания: 190,6 (132,3–422,0; р=0,1). При этом по остальным изучаемым показателям больные в зависимости от исхода отдаленного периода не различались (р<0,05).
Уровень u-NGAL у больных ОКС с альбуминурией/протеинурией (n=24) был в 2 раза достоверно выше: 7,28 (2,6–40,6), чем у пациентов с ОКС без таковой (n=55): 3,2 (1,5–7,2; р=0,02). Остальные исследуемые показатели не достигли статистической значимости в изучаемых подгруппах (р<0,05). Наличие альбуминурии/протеинурии при ОКС ассоциировалось с более высоким уровнем u-NGAL (γ=0,34; р=0,003).
Структура подгрупп больных ОКС по величине NGAL (s-NGAL и u-NGAL) и сКр представлена в табл. 2.
Частота субклинического ОПП при ОКС составила 44,1 и 6,3% (по уровню s-NGAL и u-NGAL соответственно). При этом по уровню s-NGAL субклиническое ОПП диагностировали значительно чаще, чем по величине u-NGAL (р<0,001). Следует отметить, что доля пациентов с повышенным уровнем сКр независимо от величины NGAL составила всего 16,1% (табл. 2).
Характеристика больных ОКС в зависимости от референсных значений s-NGAL (n=111) по возрасту, полу и данным анамнеза представлена в табл. 3. Больные ОКС в зависимости от референсных значений s-NGAL были сопоставимыми по возрасту и данным анамнеза, при этом в подгруппе пациентов с содержанием s-NGAL >177 преобладали мужчины (табл. 3).
Объективные данные и лабораторные показатели при госпитализации у больных ОКС в зависимости от референсных значений s-NGAL (n=111) представлены в табл. 4.
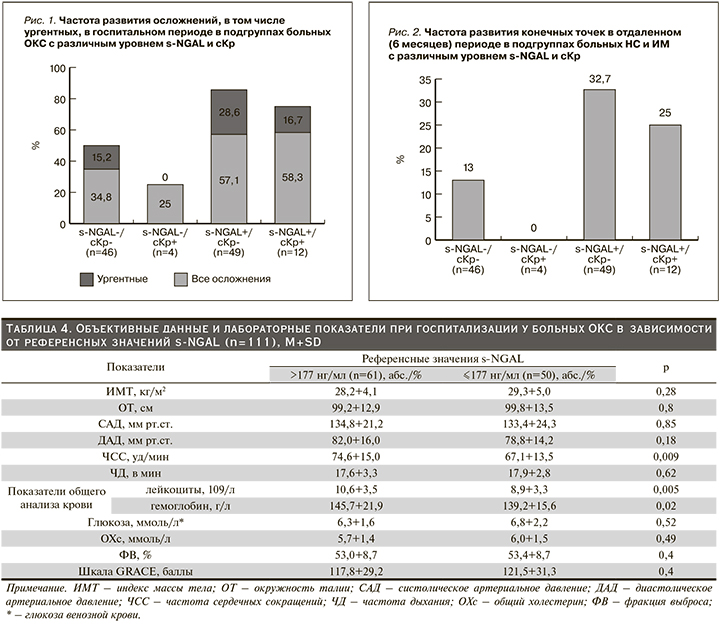
Пациенты ОКС в зависимости от референсных значений s-NGAL были сопоставимыми по объективным данным и лабораторным показателям и достоверно различались по ЧСС, количеству лейкоцитов и уровню гемоглобина, которые были выше у больных с референсными значениями s-NGAL >177 (табл. 4). Кроме этого больные ОКС с уровнем s-NGAL выше референсных значений дольше находились в ОРИТ [74,4 (54; 98 часа) против 68,5 (45; 94) часов, р=0,08].
Среди больных ОКС с содержанием s-NGAL >177 ТЛТ проведена у 25 (41%), ЧКВ – у 22 (36,1%) пациентов. В той же подгруппе у больных с ОПП (по уровню сКр) ТЛТ выполнена у 5, ЧКВ – у 4 пациентов. При этом в подгруппе больных ОКС с уровнем s-NGAL ниже референсных значений ТЛТ проведена у 16 (32%) пациентов, ЧКВ у 17 (34%) больных. Среди лиц с ОПП по сравнению с предыдущей подгруппой ТЛТ выполнена 1 (р=0,37), ЧКВ – 2 пациентам (р=0,6).
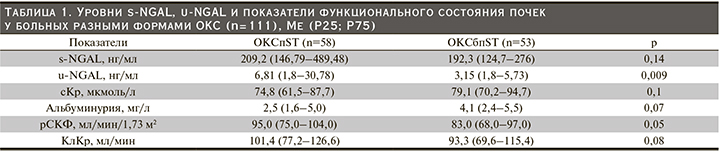
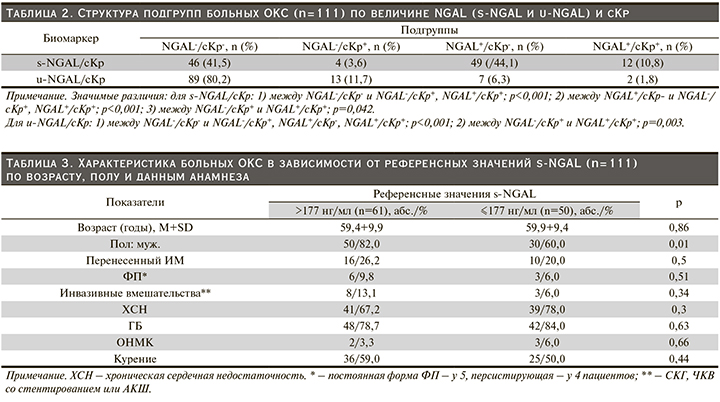
В подгруппах больных ОКС с различным уровнем NGAL и сКр проанализирована частота развития осложнений в госпитальном периоде (рис. 1) и конечных точек в отдаленном (6 месяцев) периоде НС и ИМ (рис. 2). У пациентов с ОКС подгрупп s-NGAL+/сКр- (субклиническое ОПП) и s-NGAL+/сКр+ (ОПП) частота развития всех осложнений в госпитальном периоде и конечных точек в течение 6 месяцев не различалась (р=1,0 и р=0,9 соответственно). Однако у больных подгруппы s-NGAL+/сКр- недостоверно чаще развивались ургентные осложнения (28,6 против 16,7%, р=0,4) по сравнению с s-NGAL+/сКр+.
Следует отметить, что пациенты с ОКС с субклиническим ОПП (s-NGAL+/сКр-) по сравнению с больными подгруппы s-NGAL-/сКр- чаще имели осложненное течение госпитального периода (р=0,04) (рис. 1) и неблагоприятный исход отдаленного (6 месяцев) (р=0,03) периода (рис. 2). Также отмечена тенденция к более частому развитию ургентных осложнений в подгруппе пациентов s-NGAL+/сКр- (субклиническое ОПП) по сравнению с подгруппой s-NGAL-/сКр- (28,6 против 15,2%, р=0,1).
У больных ОКС с субклиническим ОПП, выявленным по величине u-NGAL (u-NGAL+/сКр-), частота развития осложнений в госпитальном периоде и конечных точек в отдаленном (6 месяцев) периоде была сопоставимой с остальными подгруппами (u-NGAL-/сКр-, u-NGAL-/сКр+, u-NGAL+/сКр+), что, возможно, связано с небольшим числом пациентов в ряде подгрупп (табл. 2).
Частота развития осложнений в госпитальном периоде и конечных точек в течение 6 месяцев в подгруппах s-NGAL+/сКр- и u-NGAL+/сКр- оказалась сопоставимой (р=1,0 и р=0,42 соответственно).
Обсуждение
В нашей работе от больных ОКС получена достоверная связь уровня u-NGAL с некоторыми показателями функционального состояния почек (КлКр и альбуминурия).
Имеются экспериментальные и клинические данные, демонстрирующие зависимость экскреции NGAL с мочой от уровня протеинурии [10]. В ряде ранее проведенных работ выявлена корреляция u-NGAL с уровнем протеинурии, при этом в исследования включали лишь пациентов с патологией почек [11, 12]. Следует отметить, что достоверные результаты получены только в отношении u-NGAL, который, вероятно, можно считать более специфичным к изменениям функции почек. При этом на основании мета-анализа (19 исследований) указывается, что уровни NGAL в плазме, сыворотке и в моче имеют сходное диагностическое и прогностическое значение в отношении ОПП разных этиологий [13].
Более высокие значения u-NGAL у пациентов с ОКСпST по сравнению с ОКСбпST, вероятно, отражают тяжесть атеротромбоза для этой категории больных.
Принятие термина ОПП и публикация первых рекомендаций по диагностике и лечению ОПП (2012) привели к значительным успехам в этой области. При этом критерии ОПП до сих пор основываются на определении величины сКр и/или объема и скорости диуреза [1]. В то же время определение объема почасового диуреза имеет ограничения [9]. Кроме того, часть больных получают диуретики, которые могут значительно влиять на результат [9]. Увеличение концентрации сКр происходит лишь через 24–48 часов после развития ОПП, поскольку почки обладают значительным функциональным резервом [14]. Так как заболевания почек часто протекают бессимптомно, у части пациентов ОПП остается нераспознанным [15].
До недавнего времени попытки провести доклиническую диагностику ОПП оказывались безуспешными [16].
В результате многоцентрового анализа М. Haase et al. (2011) впервые был выявлен более высокий риск неблагоприятных исходов (потребность в заместительной почечной терапии, госпитальная летальность) для больных с повышенным уровнем NGAL (в крови и моче), но без диагностического повышения уровня сКр [17].
В нашем исследовании мы оценили значимость уровней NGAL в качестве маркера субклинического ОПП у больных ОКС, но уже в отношении неблагоприятных сердечно-сосудистых исходов.
Почти у половины больных ОКС в исследуеммой выборке выявлено субклиническое ОПП по уровню s-NGAL (44,1%) и значительно реже (6,3%) – по уровню u-NGAL. При этом в работе М. Haase et al. (2011) около 20% всех пациентов составляли NGAL+/сКр- [17].
Выделение подгруппы NGAL+/сКр- имеет особое значение, поскольку уровни NGAL и сКр отражают различные патофизиологические события. NGAL указывает на повреждение канальцев, которое может предшествовать функциональной почечной потере (или наоборот), выявляемой по сКр. При этом повышение уровня NGAL на несколько дней опережает таковое сКр, что позволяет диагностировать субклиническое ОПП в более ранние сроки.
Оценив значимость вероятного субклинического ОПП (NGAL+/сКр-) у больных ОКС, мы выявили более частое развитие осложнений в госпитальном периоде (р=0,04) и неблагоприятный исход через 6 месяцев после выписки из стационара (р=0,03) по сравнению с пациентами с s-NGAL-/сКр- (без ОПП). Следует отметить, что по исходам госпитального и отдаленного (6 месяцев) периодов больные в подгруппах s-NGAL+/сКр- (субклиническое ОПП) и s-NGAL+/сКр+ значимо не различались.
Таким образом, выявление субклинического ОПП у больных ОКС, вероятно, говорит о наличии (или возможном развитии) у них кардиоренального синдрома I типа. Это необходимо учитывать при выборе тактики ведения. Для ранней диагностики субклинического ОПП необходимы более чувствительные маркеры, такие как NGAL.
Выводы
- Субклиническое ОПП (повышение уровня NGAL без диагностического повышения уровня сКр) у пациентов с ОКС чаще выявляли по уровню NGAL в крови.
- У больных ОКС с субклиническим ОПП (по уровню NGAL в крови) осложнения в госпитальном периоде и конечные точки в отдаленном (6 месяцев) периоде наблюдения развивались чаще, чем при ОКС с уровнем NGAL ниже пограничного значения и независимо от величины сКр.
- При ОКС наличие альбуминурии/протеинурии ассоциировалось с более высокой величиной u-NGAL.

