Введение
Прошло больше 2 лет с момента первого случая заражения коронавирусом COVID-19 в Китае. Эмпирические данные показали, что особенности воздействия вируса различаются в зависимости от периода заражения и штамма SARS-CoV-2. До повсеместного распространения омикрона-штамма, которое зафиксировано в мире примерно с начала 2022 г., COVID-19 оставался заболеванием, представлявшим серьезную угрозу для здоровья в связи с частым поражением легких и других внутренних органов.
Судя по имеющимся на сегодня результатам, почки являются вторым по частоте поражения органом при COVID-19 у госпитализированных пациентов. В опубликованных в начале пандемии данных из Китая частота острого повреждения почек (ОПП) колебалась от 0,5 до 5,1% [1, 2]. У пациентов, получавших лечение в марте и апреле 2020 г. в США, описано более частое развитие ОПП [3, 4]. Публикации из Германии и Испании также показывают высокую частоту ОПП [5, 6].
Механизмы развития ОПП при COVID-19 до конца не выяснены. На ранних стадиях течения COVID-19 преобладают нетяжелые проявления поражения почек, такие как гематурия и/или протеинурия, что предполагает прямое воздействие SARS-CoV-2 на почечные структуры [7]. В отношении тяжелобольных пациентов с COVID-19 сообщалось о прямом почечном тропизме SARS-CoV-2, который может влиять на функцию почек и способствовать тяжести ОПП [8, 9]. Тем не менее ряд исследований биопсийного и аутопсийного материалов не выявил признаков прямого вирусного поражения почечных структур и показал, что острый канальцевый некроз является преобладающим типом повреждения [10–12]. По результатам крупных ретроспективных когортных исследований показано, что тяжелые стадии ОПП возникают почти исключительно у пациентов в критическом состоянии с дыхательной недостаточностью, находящихся на лечении в отделениях интенсивной терапии [13–15]. Клетки канальцев могут повреждаться цитокинами, у пациентов с COVID-19 описано увеличение уровня интерферона-γ, интерлейкина-21 (ИЛ-21), -8, -6, -1, фактора некроза опухоли-α, уровни которых повышаются наряду с лимфопенией [16, 17]. При COVID-19 в плазме определяются высокие уровни С-реактивного белка (СРБ), фибриногена, D-димера и ферритина, их уровни особенно высоки у пациентов с развитием ОПП [18].
Цель исследования: выявить особенности и динамику биомаркеров воспаления у пациентов с острым повреждением почек при COVID-19.
Материал и методы
Исследование было одобрено Независимым этическим комитетом Центра клинических исследований ФГАОУ ВО БФУ им. И. Канта (выписка из Протокола заседания НЭК № 23 от 27.04.2021). Проведен ретроспективный анализ историй болезни 437 пациентов, поступивших с января по июнь 2021 г. в ГБУЗ «Инфекционная больница Калининградской области» с подтвержденным диагнозом «коронавирусная инфекция, вызванная вирусом SARS-CoV-2»; у всех пациентов вирус SARS-CoV-2 был верифицирован при помощи полимеразной цепной реакции мазка из зева и/или носа на амбулаторном этапе. Лечение начиналось в амбулаторных условиях, но не сопровождалось значимым клиническим эффектом, что послужило поводом для госпитализации в инфекционный стационар.
Лечение больных в стационаре осуществлялось в соответствии с временными методическими рекомендациями «Профилактика, диагностика и лечение новой коронавирусной инфекции (COVID–19)» Минздрава РФ, действующими на момент госпитализации.
У всех пациентов определяли уровень креатинина сыворотки крови, проводили исследование уровня ферритина, ЛДГ, СРБ, ИЛ-6. Исследование креатинина, СРБ, ферритина и ЛДГ проводили в первые, а также на 3-и, 5-е и 10-е сутки лечения в стационаре, что соответствовало 1, 2, 3 и 4 точкам исследования. Уровень ИЛ-6 исследовали однократно при поступлении. Уровень креатинина в сыворотке крови определяли с помощью набора реактива BioSystems S.A.Costa Brava на анализаторе ВА 400 (Испания). Определение концентрации СРБ, ферритина и ЛДГ в сыворотке крови проводили с помощью наборов реактивов BioSystems S.A.Costa Brava на анализаторе ВА 400 (Испания) в соответствии с инструкцией производителя. Уровень ИЛ-6 в сыворотке крови исследовали методом иммуноферментного анализа с помощью реагентов «Интерлейкин-6-ИФА-БЕСТ» (Новосибирск).
ОПП и его стадии диагностировали согласно критериям KDIGO, 2012 [19].
Статистический анализ проводили с использованием пакета программ «Statistica 10.0» (StatSoft Inc., США). В связи с отличием от нормального распределения данных для описания количественных признаков использовали медиану и межквартильный размах (Me; Q1–Q3). Различия между количественными показателями в двух выборках определялись при помощи критерия Манна–Уитни, а для сравнения связанных выборок использовался критерий Вилкоксона. Доля качественных показателей вычислялась в процентах. Сравнение групп по качественному признаку проводилось с помощью критерия Фишера. Различия считали статистически значимыми при р≤0,05.
Результаты
Выявлено, что в обследованной популяции у 76 пациентов имелись признаки ОПП, что составило 20,5% от общего числа обследованных. У большинства (66; 87%) больных определялось ОПП 1-й стадии, у 9 (12%) уровень креатинина повысился в 2,0–2,9 раза, что соответствует 2-й стадии, у 1 (1%) пациента зарегистрировано повышение уровня креатинина более чем в 3 раза, т.е. определялась 3-я стадия ОПП, согласно критериям KDIGO (2012).
В зависимости от наличия ОПП все включенные в исследование пациенты были разделены на две группы:
- Группа А – 76 больных ОПП, из которых 36 (47,4%) мужчин и 40 (52,6%) женщин. Средний возраст пациентов составил 66,5±14,6 года; индекс массы тела (ИМТ) – 28,7±5,5 кг/м2; длительность болезни до госпитализации – 7,7±4,3 суток.
- Группа В – 361 пациент без признаков ОПП, из которых 153 (42,4%) мужчины и 208 (57,6%) женщин. Средний возраст составил 59,7±16,2 года; ИМТ – 28,1±5,2 кг/м2; длительность болезни до госпитализации – 7,1±3,2 суток.
Статистически значимые различия между группами выявлены по возрасту: средний возраст в группе пациентов с ОПП был статистически значимо выше (р=0,0000). По антропометрическим данным и длительности болезни до госпитализации статистически значимых различий не было (р>0,05).
При исследовании маркеров воспаления в первый день пребывания в стационаре выявлена их бóльшая активность в группе пациентов с развитием ОПП, различия статистически значимы (табл. 1).

Динамика уровня СРБ в сыворотке крови в процессе лечения представлена на рис. 1 Течение новой коронавирусной инфекции сопровождалось снижением уровня СРБ у пациентов обеих групп. Через 3 суток от начала лечения уровень СРБ в сыворотке крови статистически значимо снизился в обеих группах (p<0,05). В группе А он снизился в 1,7 раза по сравнению с первыми сутками, к 5-м и 10-м суткам произошло дальнейшее статистически значимое снижение уровня СРБ (p<0,05), но нормализации показателя не произошло. В группе В в результате лечения также на всех этапах лечения произошло статистически значимое снижение исследуемого показателя (p<0,05), но к 10-м суткам он также оставался повышенным.

Динамика уровней ферритина и ЛДГ в сыворотке крови в процессе лечения представлена на рис. 2 и 3.
К 3-м суткам лечения в группе А уровень ферритина оставался повышенным, сохранялись статистически значимые различия между группами (р=0,024). Дальнейшее течение заболевания характеризовалось нарастанием уровня ферритина: к 5-м суткам в обеих группах произошло статистически значимое повышение уровня ферритина по сравнению с первыми сутками (р=0,035; р=0,002 соответственно), к 10-м суткам в обеих группах уровень ферритина достиг максимальных показателей.
Динамика уровня ЛДГ в группе А была аналогичной уровню ферритина. Уровень фермента на протяжении всего периода лечения повышался, достигнув максимального значения к 10-м суткам лечения (р=0,05). В группе В также в течение 5 суток уровень ЛДГ был повышен, к 10-м суткам произошло статистически незначимое снижение (р>0,05), но нормализации уровня не произошло. Между группами установлены статистически значимые различия на протяжении всего периода лечения, в группе А уровень ЛДГ был выше, чем в группе В (p<0,05).
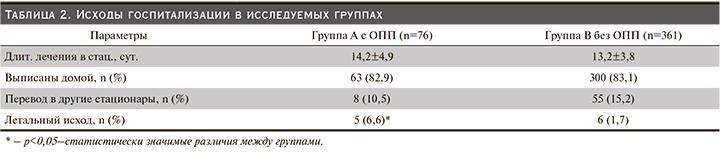
При анализе исходов госпитализации замечено, что в группе с ОПП было больше летальных исходов, различия статистически значимые. По числу дней госпитализации, а также выписанных и переведенных в другие стационары пациентов статистически значимых различий не было (табл. 2).
Обсуждение
Согласно сложившимся представлениям, сформированным более чем за 2 года пандемии, клинические проявления и последствия COVID-19 зависят от двух основных патологических аспектов: непосредственного воздействия вируса SARS-CoV-2 и иммуновоспалительного ответа макроорганизма. Когда локализованное воспаление легких переходит в синдром системного и внелегочного гипервоспаления, в крови наблюдается снижение числа Т-лимфоцитов и увеличение воспалительных цитокинов и биомаркеров [20–21]. На сегодня определено несколько параметров, которые являются независимым фактором риска для оценки интенсивности воспаления и тяжести заболевания COVID-19, в т.ч. ИЛ-6, СРБ, ЛДГ [22–24]. ИЛ-6 считается провоспалительным цитокином – инициатором цитокинового шторма, стимулирующим выработку белков острой фазы (СРБ и ферритина) в печени [25]. Ферритин при этом способствует дальнейшему высвобождению провоспалительных медиаторов, увеличивая воспалительную нагрузку и приводя к порочному кругу [26]. ЛДГ – это фермент, который высвобождается из соматических тканей при повреждении органов, вызванном либо вирусной атакой, либо воспалением при COVID-19 [22]. Уровни СРБ и ЛДГ могут также использоваться как маркеры раннего повреждения легких и развития дыхательной недостаточности [27].
По результатам проведенного исследования выявлено, что повышение концентрации ИЛ-6 в сыворотке крови при поступлении у пациентов с ОПП было значительнее. Уровни СРБ, а также ферритина и ЛДГ, отражающих степень активности воспалительного процесса и участие в нем не только легких, но и других органов, оказались на момент поступления статистически значимо выше в группе больных ОПП. При оценке динамики биомаркеров воспаления установлены разнонаправленные изменения уровней СРБ и ферритина. Концентрация СРБ снижалась в обеих группах, а уровень ферритина нарастал вплоть до 10-х суток. Примечательно, что уровень ЛДГ к 10-м суткам статистически значимо возрос лишь в группе с ОПП, тогда как в группе без ОПП несколько снизился. При сравнении динамики биомаркеров воспаления замечено, что у пациентов с ОПП на 3-и сутки пребывания в стационаре уровни СРБ, ферритина, ЛДГ были статистически значимо выше по сравнению с таковым у пациентами без ОПП, а на 5-е и 10-е сутки статистически значимым оставалось лишь повышение уровня ЛДГ.
В нашем исследовании выявлена достаточно высокая частота ОПП, она составила 20,5%, большинство больных имели признаки 1-й стадии ОПП. В группе лиц с ОПП выявлены более высокие показатели госпитальной смертности. Несмотря на то что заболеваемость COVID-19 во всем мире снижается, а число случаев легкого течения заболевания возрастает, у большого числа пациентов, выписанных из стационаров, сохраняются симптомы: одышка, усталость, головная боль и т.д. Пациенты, перенесшие ОПП, даже при условии нормализации функции почек входят в когорту лиц с высоким риском развития хронической болезни почек (ХБП). ХБП не проявляется яркой симптоматикой, ее выявление в амбулаторной практике требует пристального внимания врача, в особенности к результатам анализа мочи и уровня креатинина сыворотки. В настоящее время отсутствует достаточное число результатов амбулаторного наблюдения, чтобы получить представление о распространенности ХБП среди пациентов, перенесших ОПП во время госпитализации по поводу COVID-19. Очевидно, что такие пациенты пополнят общее число лиц с ХБП, что подтверждает актуальность тщательного мониторинга показателей функции почек у лиц, перенесших COVID-19.
Заключение
При исследовании биомаркеров воспаления уровни СРБ, ферритина, ЛДГ и ИЛ-6 были выше у пациентов, развивших ОПП на фоне COVID-19, что может свидетельствовать о взаимосвязи поражения почек и активности воспалительной реакции при COVID-19. Пациенты с ОПП были в среднем статистически значимо старше. Частота развития ОПП у госпитализированных пациентов с COVID-19 была достаточно высока и составила в нашем исследовании 20,5%, что диктует необходимость амбулаторного наблюдения больных, перенесших COVID-19, с мониторированием уровня креатинина и расчетной скорости клубочковой фильтрации для своевременной диагностики ХБП.



