Введение
Не подлежит сомнению тот факт, что минерально-костные нарушения (МКН) крайне значимы для пациентов, страдающих патологией почек. Они обеспечивают элевацию риска формирования кардиоваскулярной патологии и костных изменений у больных, находящихся на диализе [8]. Контроль уровня фосфатов у больных на диализе необходим, и это подтверждено результатами крупных исследований [16].
Сегодня в арсенале нефрологов есть разные средства, которые дают возможность индивидуального подбора схемы фосфат-снижающей терапии. Выбор фосфат-связывающих препаратов (ФСП) основывается на нескольких факторах, включающих лекарственную нагрузку, переносимость препарата, уровень гиперфосфатемии, наличие коморбидности и т.д.
Оптимальный ФСП должен обладать значимым действием в отношении снижения концентрации фосфатов, обеспечивать снижение лекарственной нагрузки, хорошие переносимость и приверженность пациентов лечению. Должно отсутствовать взаимодействие с другими препаратами, а число побочных эффектов должно быть минимальным [11]. Выбор ФСП должен осуществляться индивидуально с учетом показателей минерально-костного обмена, стадии хронической болезни почек (ХБП), сопутствующего лечения и приверженности пациента терапии.
Важным изменением в подходах к применению ФСП в последние годы, отраженными в международных и национальных клинических рекомендациях по лечению пациентов с ХБП и гиперфосфатемией, является ограничение применения кальцийсодержащих препаратов, повышающих риск развития сосудистой кальцификации и сердечно-сосудистой смертности пациентов на диализе.
Новый не содержащий кальция ФСП на основе железа комплекс оксигидроксида железа отличается самой высокой фосфат-связывающей способностью среди доступных препаратов (260 мг/1 г), долгосрочной эффективностью в лечении гиперфосфатемии, позволяет в значительной степени снижать лекарственную нагрузку и повышать приверженность пациентов на диализе фосфат-снижающей терапии [9, 18].
Формирование патологии костно-минерального обмена происходит уже на этапе ХБП С2-стадии, достигая пика у пациентов на терминальных стадиях заболевания. Центральное значение в развитии МКН принадлежит гиперфосфатемии (т.н. фосфат-центрическая парадигма) [12].
Гиперфосфатемия значимо увеличивает риск смерти от кардиоваскулярных причин, способствует развитию эктопической кальцификации сосудов, клапанов сердца и мягких тканей [17], индуцирует развитие фиброза в миокарде и почках [12]. Таким образом, коррекция гиперфосфатемии является важным компонентом терапии пациентов на диализе с точки зрения снижения риска развития МКН-ХБП, сердечно-сосудистых осложнений и смерти [3, 15].
С позиции современных рекомендаций коррекция гиперфосфатемии представляет собой комплексную 3D-терапию, включающую адекватный диализ, гипофосфатную диету и применение ФСП, что считается важнейшим терапевтическим вмешательством относительно фатальных и тяжелых осложнений МКН-ХБП у пациентов на диализе [2, 4, 11].
Эпидемиологические исследования показали, что большинство пациентов с гиперфосфатемией на диализе нуждаются в применении ФСП [5, 13]. Согласно исследованию COSMOS, в котором изучали истории болезни более 6000 больных, проходивших заместительную почечную терапию диализом [1], снижение уровня фосфатов в сыворотке крови при применении любых ФСП было в большой степени ассоциировано со снижением общей и сердечно-сосудистой смертности пациентов с гиперфосфатемией на диализе [10].
Все ФСП можно условно разделить на две группы:
- содержащие кальций;
- бескальциевые.
Первые (карбонат и ацетат кальция) могут приводить к развитию гиперкальциемии, при этом соединения в форме карбоната провоцируют появление данного осложнения в 3,5 раза чаще, чем в форме ацетата [8]. Применение кальцийсодержащих ФСП сопровождается развитием сосудистой кальцификации, существенно повышающей риск развития кардиоваскулярных осложнений [4, 10].
Таким образом, не содержащие кальция ФСП – не имеющие кальция в составе, признаны препаратами первого выбора для длительного лечения гиперфосфатемии у пациентов с ХБП. Это связано с доказанными существенными преимуществами бескальциевых ФСП перед кальцийсодержащими в отношении риска развития сердечно-сосудистой кальцификации и снижения показателей сердечно-сосудистой и общей смертности пациентов с ХБП. В частности, мета-анализ, в который вошли 11 рандомизированных контролируемых исследований (РКИ), включающих результаты лечения более 4500 пациентов, выявил снижение смертности от всех причин на 22% среди пациентов, получавших фосфат-биндеры, не содержащие кальция [12]. Бескальциевые ФСП способны снижать у пациентов с гиперфосфатемией на диализе уровни паратгормона в сыворотке крови [11].
В рекомендациях по диагностике и лечению МКН-ХБП KDIGO 2017 г. и Российских национальных рекомендациях по ХБП 2021 г. также подчеркивается необходимость ограничения применения кальцийсодержащих ФСП и отдавать предпочтение бескальциевым фосфат-биндерам [4].
В последнее время в клиническую практику внедрены бескальциевые ФСП на основе железа. Эффекты препаратов железа по снижению уровня фосфатов в крови были установлены еще в середине XX в., однако безопасные препараты для коррекции гиперфосфатемии у пациентов с ХБП на основе железа появились только в последнее десятилетие.
В Российской Федерации в 2016 г. был зарегистрирован комплекс оксигидроксида железа (III), сахарозы и крахмала (Вельфоро® 500). Этот препарат является первым не содержащим кальция ФСП на основе железа. Процесс связывания основных компонентов данного препарата с фосфатом представляется как обмен молекулами. Последние перемещаются от OH-групп и/или воды к фосфат-ионам. Интенсивность связывания фосфатов при применении Вельфоро® постоянна во всем диапазоне физиологических значений pH на протяжении желудочно-кишечного тракта [9]. Следует отметить, что активность комплекса оксигидроксида железа в отношении связывания фосфатов значимо превышает тот же показатель у других ФСП [20].
Данные крупного РКИ, изучавшего эффективность и безо-пасность применения комплекса из оксигидроксида трехвалентного железа, сахарозы и крахмала, были представлены J. Floege и его коллегами в 2014 г. [19] Более тысячи пациентов с ХБП попали в выборку, они проходили лечение посредством гемо- или перитонеального диализа. Из них 707 больным для коррекции нарушений фосфорного обмена назначали Вельфоро® в течение года. При этом дозировка составляла от 1,3 до 3,0 г/сут.
В другую группу вошли 348 больных, им был назначен севеламера карбонат в дозировке по 4,8–14,4 г/сут. Уже в первые 12 из 52 недель лечения содержание фосфора в сыворотке изменилось: оно снизилось соответственно на 2,2 и 2,4 мг/дл. Высокая эффективность Вельфоро® в рамках долгосрочного крупного рандомизированного исследования III фазы достигалась при трехкратном снижении лекарственной нагрузки по сравнению с карбонатом севеламера. Это обеспечило достоверное повышение приверженности пациентов терапии. Отмечено, что комплекс оксигидроксида железа не оказывал значимого влияния на метаболизм железа. Наиболее частыми побочными эффектами были изменения стула (диарея и изменения цвета), в основном умеренные, в большинстве случаев не требовавшие прекращения терапии [19].
A. Covic и соавт. (2016) продемонстрировали, что комплекс оксигидроксида железа при долгосрочном применении не оказывал значимого влияния на параметры метаболизма железа. Таким образом, применение препарата безопасно и не требует мониторирования показателей обмена железа.
В исследовании 2018 г. М.М. Батюшина и А.А. Кастанаяна изучалось использование комплекса оксигидроксида железа пациентами с диабетической болезнью почек и гиперфосфатемией. Применение препарата в течение 1 месяца обеспечивало достижение целевых уровней фосфатов в сыворотке крови у 87% пациентов, в течение 2 месяцев – 96,7%. Важным результатом данного исследования стало отсутствие проявлений межлекарственного взаимодействия комплекса оксигидроксида железа с аторвастатином и пероральными противодиабетическими препаратами [6]. Это важно при наличии сахарного диабета и/или атеросклеротических изменений у пациентов на программном гемодиализе (ПГД).
Фармако-экономические преимущества применения комплекса оксигидроксида железа представлены в публикациях как российских, так и зарубежных специалистов. Результаты российского фармако-экономического исследования убедительно показали, что применение Вельфоро 500 является наименее затратной схемой лечения гиперфосфатемии у больных ХБП в Российской Федерации [14]. Опубликованные недавно результаты сравнительного влияния ФСП на клинические результаты лечения гиперфосфатемии демонстрируют, что у пациентов, которым назначался комплекс оксигидроксида железа, отмечались более низкие показатели частоты госпитализаций по сравнению с больными, получавшими другие ФСП (7,97 на 100 пациентов/мес.). Применение комплекса оксигидроксида железа обеспечивало снижение частоты госпитализаций на 32%, по сравнению с севеламером. Снижение расходов на госпитализацию при лечении Вельфоро определяет экономическую целесообразность применения данного препарата пациентами на диализе [15].
В недавнем РКИ 2020 г. Е.В. Шутова и соавт. оценивалась эффективность лечения не содержащими кальций ФСП на протяжении 4 месяцев. Изучалось влияние терапии на показатели обмена кальция и фосфора у пациентов с превышающим норму уровнем последнего и получающих ПГД: одна группа получала Вельфоро® 500, другая – севеламер. Терапия комплексом оксигидроксида железа обеспечивала достижение целевых уровней фосфатов в сыворотке крови на момент завершения исследования, тогда как при лечении севеламера карбонатом достижения данной конечной точки не произошло. Применение комплекса оксигидроксида железа позволило значительно уменьшить лекарственную нагрузку: число таблеток, принятых больными за сутки, было в 3 раза меньше в группе больных, принимавших Вельфоро® 500, по сравнению с получавшими севеламера карбонат.
Препарат не оказывал значимого влияния на метаболизм железа. Анализ частоты побочных эффектов существующих ФСП на основании инструкций по применению свидетельствует о том, что комплекс оксигидроксида железа обладает лучшим профилем безопасности.
Цель проспективного РКИ
Оценить эффективность и безопасность нового железосодержащего ФСП – оксигидроксида железа (Вельфоро® 500) и севеламера карбоната для пациентов с гиперфосфатемией, находящихся на лечении ПГД.
Материал и методы
В 2021 г. на базе диализных центров ООО «Медикал групп» (Московская область) проведено проспективное рандомизированное контролируемое исследование, в которое были включены стабильные пациенты (n=100) с ХБП 5, получавшие лечение ПГД в течение не менее 24 недель до начала исследования и соответствовавшие критериям включения и исключения.
Критерии включения: возраст 18 лет и старше независимо от пола, стандартный режим ГД – 3 раза в неделю, диализный Kt/V не менее 1,2 за процедуру, отсутствие изменения дозы ФСП и других препаратов для коррекции МКН (активаторов рецептора витамина D, кальцимиметиков) в течение не менее 4 недель до начала периода отмывания, при скрининговом визите уровни фосфора до процедуры ГД должны были быть ≥1,3 ммоль/л и <2,6 ммоль/л, в течение периода отмывания ≥1,78 ммоль/л, уровни сывороточного ферритина <1000 мкг/л и насыщения трансферрина железом (НТЖ) <50%.
Критерии исключения: скорректированный уровень сывороточного кальция менее 1,88 или более 2,75 ммоль/л, уровень интактного паратиреоидного гормона (ПТГ) более 800 пмоль/л, паратиреоидэктомия в анамнезе не менее чем за 6 месяцев до начала исследования, активное/состоявшееся желудочно-кишечное кровотечение или воспалительные заболевания кишечника, стабильно высокие ежемесячные уровни сывороточного фосфора >3,2 ммоль/л на протяжении 3 месяцев до скрининга, поливалентная лекарственная аллергия или непереносимость компонентов лекарств, злокачественные новообразования в анамнезе в течение предшествовавших 5 лет, непереносимость препаратов железа, гемохроматоз в анамнезе или любые другие нарушения накопления железа.
Исследование включало скрининг, периоды отмывания (4 недели), титрации доз и лечения (24 недели). Перед началом исследования проводилась рандомизация пациентов с помощью интерактивной системы случайных чисел. Пациенты были распределены для лечения комплексом оксигидроксида железа или севеламера карбонатом в соотношении 1:1. Дозы препаратов изначально назначались в соответствии с инструкциями по применению. Оба исследуемых препарата назначали перорально 3 раза в сутки непосредственно во время приема пищи. Начальные дозы оксигидроксида железа составляли 0,5 таблетки (250 мг Fe) 3 раза в сутки, севеламера карбоната – 1 таблетку (800 мг) 3 раза в сутки. В дальнейшем дозы препаратов титровали каждые 4 недели, исходя из показателей фосфора, для достижения целевых значений фосфора (1,3–1,78 ммоль/л). Для коррекции дозы использовались следующие критерии: если концентрация фосфора в сыворотке была более 1,78 ммоль/л, дозу оксигидроксида железа увеличивали на 0,5–1,5 таблетки в сутки, дозу севеламера – на 800–2400 мг/сут., если она находилась в целевом диапазоне 1,3–1,78 ммоль/л, дозы обоих препаратов не менялись и если уровни фосфора были менее 1,3 ммоль/л, доза оксигидроксида железа уменьшалась на 0,5 таблетки, а севеламера карбоната – на 800–2400 мг/сут. Суточные дозы препаратов определялись в соответствии с инструкциями по применению: для комплекса оксигидроксида железа рекомендуемая доза составила 500 мг 3 раза в сутки (1500 мг/сут= 3 таблетки), доза севеламера карбоната – 1600 мг 3 раза в сутки (4800 мг/сут.=6 таблеток). В течение всего периода исследования был запрещен прием одновременно с исследуемыми препаратами других ФСП.
Критерии прекращения участия пациентов в исследовании: развитие любого нежелательного явления (НЯ), которое затруднило бы продолжение лечения; определение уровней фосфора сыворотки крови менее 0,97 или более 3,23 ммоль/л в нескольких анализах крови подряд; определение скорректированного уровня кальция в сыворотке крови менее 1,88 ммоль/л и концентрации ферритина более 1000 мкг/л. Прием активных метаболитов витамина D и кальцимиметиков был разрешен, если пациенты получали их до начала исследования в течение 4 недель или более, а дозы этих препаратов оставались неизменными на протяжении всего периода исследования. Ни одному из пациентов эти препараты (активные метаболиты витамина D или кальцимиметики) в течение всего периода исследования не были назначены de novo. Не было существенных различий пациентов в исследуемых группах по полу, возрасту, антропометрическим параметрам и основным показателям костно-минерального обмена. Диета, согласно опросу пациентов, на протяжении всего исследования изменялась незначительно.
Отбор крови всем больным проводился после двухдневного перерыва до процедуры ГД во время каждого из этапов исследования (период отмывания, титрации доз и лечения). У всех пациентов ежемесячно оценивались уровни фосфора, кальция, ПТГ, гемоглобина, ферритина, НТЖ, С-реактивного белка.
Первичным результатом эффективности применения фосфат-биндеров была концентрация фосфатов в сыворотке крови в конце лечения. Дополнительные оценки включали концентрацию фосфатов в сыворотке крови в каждый момент времени, изменение концентрации фосфатов в сыворотке от исходного уровня до конца лечения и показатели достижения целевых концентраций фосфатов в сыворотке как 1,3–1,78 ммоль/л.
Вторичными результатами эффективности лечения фосфат-биндерами были показатели концентрации кальция в сыворотке, концентрации интактного ПТГ сыворотки, обмена железа (ферритин, НТЖ), гемоглобина, С-реактивного белка (СРБ).
Безопасность и переносимость оценивались по числу НЯ, серьезных НЯ и отказов больных от продолжения лечения препаратами. Что касается безопасности, НЯ не включали изменения цвета фекалий и языка, вызванные железом, содержащимся в комплексе оксигидроксида железа. Число пациентов с событиями и частота событий были рассчитаны в каждой группе.
Статистический анализ: сравнения между группами проводили с использованием критерия Фишера. Уровень значимости был установлен на уровне р-value<0,05. Статистический анализ данных проводили в программах Statistica v.10, SPSS v.23, GraphPad Prism v.6.
Результаты
В исследование были включены 100 пациентов. После рандомизации 1:1 были сформированы две группы: I группа – пациенты, получавшие терапию комплексом оксигидроксида железа (Вельфоро 500), и II группа – пациенты, получавшие севеламера карбонат (Селамерекс). Из-за развития НЯ из I группы выбыли 8 (16%) пациентов, из II группы – 6 (12%).
В общей сложности завершили исследование 42 (84%) и 44 (88%) пациента I и II групп соответственно. Базовые характеристики пациентов приведены в таблице. Статистически значимых различий между группами не было в начале лечения.
Влияние терапии комплексом оксигидроксида железа и севеламера карбонатом на сывороточные уровни фосфатов представлено на рис. 1.
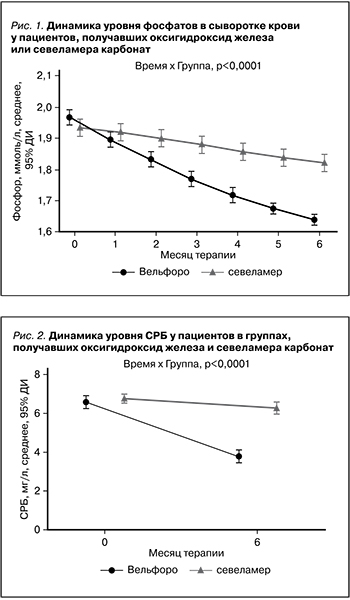
Применение комплекса оксигидроксида железа обеспечивало достоверное снижение уровня фосфора с 1,96±1,2 до 1,63±0,8 ммоль/л (р<0,01), в то время как использование севеламера карбоната не оказало статистически значимого влияния на этот показатель.
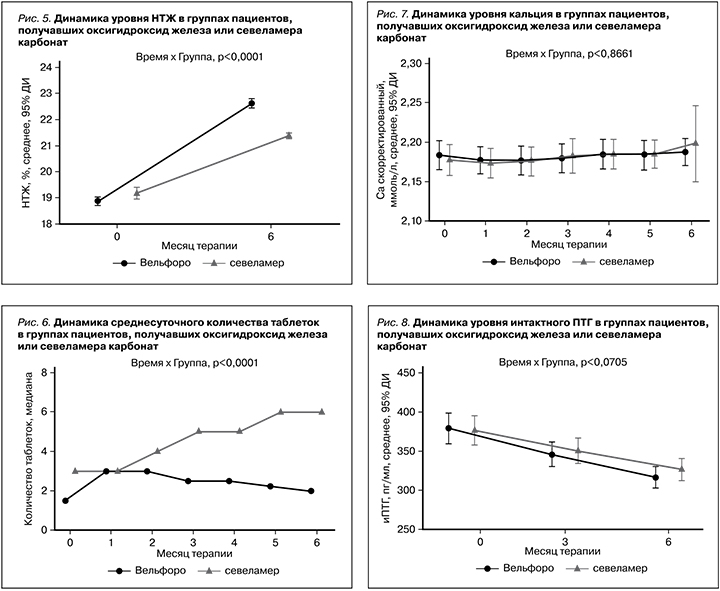
Анализ полученных данных, приведенный на рис. 2–5, свидетельствует о значимом снижении уровней СРБ – более чем на 40% – и достоверном увеличении уровней гемоглобина в группе комплекса оксигидроксида железа без существенных изменений показателей обмена железа. Применение севеламера карбоната не оказало влияния ни на один из этих показателей.
Среднее число принимаемых ежедневно таблеток комплекса оксигидроксида железа в настоящем исследовании составило 1,8±0,5 и 5,8±1,2 для севеламера карбоната. Показатели лекарственной нагрузки ФСП представлены на рис. 6.
Изменения лабораторных параметров, отражающих МКН у пациентов исследуемых групп, представлены на рис. 7, 8. Достоверных изменений уровней сывороточного кальция, интактного ПТГ отмечено не было.
Существенных различий в частоте возникновения НЯ, связанных с приемом исследуемых препаратов, не наблюдалось. Наиболее частыми НЯ во время приема комплекса оксигидроксида железа были тошнота (10%) и диарея (15%). Большинство случаев диареи были легкими, преходящими, развивались только в начале лечения и разрешались самопроизвольно без дополнительной терапии. При назначении севеламера карбоната у пациентов очень часто отмечались запоры (15%), тошнота (5%), дискомфорт (5%) и боли в животе (5%), диарея отмечалась в 3% случаев.
Обсуждение
Применение препарата Вельфоро® 500 у всех пациентов на ПГД с гиперфосфатемией обеспечивало достижение целевых значений фосфатов в сыворотке крови (<1,7 ммоль/л).
В группе пациентов, получавших лечение севеламера карбонатом, фосфат-связывающая терапия не привела к достижению целевых уровней фосфатов в крови. Более высокая эффективность в контроле фосфатов комплекса оксигидроксида железа по сравнению с севеламера карбонатом может быть обусловлена различиями в фосфат-связывающей способности препаратов, измеряемой в мг фосфатов, связываемых 1 г действующего вещества ФСП (260 мг/г для Вельфоро против 21 мг/г для севеламера).
Среднесуточное потребление таблеток в нашем исследовании было более чем в 3 раза меньше в группе пациентов, получавших Вельфоро® 500 (1,8 табл./сут.), по сравнению с пациентами, получавшими севеламера карбонат (5,8 табл./сут.).
В исследованиях, проведенных ранее, было показано, что прием большого количества таблеток пациентами с ХБП по различным причинам (в среднем 19 табл./сут.), 50% от которых составляют ФСП, негативно влияет на качество жизни пациентов на гемодиализе, а также ухудшает их приверженность лечению и контроль уровней фосфатов и ПТГ. В то время как уменьшение лекарственной нагрузки способствует повышению приверженности и эффективности фосфат-связывающей терапии.
Повышение уровня гемоглобина на фоне приема комплекса оксигидроксида железа в нашем исследовании свидетельствует о возможном дополнительном положительном действии данного препарата для коррекции анемии. Положительное влияние Вельфоро® на уровни гемоглобина, отмеченное в нашем исследовании, продемонстрировано и в работах других исследователей. Авторы объясняли эти результаты возможной частичной кишечной абсорбцией железа, входящего в состав препарата.
В нашем исследовании, как и у других авторов, достоверных изменений уровней ферритина и НТЖ при применении комплекса оксигидроксида железа отмечено не было. Прием Вельфоро®, по мнению экспертов, является в этом смысле безопасным и не требует дополнительного контроля показателей железа.
Стоит отметить наблюдавшийся в нашем исследовании положительный эффект комплекса оксигидроксида железа в отношении уменьшения уровня маркеров воспаления (достоверное уменьшение уровня СРБ), что, возможно, также повлияло на увеличение гемоглобина у пациентов этой группы. Влияние ФСП на уровень воспаления был также показан ранее и в других работах.
Количество побочных эффектов препаратов было сопоставимым в обеих группах. Диарея была самым частым НЯ в группе Вельфоро, но за счет плавного титрования дозы препарата (старт приема по 0,5 таблетки 3 раза в сутки строго во время еды, соблюдение диеты) большинство случаев были легкими и преходящими. Только три пациента прекратили участие в исследовании из-за диареи. После прекращения приема препарата диарея прекратилась у всех больных.
Многие пациенты с ХБП, получающие процедуры ГД, страдают от запоров. Развитие запоров у 5 пациентов, принимавших севеламера карбонат, привело к прекращению лечения препаратом.
К недостаткам исследования можно отнести открытый дизайн, стандартизацию лабораторных анализов (пациенты посещали диализный центр в разное время суток), потребление фосфатов в рационе пациентов.
Заключение
Применение в условиях 6-месячного РКИ комплекса оксигидроксида железа (Вельфоро® 500) в группе пациентов с ХБП, получавших лечение ПГД, и гиперфосфатемией обеспечивает достижение целевых уровней фосфатов в сыворотке крови при высокой безопасности и хорошей переносимости препарата.
Средняя эффективная суточная доза Вельфоро® 500 в настоящем исследовании (1,8 табл./сут.) была существенно ниже рекомендованной средней дозы (3,0 табл./сут.) в соответствии с инструкцией по применению.
Применение для лечения гиперфосфатемии севеламера карбоната в группе активного контроля в дозировках, рекомендованных инструкцией по применению, не позволило нам достичь целевых уровней фосфатов.
Различия в эффективности двух не содержащих кальция ФСП, назначаемых в соответствии инструкциями по применению, требуют дальнейшего более углубленного изучения, но, возможно, могут быть обусловлены более высокой фосфат-связывающей способностью комплекса оксигидроксида железа и лучшими показателями приверженности пациентов терапии данным препаратом по сравнению с севеламером, продемонстрированными ранее как в условиях РКИ, так и в многочисленных исследованиях реальной практики.
Отмеченное при применении комплекса оксигидроксида железа увеличение у пациентов уровня гемоглобина на фоне отсутствия значимых изменений показателей метаболизма железа также требует дальнейшего изучения, но, безусловно, является важным преимуществом в терапии гиперфосфатемии пациентов на диализе. Существенное снижение уровня СРБ в группе пациентов, получавших терапию комплексом оксигидроксида железа, свидетельствует о подавлении препаратом системного воспаления, что является доказанным фактором улучшения клинических исходов и повышения качества лечения пациентов на диализе.



