Введение
Хроническая болезнь почек (ХБП) остается одной из актуальных медицинских и социальных проблем вследствие ее высокой распространенности и прогрессирующего характера патологического процесса, в конечном итоге заканчивающегося развитием у пациента почечной недостаточности (ПН) [1, 2]. Среди причин, приводящих к развитию ХБП, хронические гломерулонефриты (ХГН) занимают лидирующие позиции, а по некоторым данным, даже выходят на первое место [3–5]. Вместе с тем при ХГН скорость прогрессирования ПН зависит и от выраженности неиммунных факторов, в частности анемии [6]. Малокровие, связанное с патологией почек, может обнаруживаться на ранней стадии болезни [7, 8]. По результатам отдельных исследований, анемия при ХБП может наблюдаться при скорости клубочковой фильтрации (СКФ) более 90 мл/мин/1,73 м² у мужчин и свыше 70 мл/мин/1,73 м² у женщин [8, 9]. При выраженном снижении функции почек практически у всех больных ХБП развивается анемия. Спад содержания гемоглобина (Hb) связан с уменьшением продукции эритропоэтина, который сопровождает замедление СКФ, а также изменение вариабельности уровня Hb при различных режимах СКФ [10, 11]. Так, самый низкий уровень Hb находят при ренопривном состоянии, т.е. среди пациентов, страдающих ХГН, и лиц, которые начали диализ при низкой остаточной функции почек.
Анемия при ХГН характеризуется наличием нормохромных нормоцитарных эритроцитов в периферической крови, гипоплазией эритроидных клеток в костном мозге и относительно низким содержанием ретикулоцитов [12, 13–15]. Несмотря на довольно многочисленные исследования анемического синдрома при ХБП, вопрос о клиническом значении эритроцитарных индексов при ХГН на ранней додиализной стадии заболевания изучен недостаточно. Не до конца решен вопрос об особенностях клинико-лабораторных проявлений анемии в зависимости от половых различий при ХБП, обусловленной гломерулонефритом. Результаты проводимых клинических исследований в этом направлении неоднозначны, что, по-видимому, объясняется гетерогенностью исследуемых групп пациентов с ХБП и различными методологическими подходами. Вклад нефрогенной анемии определен в основном у пациентов с ХБП, находящихся на этапе лечения диализом [16, 17]. В то же время влияние почечной анемии на течение ХГН на ранней стадии заболевания изучено недостаточно.
Цель исследования: изучить клинико-лабораторные особенности эритроцитарных индексов и структурной перестройки миокарда левого желудочка (ЛЖ) у пациентов с ХГН в зависимости от половых различий.
Материал и методы
Для выполнения поставленных задач обследованы 305 пациентов с установленным клиническим диагнозом ХГН, которым проведено комплексное клинико-инструментальное и лабораторное вмешательства. Возраст пациентов варьировался от 17 до 65 лет (средний возраст – 35,4±12,2 года). В исследование не включались лица с сахарным диабетом, находившихся на антианемической терапии или этапе почечной заместительной терапии, болезнями системы крови, сопровождающимися изменениями эритроцитарных индексов периферической крови.
Тип исследования – случай–контроль. Все обследованные лица в зависимости от половых различий были подразделены на две группы. В 1-ю группу (n=206) вошли пациенты с ХГН мужского пола, во 2-ю (n=99) – лица с ХГН женского пола. Всем пациентам проводили сбор анамнеза (длительность течения мочевого синдрома, артериальной гипертензии – АГ и ХБП). Артериальное давление (АД) измеряли по методу Короткова, выполняли подсчет числа сердечных сокращений (ЧСС). Индекс массы тела (ИМТ) рассчитывали по общепринятой формуле. Лабораторное обследование включило измерение показателей периферической крови с оценкой эритроцитарных индексов: определение уровня гемоглобина (Hb, г/л), гематокрита (Ht, %), ретикулоцитов (‰), числа (×1012/л) и диаметра (мкм3) эритроцитов с оценкой содержания Hb в эритроцитах (MHС, пг), средней концентрации гемоглобина в эритроцитах (МСНС, г/дл), среднего корпускулярного объема эритроцитов (MCV, мкм2), числа тромбоцитов и скорости оседания эритроцитов (СОЭ). Дополнительно исследовали параметры биохимического анализа крови всех пациентов, такие как концентрация электролитов, холестерина, мочевой кислоты, фибриногена, С-реактивного (СРБ) и общего белка, антистрептолизина-О и креатинина. Кроме того, анализировали величины суточной протеинурии и относительной плотности мочи. Стадии ХБП определяли на основании СКФ, рассчитанной по формуле CKD-EPI, 2011 (Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration) [18].
Характер структурных изменений сердца выявляли с помощью неинвазивного ультразвукового эхокардиографического (ЭхоКГ) исследования на аппарате «Sequoia-512» корпорации «Siemens-Acuson» (Германия, США) по общепринятой методике. При этом оценивали толщину стенок, размеры полости ЛЖ, диаметр левого предсердия (см) из парастернального доступа по длинной оси ЛЖ. Измеряли толщину межжелудочковой перегородки (МЖП, см) и задней стенки левого желудочка (ЗСЛЖ, см) в диастолу, определяли конечный диастолический (КДР, см) и конечный систолический размеры (КСР, см) ЛЖ. Исследовали также фракцию выброса (ФВ, %). Массу миокарда ЛЖ (ММЛЖ) рассчитывали по формуле R.B. Devereux et al. (1986): ММЛЖ (г)=0,8 – [1,04-(КДР+МЖП+ЗСЛЖ)3-КДР3]+0,6 [19].
Индекс массы миокарда ЛЖ (ИММЛЖ) определяли как отношение ММЛЖ к площади поверхности тела. Критерии гипертрофии левого желудочка (ГЛЖ) и типов ремоделирования миокарда определяли в соответствии с рекомендациями ЕОК от 2013 г. [20]. Для оценки ГЛЖ рассчитывали ИММЛЖ, верхнее значение нормы которого составило для женщин 95 г/м2, для мужчин – 115 г/м2. Относительную толщину стенок (ОТС) ЛЖ рассчитывали для каждого больного как (МЖП+ЗСЛЖ)/КДР ЛЖ. За увеличение ОТС принимали величину более 0,42 [20]. В зависимости от величины ИММЛЖ и ОТС выделены следующие типы структурного состояния геометрии ЛЖ: нормальная геометрия ЛЖ (ОТС<0,42; нормальный ИММЛЖ), концентрическое ремоделирование (ОТС>0,42; нормальный ИММЛЖ), концентрическая гипертрофия (ОТС>0,42; ИММЛЖ больше нормы), эксцентрическая гипертрофия (ОТС<0,42; ИММЛЖ больше нормы). Показатель «двойное произведение» (ДП), являющийся объективным отражением обменных процессов в миокарде, рассчитывали по формуле: ДП=ЧСС×СД/100 (усл. ед.). За сердечно-сосудистые осложнения принимали верифицированные случаи стабильной стенокардии, перенесенные инсульты и рубцовые изменения на электрокардиографии.
При статистическом анализе использован стандартный пакет программ «Statistica 10,0», предусматривающий возможность пара- и непараметрического анализов. Значимость различий между группами оценивалась с помощью t-критерия Стьюдента (для переменных с нормальным распределением) и теста Манна–Уитни (для переменных с непараметрическим распределением) [21]. Данные представлены как среднее±стандартное отклонения для переменных с нормальным распределением, медиана (25–75%) – для переменных с непараметрическим распределением. Для оценки корреляционной взаимосвязи применялся способ Пирсона. Уровнем статистической достоверности считалось значение p<0,05.
Результаты исследования
Настоящее исследование базировалось на комплексной оценке эритроцитарных индексов периферической крови и их клинического значения в стратификации сердечно-сосудистого риска у пациентов с ХГН на додиализной стадии заболевания.
В табл. 1 представлена общая клиническая характеристика пациентов, вошедших в исследование. Из нее видно, что в обеих группах доля лиц с гипертоническим, латентным, нефротическим и смешанным типами ХГН была схожей. Однако пациенты с гематурическим гломерулонефритом в группе женщин отсутствовали. Исходно в группе мужчин число пациентов с 1-й стадией ХБП достоверно превалировало по сравнению с женщинами (табл. 1). Примечательно, что численность пациентов с АГ в обследованных выборках существенно не различалась.
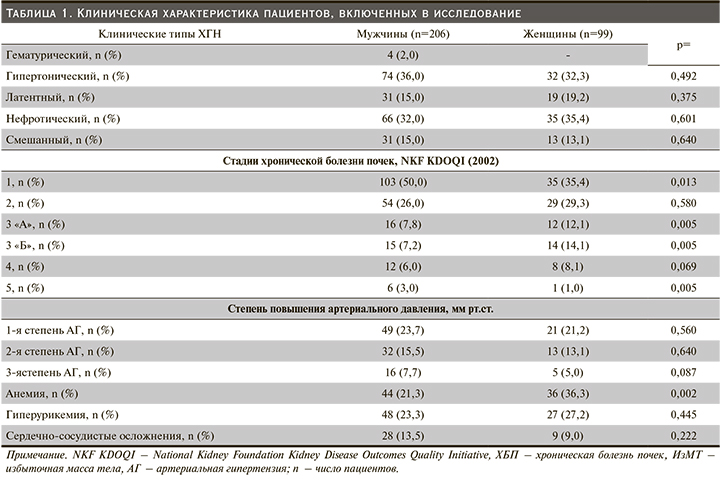
В группе женщин численность пациентов, имеющих лабораторные признаки анемии, была достоверно выше (36,3 против 21,3%; р=0,002) по сравнению с таковой мужского пола. Межгрупповых различий по частоте гиперурикемии получено не было. В то же время в когорте мужчин преобладали пациенты с сердечно-сосудистыми осложнениями (табл. 1). Важно отметить, что в обследованных группах увеличение уровня мочевой кислоты сыворотки крови регистрировалось уже на ранних стадиях ХБП.
Как видно из табл. 2, исходно пациенты, включенные в исследование по возрасту, продолжительности болезни, ИМТ, ЧСС и ДП, достоверно не различались. Тенденция увеличения уровня систолического (137±25 против 131±26 мм рт.ст.; р=0,050) и среднего (46±8 против 44±6 мм рт.ст; р=0,050) АД отмечалась в группе лиц мужского пола (табл. 2). Одновременно в той же группе показатели диастолического АД были достоверно выше (89±15 против 83±16 мм рт.ст.; р=0,004) по сравнению с таковыми у женщин (табл. 2). Напротив, во 2-й группе (женского пола) отмечено ощутимое повышение индекса ДП (122,4±26,2 против 114,8±26,6 ЕД; р=0,027) по сравнению с 1-й группой (мужского пола).
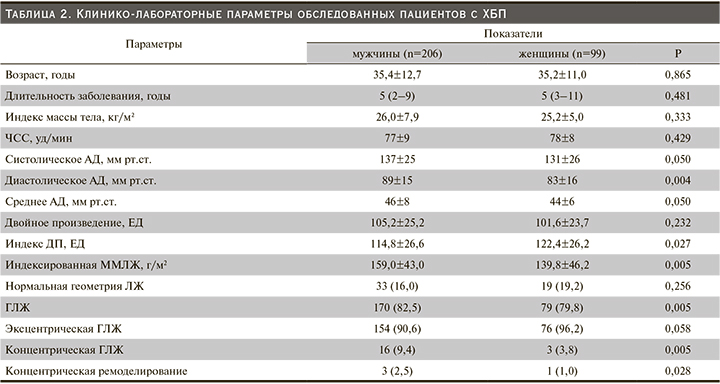
Дальнейший внутригрупповой анализ показал, что в когорте лиц мужского пола показатели ИММЛЖ были существенно выше (159,0±43,0 против 139,8±46,2 г/м2; р=0,027), а также чаще выявлялись признаки ГЛЖ (82,5 против 79,8%; р=0,005), чем в группе женщин. Следует отметить тот факт, что как в 1-й, так и во 2-й группе распространенным типом структурной перестройки миокарда ЛЖ оказался эксцентрический вариант ГЛЖ. Однако доля лиц с концентрическим типом ГЛЖ и концентрическое ремоделирование ЛЖ достоверно чаще регистрировались также у лиц мужского пола (табл. 2).
При рассмотрении параметров периферической крови (табл. 3) в группе лиц женского пола выявлялись статистически значимые снижения содержания Hb (125,7±21,2 против 144,2±21,8 г/л; р=0,005), Ht (36,9±4,83 против 41,1±5,51%; р=0,005), числа тромбоцитов (240,1±29,8x109/л против 247,3±28,0×109/л; р=0,045), эритроцитов (4,23±0,45×1012/л против 4,64±0,52 ×1012/л; р=0,005), диаметра эритроцитов (5,65±0,82 против 6,0±0,65 мкм3; р=0,005), МСН (29,0±2,20 против 30,7±2,08 пг; р=0,005), МСНС (33,5±2,29 против 34,5±2,23 г/дл; р=0,005) и MCV (86,4±2,70 против 88,4±2,77 мкм2; р=0,005) по сравнению с мужчинами. У женщин также отмечено статистически значимое увеличение числа ретикулоцитов в периферической крови по сравнению с таковым у лиц мужского пола (4,57±1,24 против 4,25±1,16‰; р=0,036 соответственно). Следует отметить, что концентрация железа сыворотки крови между группами достоверно не различалась. Примечательно, что показатели ретикулоцитарного индекса были схожими (табл. 3). Однако более высокие значения СОЭ были свойственны лицам женского пола.
По результатам исследования в группе мужчин среднее значение содержания натрия крови было существенно выше по сравнению с таковым у женщин (141,5±5,81 против 139,1±5,79 ммоль/л; р=0,003 соответственно). Концентрации холестерина, калия, кальция, общего белка и фибриногена крови в обеих группах были схожими. В группе мужчин уровень мочевой кислоты сыворотки крови был достоверно выше (0,38±0,09 против 0,33±0,10 ммоль/л; р=0,002). Доля лиц с высоким содержанием СРБ и антистрептолизина-0 сыворотки в группе как мужчин, так и женщин были одинаковыми. Полученная межгрупповая разница в показателях креатинина сыворотки крови и величине суточной экскреции белка с мочой не достигала статистически значимого порога (табл. 3). Существенное замедление СКФ: 69,2 (42,2–98,6) против 89,9 (62,0–113,0) мл/мин/1,73 м² (р=0,005), и снижение относительной плотности мочи: 1010 (1008–1012) против 1011 (1009–1013) ЕД (р=0,005), были свойственны лицам женского пола.
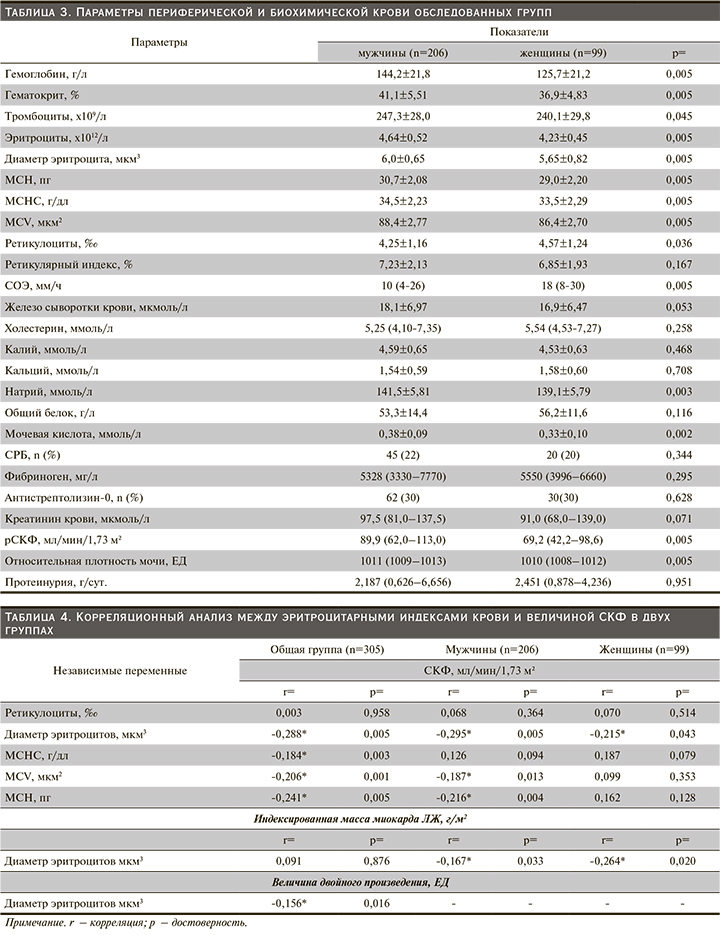
С учетом возможности влияния индекса эритроцитов на тяжесть азотовыделительной функции почек нами проведен корреляционный анализ между показателями СКФ и лабораторными параметрами периферической крови как внутри каждой группы, так и в общей выборке. Как следует из табл. 4, не выявлены какие-либо связи между содержанием ретикулоцитов периферической крови и величиной СКФ. В то же время корреляционный анализ как в общей, так и в отдельных подгруппах пациентов выявил отчетливую связь между диаметром эритроцитов и величиной СКФ (табл. 4). Схожая связь между МСНС и СКФ обнаружена в общей группе (r=-0,184; р=0,003). Наличие тесной корреляционной связи отмечено между средним объемом эритроцита и СКФ в общей (r=-0,206; р=0,001) и в группе мужчин (r=-0,187; р=0,013). Указанные взаимовлияющие сдвиги выявлены также между индексом МСН и СКФ (r=-0,241; р=0,005 в общей группе и r=-0,216; р=0,004 в группе мужчин). Как видно из табл. 4, корреляционные связи между эритроцитарными индексами и СКФ, за исключением диаметра эритроцитов, в группе женщин получены не были.
Как отмечено, в общей выборке между диаметром эритроцитов и уровнем расчетной СКФ регистрировалась отрицательная связь (r=-0,288; р=0,005). Одновременно в группе как мужчин, так и лиц женского пола уменьшение диаметра эритроцитов сопровождалось снижением расчетной СКФ (r=-0,295; р=0,005 и r=-0,215; р=0,043 соответственно). В исследуемых подгруппах отмечена зависимость между уменьшением диаметра эритроцитов и увеличением индекса массы миокарда ЛЖ (табл. 4). Однако существенная корреляционная связь прослеживалась между уменьшением диаметра эритроцитов и потребностью миокарда в кислороде, т.е. индекса двойного произведения в общей выборке (r=-0,156; р=0,016).
Обсуждение
Одним из значимых и независимых факторов риска прогрессировании ХГН является анемия [22, 23]. Для диагностики и дальнейшего контроля анемии у больных ХГН имеют значение уровень Hb (степень анемии) и следующие индексы красной крови: MCV, MCH, ретикулоцитарное число (эритропоэтическая активность). Для оценки тканевых запасов железа измеряют его уровень в сыворотке крови [22, 23]. Кроме того, целесообразно исследование СРБ крови больных ХГН как острофазового параметра для выявления и оценки воспаления. При обнаружении повышения содержания СРБ показано обследование больного ХГН на предмет выявления сопутствующего или сохраняющегося воспалительного процесса, проведения последующего антибактериального и/или противовоспалительного лечения перед началом терапии эритропоэтином. Критерием диагноза анемии у больных ХГН на додиализной стадии служит снижение концентрации Hb менее 130 г/л у мужчин и менее 120 г/л у женщин [24]. Традиционно считалось, что нормоцитарная, нормохромная анемия при ХГН развивается при достаточно выраженной ПН с СКФ менее 30 мл/мин/1,73 м² и достигает максимальной выраженности к диализному периоду [25, 26]. Однако, как показал ряд исследований, это не соответствует истине [27, 28]. У пациентов с ХГН анемия развивается еще до развития азотемии при больших показателях протеинурии, гиперлипидемии, а в стадии гиперкреатининемии встречается почти в 95% случаев. Примечательно, что в наших исследованиях большинство пациентов представлены на 1-й и 2-й стадиях ХБП. Вместе с тем доля лиц с протеинурическим типом ХГН была также многочисленной (табл. 1). Наличие анемии может вызывать патологическую гиперактивацию симпатической и ренин-ангиотензиновой систем, способствующих развитию у пациентов на додиализном этапе ХГН протеинурии до нефротического уровня, внутриклубочковой гипертензии, наступлению терминальной ПН [29]. Этот факт находит подтверждение и в наших исследованиях, т.е. у лиц женского пола снижение содержания Hb и уменьшение эритроцитарных индексов достоверно ассоциируются с ощутимым замедлением СКФ (табл. 3) с одной стороны, а наличие тесной прямой связи между спадом азотовыделительной функции почек и уменьшением диаметра эритроцитов – с другой (табл. 4).
В ряде популяционных и эпидемиологических работ показано, что даже небольшое снижение концентрации Hb ассоциируется с отчетливым увеличением градации ХБП [29, 30]. В то же время установлено, что коррекция анемии препаратами эритропоэтина может отсрочить сроки наступления диализной терапии [30, 31]. При этом следует отметить, что анемия при ХГН имеет двоякую клиническую значимость. Поздняя диагностика анемии приводит к более быстрому прогрессированию ХГН и увеличению частоты сердечно-сосудистых событий, более ранней инвалидизации и смерти. В частности, анемия ускоряет структурно-функциональные изменения в сердечно-сосудистой системе. По данным отдельных авторов, сердечно-сосудистые события выявляются у 27% пациентов при уровне СКФ более 50 мл/мин/1,73 м² [32, 33]. Возникающая на фоне анемии гипоксия приводит к периферической вазодилатации и снижению сосудистого сопротивления, что в свою очередь ведет к снижению периферического кровотока. Однако далее в ответ на гипотензию включаются механизмы вазоконстрикции не только периферических, но и как результат активации симпатической нервной системы, ренальных сосудов, что приводит к замедлению кровотока и ишемии почечной паренхимы. В то же время увеличивается выработка антидиуретического гормона. Указанные процессы приводят к задержке жидкости в организме и гиперволемической нагрузке миокарда, в последующем – к дилатации полостей сердца. Среди наших пациентов (табл. 2) распространенным типом структурных изменений миокарда оказалась эксцентрическая ГЛЖ, с развитием которой связано формирование расширения полостей сердца и интрадиализное падение АД. Таким образом, анемия независимо влияет на характер структурных изменений сердца пациентов с додиализной стадией ХГН. Из содержания табл. 2 следует, что концентрический тип структурной модификации ЛЖ чаще встречался в когорте лиц мужского пола. На наш взгляд, это связано с тем, что в группе мужчин отмечена тенденция увеличения всех параметров гемодинамики, где повышенное АД могло служить ведущим фактором перегрузки миокарда ЛЖ. Аргументом в пользу данного вывода выступает существенное увеличение ИММЛЖ в указанной группе.
В некоторых исследованиях продемонстрировано, что именно концентрический тип ГЛЖ приводит к развитию тяжелой ишемии миокарда и ее электрической негомогенности [34, 35]. Важно отметить, что данные по частоте развития той или иной структурной модификации ЛЖ при ХБП на додиализной стадии до сих пор остаются противоречивыми. Тем не менее уже известно, что в популяции людей, страдающих патологией почек, гиперкинетический тип кровообращения (перегрузка миокарда давлением) обусловливает возникновение концентрического типа, а анемия и гиперволемия (перегрузка миокарда объемом) – развитие эксцентрического варианта ГЛЖ. Таким образом, по результатам нашего исследования для мужчин с ХГН характерно развитие ГЛЖ преимущественно эксцентрического типа уже на додиализной стадии. По мере прогрессирования дисфункции почек увеличивается частота формирования концентрического типа ГЛЖ как прогностически неблагоприятного варианта структурных изменений ЛЖ. В группе женщин снижение концентрации Hb, Ht и уменьшение эритроцитарных индексов сопровождаются существенным снижением СКФ и присоединением эксцентрического типа ГЛЖ.
Выводы
На основании полученных нами данных можно предположить, что присутствие анемии при ХГН существенно повышает риск развития структурной перестройки ЛЖ еще на додиализной стадии заболевания. Наиболее частым проявлением структурных изменений сердца при ХГН был эксцентрический тип ГЛЖ. В то же время увеличение частоты концентрического типа ГЛЖ у лиц мужского пола было связано с приростом АД, а эксцентрического тип ГЛЖ у женщин – с анемией и снижением СКФ. Таким образом, проблема ХГН и анемии в ассоциации с АГ остается краеугольным камнем в клинической нефрологии и требует активного изучения уже на ранней додиализной стадии ХБП.



