Острое почечное повреждение (ОПП) продолжает оставаться глобальной проблемой неотложной медицины, сопровождается высокой летальностью, особенно в группе пациентов, требующих проведения заместительной почечной терапии (ЗПТ), нередко приводит к развитию хронической болезни почек (ХБП) и неблагоприятным отдаленным результатам, требует значительных финансовых затрат. ОПП развивается у 8–43% пациентов с новой коронавирусной инфекцией SARS-CoV2 (COVID-19), в 3,6–58% требует проведения ЗПТ и сопровождается значительной летальностью [1]. Мета-анализ P. Hansrivijit et al., включивший 26 исследований 5497 пациентов, показал, что ОПП развивается у 8,4% пациентов с COVID-19 и в 3,6% необходимо ЗПТ. Среди больных, находящихся в отделении реанимации и интенсивной терапии (ОРИТ), частота развития ОПП достигает 19,9%. Развитие ОПП сопровождается повышением относительного риска смерти в 13 раз. Пожилой возраст, сахарный диабет, артериальная гипертензия являются факторами риска развития ОПП [2]. В мета-анализе M. Shao et al. [3], на основании 40 исследований, включивших 24 527 пациентов с COVID-19, выявлено, что частота развития ОПП составляет 10%. Летальность среди пациентов с ОПП составляет 63,1% по сравнению с 12,9% без ОПП; авторы отмечают, что более высокие значения сывороточного креатинина и мочевины сопровождаются худшим прогнозом.
Патогенез ОПП при COVID-19 носит многофакторный характер [4]. Отмечается прямое цитопатическое действие короновируса SARS-CoV-2 на эпителиальные клетки проксимальных канальцев и подоциты, через мембранно связанный ангиотензинпревращающий фермент 2 (ACE2) [5], Выраженный дисбаланс концентраций про- и противовоспалительных медиаторов обусловливает развитие дисфункции эндотелия и канальцев, запускает апоптоз клеток, приводит к микроциркуляторным нарушениям, в конечном счете – к развитию ОПП [6, 7]. Кроме этого к факторам развития ОПП у пациентов с COVID-19 относят сахарный диабет, артериальную гипертензию, ХБП, применение нефротоксичных антибиотиков, противовирусных препаратов, рентгенконтрасных веществ. Нарушение микроциркуляции, агрегация эритроцитов, признаки рабдомиолиза обнаружены у пациентов с ОПП и COVID-19 [8].
В ОРИТ многопрофильных стационаров кроме пациентов с ОПП ЗПТ применяется в отношении больных с декомпенсацией ХБП, находящихся на программном гемодиализе, в т.ч. с COVID-19.
Цель нашей работы – предоставить данные по организации ЗПТ в неотложной медицине в стационарах Департамента здравоохранения г. Москвы в условиях развития пандемии новой коронавирусной инфекции COVID-19.
Материал и методы
Использовались ежегодные отчеты главного внештатного специалиста-нефролога за 2018–2020 гг. Данные получены из 43 медицинских организаций (МО) Департамента здравоохранения г. Москвы, где применяются методы ЗПТ для лечения ОПП и декомпенсации ХБП, в ОРИТ круглосуточных стационаров, из них в 33 МО методы ЗПТ применялись в отношении пациентов с COVID-19. В общие данные 2020 г. включены пациенты с COVID-19, кроме этого результаты этой группы больных представлены отдельно.
Для статистической обработки полученных результатов использовали программу STATISTIKA 12.0 (Stat.Soft, Inc.). Для сравнения номинативных данных использовали критерий хи-квадрат (χ2). Полученные результаты признавали статистически значимыми при уровне р<0,05.
Результаты
Оснащение аппаратурой. За 2020 г. в рамках оснащения МО г. Москвы на 30,1% увеличилось количество аппаратов для постоянной заместительной почечной терапии (ПЗПТ) (табл. 1). Так, на 01.01.2021 в МО находится 296 аппарата для ПЗПТ, исправных – 96,7%, 181 (61,1%) из них поставлены после 2015 г. Для лечения пациентов с COVID-19 использовались 175 аппаратов для ПЗПТ (59,1%). Также за 2020 г. обновлен парк аппаратов «искусственная почка» (АИП), из 86 аппаратов АИП 100% исправных, 74 (86,0%) из них установлены после 2015 г., 45 (52,3%) использовались для лечения пациентов с новой коронавирусной инфекцией. Применение АИП с мобильными системами водоподготовки дает возможность гибко применять различные методы ЗПТ пациентов как с ОПП, так и с ХБП.
Укомплектованность медицинскими кадрами. Обеспечение эффективности использования аппаратов для ЗПТ невозможно без увеличения подготовленных врачей и среднего медицинского персонала (табл. 2). По сравнению с 2018 г. в 2020-м на 30,2% увеличилось число врачей и на 24,6% медицинских сестер, владеющих методами ЗПТ [9]. Тем не менее, по данным МО, в 2020 г. нуждалось в обучении 380 врачей и 539 медицинских сестер. Увеличение обученного персонала приводит к тому, что уменьшается число МО, которые не могут проводить процедуры ЗПТ круглосуточно. Так, в 2017 г. их было 9, в 2018-м – 7, в 2020 г. –5.
Обучение методам ЗПТ в неотложной медицине проводится как на рабочем месте, так и на циклах тематического усовершенствования врачей, в рамках непрерывного медицинского образования Министерства здравоохранения Российской Федерации, таких как:
1. «Заместительная почечная терапия и экстракорпоральная гемокоррекция в интенсивной терапии», проводит ГБУЗ НИИ СП им. Н.В. Склифосовского ДЗМ.
2. «Экстракорпоральные методы детоксикации и кровосберегающие технологии в анестезиологии и реаниматологии», проводит Российская медицинская академия непрерывного профессионального образования МЗ РФ.
Применение методов ЗПТ. Основные показания к использованию методов ЗПТ в неотложной медицине: ОПП, декомпенсация ХБП и т.н. внепочечные показания у пациентов с сепсисом, тяжелым острым панкреатитом, тяжелыми ожогами, с острым респираторным дистресс синдромом (ОРДС), после кардиохирургических вмешательств, с тяжелой сочетанной травмой, острыми отравлениями и другими критическими состояниями для коррекции водно-электролитного баланса, кислотно-щелочного равновесия, системного воспаления, гиперкатаболизма, тяжелых нарушений терморегуляции, элиминации токсинов. У пациентов с COVID-19 встречались как почечные: ОПП, ХБП, так и внепочечные показания к ЗПТ для лечения ОРДС, «цитокинового шторма», сепсиса, гипергидратации, гипертермии.
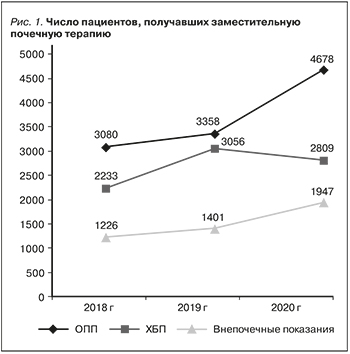 В 2020 г. отмечен существенный рост пациентов, получавших ЗПТ в ОРИТ, составивший 9434, что на 20,7% больше, чем в 2019 г. (7815), и на 44,3% больше, чем в 2018 г. (6539). Если же оценивать применение методов ЗПТ за последние 5 лет, то с 2016 г. число пациентов, получавших ЗПТ в ОРИТ, увеличилось в 1,98 раза [9]. В 2020 г. пациенты с COVID-19 составили 34,7% (3274) от всех пациентов, получавших ЗПТ.
В 2020 г. отмечен существенный рост пациентов, получавших ЗПТ в ОРИТ, составивший 9434, что на 20,7% больше, чем в 2019 г. (7815), и на 44,3% больше, чем в 2018 г. (6539). Если же оценивать применение методов ЗПТ за последние 5 лет, то с 2016 г. число пациентов, получавших ЗПТ в ОРИТ, увеличилось в 1,98 раза [9]. В 2020 г. пациенты с COVID-19 составили 34,7% (3274) от всех пациентов, получавших ЗПТ.
В 2020 г. статистически значимо увеличилось число пациентов с ОПП, получавших ЗПТ (рис. 1), по сравнению с 2019 г. на 39,3%, р<0,0001, и на 51,9% по сравнению с 2018 г., р=0,002. Из них с COVID-19 было 1570 (33,6%) больных. Также в 2020 г. отмечался статистически значимый рост числа пациентов с внепочечными показаниями ЗПТ по сравнению с 2018–2019 гг.: на 38,9% (р<0,0001) и 58,8% (р=0,0033) соответственно. Пациенты с COVID-19 составили в этой группе 32,4% (630 пациентов).
В то же время число пациентов с ХБП, в отношении которымх применяли методы ЗПТ в условиях ОРИТ, снизилось статистически значимо по сравнению с 2019 г. – на 8,1% (р<0,0001). По сравнению с 2018 г. в 2019-м прирост составил 25,8% и это различие было статистически значимым (р<0,0001). Среди больных ХБП 55,2% составили пациенты с COVID-19 (1074).
При анализе пациентов по полу и возрасту выявлено (табл. 3), что в 2018 г. мужчин было 56,1%, в 2019 г. – 5 6,2% и в 2020-м – 58,6%, различия между 2018-м и 2020-м были статистически значимыми (р=0,0011). Среди пациентов с COVID-19 мужчины составили 58,5%. В 2018 г. пациентов до 18 лет было 2,5%, в 2019-м – 2,4% и в 2020-м – 2,3%, больных трудоспособного возраста – 48,4, 47,3 и 42,0% соответственно. Относительное снижение в 2020 г. по сравнению с предыдущими годами было статистически значимым. Пациентов с COVID-19 трудоспособного возраста было 36,7%. В 2020 г. статистически значимо увеличилось число пациентов пенсионного возраста по сравнению с 2018 и 2019 гг. – на 63,7 и 33,7% соответственно. Среди пациентов пенсионного возраста с COVID-19 было 63,3%.
Общее число процедур ЗПТ в 2020 г. увеличилось на 15% по сравнению с 2019-м и на 26,9% по сравнению с 2018 г. (рис. 2), при этом 8600 процедур (34% от общего числа за год) выполнено пациентам с COVID-19. Статистически значимый прирост осуществлен за счет продолжительных (постоянных) процедур ЗПТ, на 55,9% отмечено увеличение по сравнению с 2019 г. (р<0,0001) и на 82% по сравнению с 2018 г. (р<0,0001). В процентном отношении за последние 3 года их количество существенно выросло (31,9, 33,8 и 45,8% соответственно). Продолжительные методы ЗПТ пациентов с COVID-19 составили 5094 (рис. 3), т.е. 44,0% от общего числа продолжительных процедур в 2020 г. С 2018 по 2020 г. уменьшилось абсолютное и относительное количество интермиттирующих процедур ЗПТ, выполняемых на аппаратах «искусственная почка» и составивших 49,9, 40,8 и 33,4% соответственно. У пациентов с COVID-19 их было 1884, 22,3% от общего числа интермиттирующих процедур в 2020 г. Количество продленных методов ЗПТ увеличилось в 2019 г., затем снизилось в 2020 г. Больным COVID-19 выполнены1622 процедуры, 30,7% от общего числа продленных процедур в 2020 г.

При сравнении режимов проведения продленных и продолжительных методов заместительной почечной терапии (ПЗПТ) выявлено (рис. 4), что с 2018 г. статистически значимо увеличилось количество процедур гемодиафильтрации – метода, комбинирующего конвекцию и диффузию. Так, в 2020 г. по сравнению с 2019-м разница составила 33,3% (р=0,0004), по сравнению с 2018 г. – 86,2% (р<0,0001). Среди всех методов ПЗПТ в 2018 г. гемодиафильтрация составила 64,3%, в 2019 г. – 68,4%, в 2020-м – 70,4% соответственно. Пациентам с COVID-19 их было выполнено 5260, 44,4% от общего числа процедур. Гемодиализ интермиттирующий продленный и гемодиализ продолжительный в 2018-м и 2019 г. выполнялись в 26,2% процедур ПЗПТ, в 2020 г., несмотря на рост абсолютного числа процедур до 3795, относительное количество снизилось до 22,5%. Больным COVID-19 их было выполнено 1058, 27,9% от общего количества процедур. Гемофильтрация оказалась наименее используемой процедурой ПЗПТ и составила за последние 3 года 9,5, 5,4 и 7,1% соответственно. Пациентам с COVID-19 их было выполнено 395 (5,9%).
По сравнению с 2018 г. в 2019 и 2020 гг. отмечен статистически значимый рост летальности среди пациентов, которым в ОРИТ потребовалось проведение ЗПТ (табл. 4), составивший 32,0, 33,6 и 46,6% соответственно. При этом статистически значимое увеличение летальности в 2020 г. отмечено среди пациентов как с COVID-19, составившее 62,5%, так и без COVID-19 – 38,1%. Также по сравнению с 2018 г. в 2019 и в 2020 гг. статистически значимо выросла летальность в группах ОПП (36,9, 40,4 и 51,3% соответственно) и внепочечными показаниями к ЗПТ (39,6, 45,3 и 52,2% соответственно). При сравнении групп с и без COVID-19 выявлено, что среди пациентов с ОПП летальность составила 73,2 и 40,2% соответственно, в группе с внепочечными показаниями к ЗПТ – 67,3 и 45,0%. Различия между группой без COVID-19 в 2019 г. были статистически не значимыми. В 2020 г. по сравнению с 2018 и 2019 гг. статистически значимо выросла летальность среди пациентов с ХБП и составила в группах с и без COVID-19 43,9 и 29,1% соответственно.
Аналитика. В настоящее время в рамках Единой медицинской информационно-аналитической системы города Москвы разработаны и используются протоколы методов ЗПТ. Остаются нерешенными проблемы с созданием реестра пациентов, требующих проведение ЗПТ в ОРИТ.
Обсуждение
Развитие пандемии COVID-19 значительно увеличило нагрузку на систему здравоохранения, особенно на систему интенсивной терапии. Как видно из нашего исследования, в 2020 г. 34,7% от всех пациентов, нуждавшихся в проведении ЗПТ в условиях ОРИТ, составили больные COVID-19, при этом прирост по сравнению с 2019 г. был 20,7%, на 15% увеличилось количество методов ЗПТ. Такое значительное увеличение использования ЗПТ невозможно без увеличения оснащенности стационаров. Так, Департамент здравоохранения г. Москвы дооснастил МО 89 аппаратами для постоянной заместительной почечной терапии ведущих мировых производителей, аппаратами для ЗПТ были оснащены и временные госпиталя для больных COVID-19. На 22,9% увеличилось количество аппаратов «искусственная почка». Необходимо отметить, что применение методов ЗПТ с использованием современной аппаратуры невозможно без подготовки профессиональных кадров: врачей-анестезиологов-реаниматологов, трансфузиологов, токсикологов, нефрологов и среднего медицинского персонала. Так, за последние 5 лет в МО ДЗМ на 78% увеличилось число врачей и на 71,2% медицинских сестер, владеющих методами проведения процедур ЗПТ [9].
ЗПТ все больше и больше используется в ОРИТ, особенно в отношении пациентов с COVID-19, не только при почечной недостаточности, но и в качестве поддерживающей терапии полиорганной дисфункции. Для принятия решения о выборе метода ЗПТ оцениваются клиническое состояние пациента, тяжесть органной дисфункции, доступность метода ЗПТ и опыт его применения в конкретной клинической ситуации с возможностью смены процедур по мере изменения состояния пациента и динамики почечного повреждения. При выборе режима продленных и продолжительных методов ЗПТ: гемофильтрации, гемодиафильтрации либо гемодиализа, необходимо отметить, что опубликованный в 2012 г. мета-анализ [10] не выявил улучшения выживаемости пациентов, потребности в ЗПТ при сравнении этих методик. Не было обнаружено различий между группами через 72 часа после начала ПЗПТ при сравнении тяжести состояния по шкале SOFA, вазопрессорной поддержки. Гемофильтрация и гемодиафильтрация сопровождались более коротким «временем жизни» гемофильтра по сравнению с продолжительным гемодиализом (в среднем на 7,3 и 5,4 часа соответственно) даже с использованием режима предилюции. Не было статистически значимых различий между группами по клиренсу низкомолекулярных веществ, в то же время при гемофильтрации и гемодиафильтрации достоверно выше клиренс среднемолекулярных веществ, таких как Ванкомицин (молекулярный вес 1,8 кДа) на 18%, β2-микроглобулин (11,8 кДа) на 94%, IL-1ra (16–18 кДа) на 77%. Таким образом, использование гемодиафильтрации как основного метода ЗПТ пациентов с COVID-19 оправданно.
К сожалению, у больных COVID-19 рост числа пациентов с ОПП сопровождался значительной летальностью. Мета-анализ S.Y Robbins-Juarez. et al. [11] показал, что ОПП развивается у 17% пациентов с COVID-19, с частотой применения ЗПТ – 5% и летальностью – 52%. В исследовании F. Zhou et al. [12] медиана развития ОПП от начала клинических проявлений COVID-19 составила 15 дней, при этом у умерших больных ОПП развилось в 50% случаев, с потребностью в ЗПТ – 19%. По данным P. Gabarre et al. [13], у пациентов с COVID-19 в условиях ОРИТ частота развития ОПП достигала 42,9%, при этом в 74,4% развивалась тяжелое повреждение почек (3-я стадия по критериям KDIGO) с потребностью в ЗПТ – 13,4%. Тяжелое ОПП у пациентов с COVID-19 сопровождается крайне неблагоприятными исходами. Так, по данным китайских авторов [14], при развитии 2-й стадии ОПП летальность составила 75%, 3-й – 0%. В США [15] ОПП, требующее применения ЗПТ, сопровождалось летальностью в 72%. В Великобритании, по данным Национального центра аудита в интенсивной терапии (ICNARC), летальность в ОРИТ среди пациентов с COVID-19, требовавших ЗПТ, составляла 56,4% до 1 сентября 2020 г., с 1 сентября 2020 по март 2021 г. – 66,9% [16], потребность в ЗПТ в ОРИТ составила в эти сроки 26,2 и 16% соответственно. В мультицентровом исследовании «STOP-COVID» [17], проведенном в США, предшествовавшие заболевания почек у пациентов с COVID-19 значительно ухудшали исход заболевания. Так, летальность среди пациентов с ХБП, не находившихся на диализе; с ХБП 5-й ст. нуждавшихся в ЗПТ, и не имевших до поступления в ОРИТ признаков почечной недостаточности, составляли 51, 50 и 35% соответственно. В целом наши данные соответствуют общемировым тенденциям: отмечается увеличение числа пациентов с ОПП, увеличение потребности в ЗПТ в ОРИТ, рост пациентов пожилого возраста, сопоставимая с иностранными авторами высокая летальность.
Заключение
Таким образом, развитие пандемии COVID-19 потребовало от Департамента здравоохранения г. Москвы значительного дооснащения МО аппаратами для ПЗПТ, рост составил 43%. Обновлен парк АИП, прирост составил 22,9%. Использовались для лечения больных COVID-19 59,1% аппаратов для ПЗПТ и 52,3% АИП.
Несмотря на существенный рост числа врачей и среднего медицинского персонала МО, способных выполнять методы ЗПТ в ОРИТ, нуждаются в обучении в рамках непрерывного медицинского образования 380 врачей и 539 медицинских сестер.
Пандемия COVID-19 привела к существенному росту числа пациентов в ОРИТ, получавших ЗПТ. В 2020 г. прирост составил 20,7% по сравнению с 2019 г., а пациенты с COVID-19 составили 34,7% от всех пациентов, получавших ЗПТ.
В 2020 г. статистически значимо увеличилось число пациентов с ОПП, получавших ЗПТ, прирост к 2019 г. составил 39,3%.
Из них 33,6% составили больные COVID-19. Также в 2020 г. отмечался статистически значимый рост числа пациентов с внепочечными показаниями ЗПТ на 38,9% по сравнению с 2019 г. Пациенты с COVID-19 составили в этой группе 32,4%. В то же время число пациентов с ХБП, к которым применяли методы ЗПТ в условиях ОРИТ, снизилось статистически значимо по сравнению с 2019 г. – на 8,1%. Среди больных ХБП 55,2% составили пациенты с COVID-19.
В 2020 г. статистически значимо увеличилось число пациентов пенсионного возраста, достигшее 55,7%. Среди пациентов с COVID-19 их было 63,3%.
Общее число процедур ЗПТ в 2020 г. увеличилось на 15% по сравнению с 2019 г., при этом 34% от общего числа за год выполнено пациентам с COVID-19. Статистически значимый прирост осуществлен за счет продолжительных процедур ЗПТ (44,0% у пациентов с COVID-19), на 55,9% отмечено увеличение по сравнению с 2019 г.
Увеличилось количество процедур гемодиафильтраци (44,4% у пациентов с COVID-19) по сравнению с 2019 г., разница составила 33,3%.
По сравнению с 2019 г. в 2020-м отмечен статистически значимый рост летальности среди пациентов, которым в ОРИТ потребовалось проведение ЗПТ, составивший 33,6 и 46,6% соответственно. При этом рост летальности отмечен как среди пациентов с COVID-19, составивший 62,5%, так и среди больных без COVID-19 – 38,1%.



